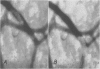
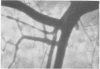
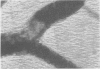
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANASZAK E. F., STEKIEL W. J., SMITH J. J. Comparative effect of heparin and other agents on traumatic shock in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Nov;197:989–992. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.5.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURRAGE W. S., IRWIN J. W. Microscopic observations of the pulmonary arterioles, capillaries, and venules of living mammals before and during anaphylaxis. J Allergy. 1953 Jul;24(4):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(53)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLUFF L. E., BERTHRONG M. The inhibition of the local Shwartzman reaction by heparin. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1953 May;92(5):353–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWELL J. W., READ W. L. In vivo coagulation; a probable cause of irreversible shock. Am J Physiol. 1955 Dec;183(3):565–569. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.183.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS R. B., MEEKER W. R., Jr, BAILEY W. L. Serotonin release by bacterial endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Dec;108:774–776. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-27063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHRAEUS R. Acquired tolerance for micro-embolism. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1960;65:77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAIBIS A. Studies on the pathogenesis of circulatory disturbances in pulmonary embolism. Cor Vasa. 1961;3:273–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINE J. Host resistance to bacterial infection in traumatic shock. Br J Anaesth. 1958 Oct;30(10):485–494. doi: 10.1093/bja/30.10.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK H. A., GLOTZER P., JACOB S. W., FINE J. Traumatic shock. XIX. Hemorrhagic shock in Eck-fistula dogs. Am J Physiol. 1951 Nov;167(2):508–513. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.2.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANS H., KRIVIT W. Effect of endotoxin shock on the clotting mechanism of dogs. Ann Surg. 1960 Jul;152:69–76. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196007000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANS H., KRIVIT W. Study of fibrinogen and plasminogen concentrations in rabbits during anaphylactic shock. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Aug;58:259–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERST P. H., RATTENBORG C., HOLADAY D. A. The effects of hemorrhage of pulmonary circulation and respiratory gas exchange. J Clin Invest. 1959 Mar;38(3):524–538. doi: 10.1172/JCI103830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD R. A., THOMAS L. Studies on the generalized Shwartzman reaction. IV. Prevention of the local and generalized Shwartzman reactions with heparin. J Exp Med. 1953 Jun;97(6):871–888. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.6.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFIN G. D. J., ESSEX H. E., MANN F. C. Experimental evidence concerning death from small pulmonary emboli. Int Abstr Surg. 1951 Apr;92(4):313–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDAWAY R. M., BRUNE W. H., GEEVER E. F., BURNS J. W., MOCK H. P. Studies on the role of intravascular coagulation in irreversible hemorrhagic shock. Ann Surg. 1962 Feb;155:241–250. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196200000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDAWAY R. M., HUSNI E. A., GEEVER E. F., NOYESHE, BURNS J. W. Endotoxin shock. A manifestation of intravascular coagulation. Ann Surg. 1961 Nov;154:791–802. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196111000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDAWAY R. M., JOHNSON D. G. Influence of fibrinolysin on shock. JAMA. 1963 Feb 16;183:597–599. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63700070034020a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDAWAY R. M., NEIMES R. E., BURNS J. W., MOCK H. P., TRENCHAK P. T. Role of norepinephrine in irreversible hemorrhagic shock. Ann Surg. 1962 Jul;156:57–60. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196207000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONOUR A. J., RUSSELL R. W. Experimental platelet embolism. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:350–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILLEHEI R. C., MACLEAN L. D. The intestinal factor in irreversible endotoxin shock. Ann Surg. 1958 Oct;148(4):513–525. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195810000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUTZ B. R. Intravascular agglutination of the formed elements of blood. Physiol Rev. 1951 Apr;31(2):107–130. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1951.31.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANSBERGER A. R., Jr, WISE H. A comparison of shock from massive soft tissue wounds and shock induced by the intravenous injection of gram-negative endotoxin. Am Surg. 1960 May;26:367–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKAY D. G., SHAPIRO S. S. Alterations in the blood coagulation system induced by bacterial endotoxin. I. In vivo (generalized Shwartzman reaction). J Exp Med. 1958 Mar 1;107(3):353–367. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAYNER R. R., MACLEAN L. D., GRIM E. Intestinal tissue blood flow in shock due to endotoxin. Circ Res. 1960 Nov;8:1212–1217. doi: 10.1161/01.res.8.6.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBB H. J., INGHAM D. E., NELSON H. M., JOHNSTON C. G. Observations in vascular dynamics during hemorrhagic shock and its therapy. Am J Surg. 1958 Apr;95(4):659–663. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(58)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBB H. J., JACOBSON L. F., JORDAN P. Dissolution of a clot studied by cinephotomicrography. Arch Surg. 1963 May;86:846–851. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1963.01310110156021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STETSON C. A., Jr Studies on the mechanism of the Shwartzman phenomenon; certain factors involved in the production of the local hemorrhagic necrosis. J Exp Med. 1951 May;93(5):489–504. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.5.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURPINI R., STEFANINI M. The nature and mechanism of the hemostatic breakdown in the course of experimental hemorrhagic shock. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):53–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI103795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTER J. B., FRANK J. A., IRWIN J. W. Hyaline emboli in the microcirculation of rabbits during anaphylaxis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1961 Dec;42:603–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZANETTI M. E. Significance of elevated portal vein pressure in etiology of hemorrhagic shock. Am J Physiol. 1952 Dec;171(3):538–544. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.171.3.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]