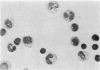
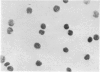
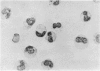
Abstract
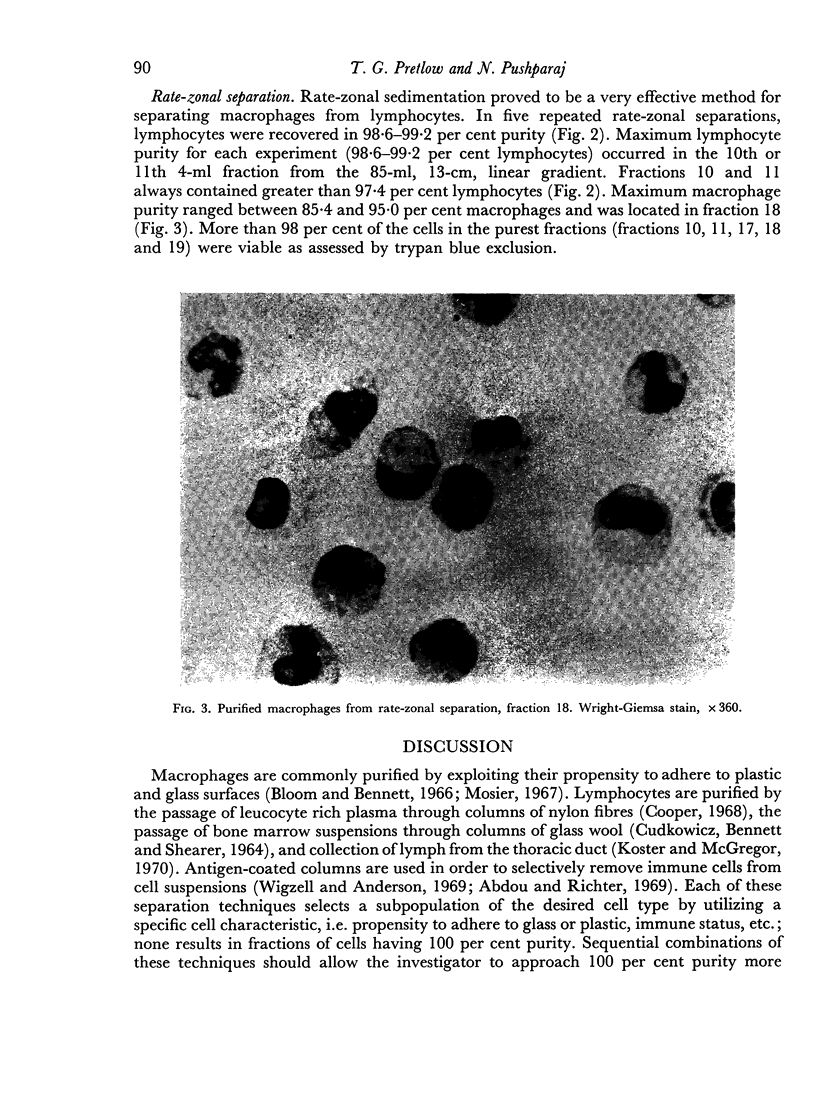
A simple method has been developed for separating sterile, viable mouse peritoneal lymphocytes from suspension of peritoneal cells using velocity sedimentation. Lymphocytes are obtained in 98.6–99.2 per cent purity; macrophages in 85.4–95.0 per cent purity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Richter M. Cells involved in the immune response. X. The transfer of antibody-forming capacity to irradiated rabbits by antigen-reactive cells isolated from normal allogeneic rabbit bone marrow after passage through antigen-sensitized glass bead columns. J Exp Med. 1969 Jul 1;130(1):141–163. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeloff M. D., Mangi R. J., Pretlow T. G., Mardiney M. R., Jr Isolation of leukemic blasts from peripheral blood by density gradient centrifugation. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Apr;75(4):703–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argyris B. F. Role of macrophages in immunological maturation. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):459–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin R. W., Embleton M. J. Immunology of spontaneously arising rat mammary adenocarcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1969 Jul 15;4(4):430–439. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910040408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Bennett B. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone C. W., Harell G. S., Bond H. E. The resolution of mixtures of viable mammalian cells into homogeneous fractions by zonal centrifugation. J Cell Biol. 1968 Feb;36(2):369–378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUDKOWICZ G., BENNETT M., SHEARER G. M. PLURIPOTENT STEM CELL FUNCTION OF THE MOUSE MARROW "LYMPHOCYTE". Science. 1964 May 15;144(3620):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3620.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. L. Ribonucleic acid metabolism in lymphocytes stimulated by phytohemagglutinin. II. Rapidly synthesized ribonucleic acid and te production of ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman M. Induction of antibodies in vitro. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:199–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F., McGregor D. D. Rat thoracic duct lymphocytes: types that participate in inflammation. Science. 1970 Feb 20;167(3921):1137–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3921.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E. A requirement for two cell types for antibody formation in vitro. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1573–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretlow T. G., 2nd, Boone C. W. Separation of malignant cells from transplantable rodent tumors. Exp Mol Pathol. 1970 Jun;12(3):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(70)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretlow T. G., 2nd, Boone C. W. Separation of mammalian cells using programmed gradient sedimentation. Exp Mol Pathol. 1969 Oct;11(2):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(69)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretlow T. G., 2nd, Cassady I. M. Separation of mast cells in successive stages of differentiation using programmed gradient sedimentation. Am J Pathol. 1970 Dec;61(3):323–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H., Andersson B. Cell separation on antigen-coated columns. Elimination of high rate antibody-forming cells and immunological memory cells. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):23–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]