Abstract
Ten previously untransfused Rh(D)-negative subjects were given an intravenous injection of approximately 0.3 ml of Rh(D)-positive red cells and at about the same time, or 24–48 hours previously, were given an intramuscular injection of 1–1000 μg of anti-D.
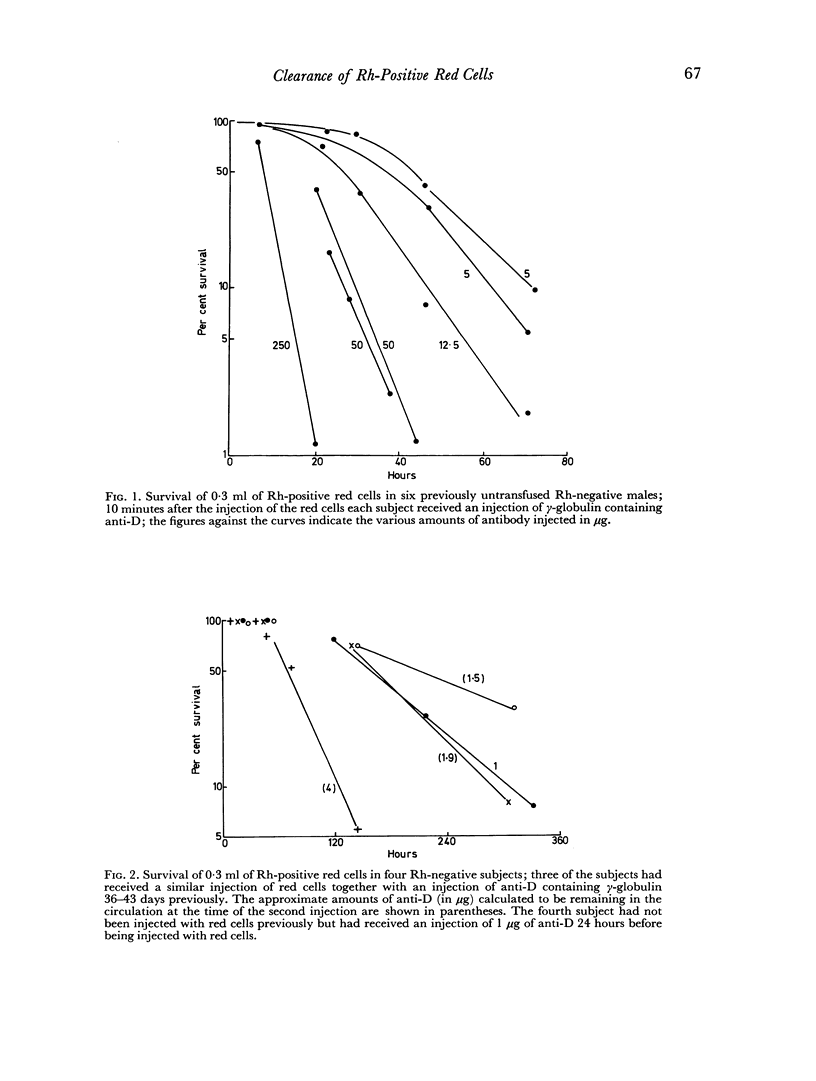
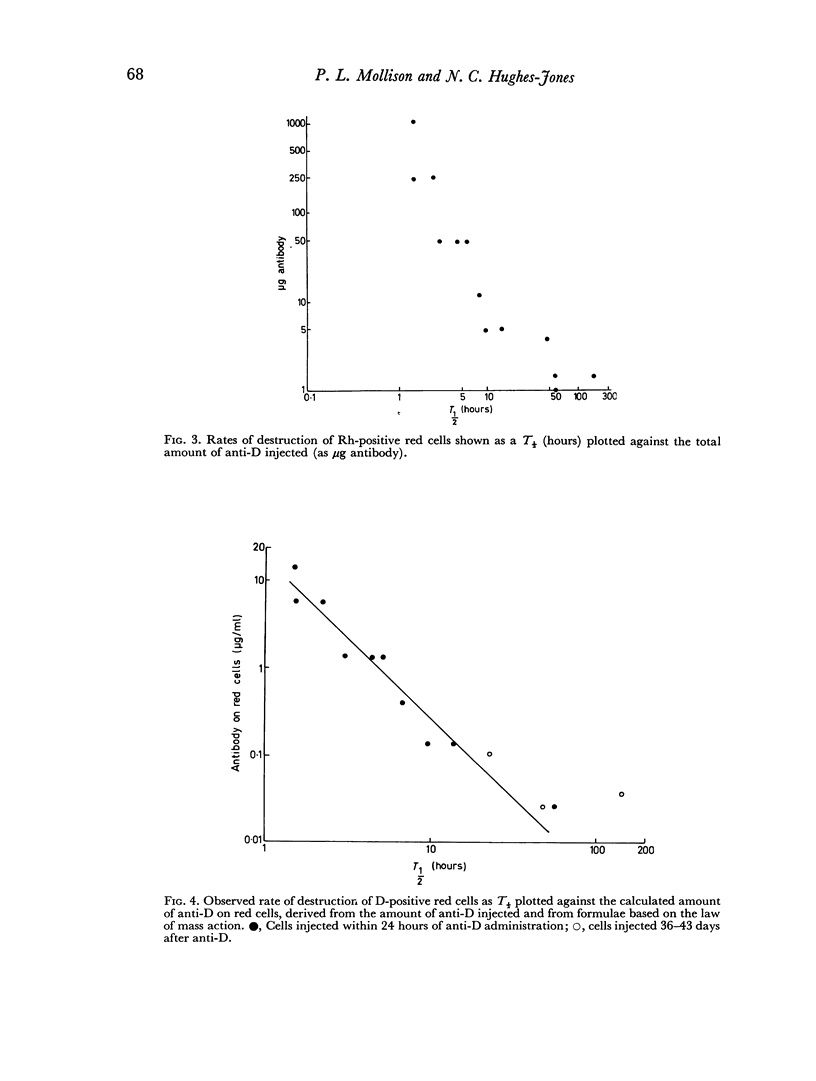
Following the injection of the red cells there was a variable period before the onset of red cell destruction; when the antibody was injected at the same time as the red cells the delay was due partly to the time taken for the antibody to reach the circulation; when the antibody was injected at least 24 hours before the red cells there was still some delay due to the time required for the antibody to be taken up by the red cells; the delay before the onset of a maximum rate of red cell destruction varied from about 0.2 hours following the injection of 1000 μg of antibody to approximately 100 hours following the injection of 1 μg.
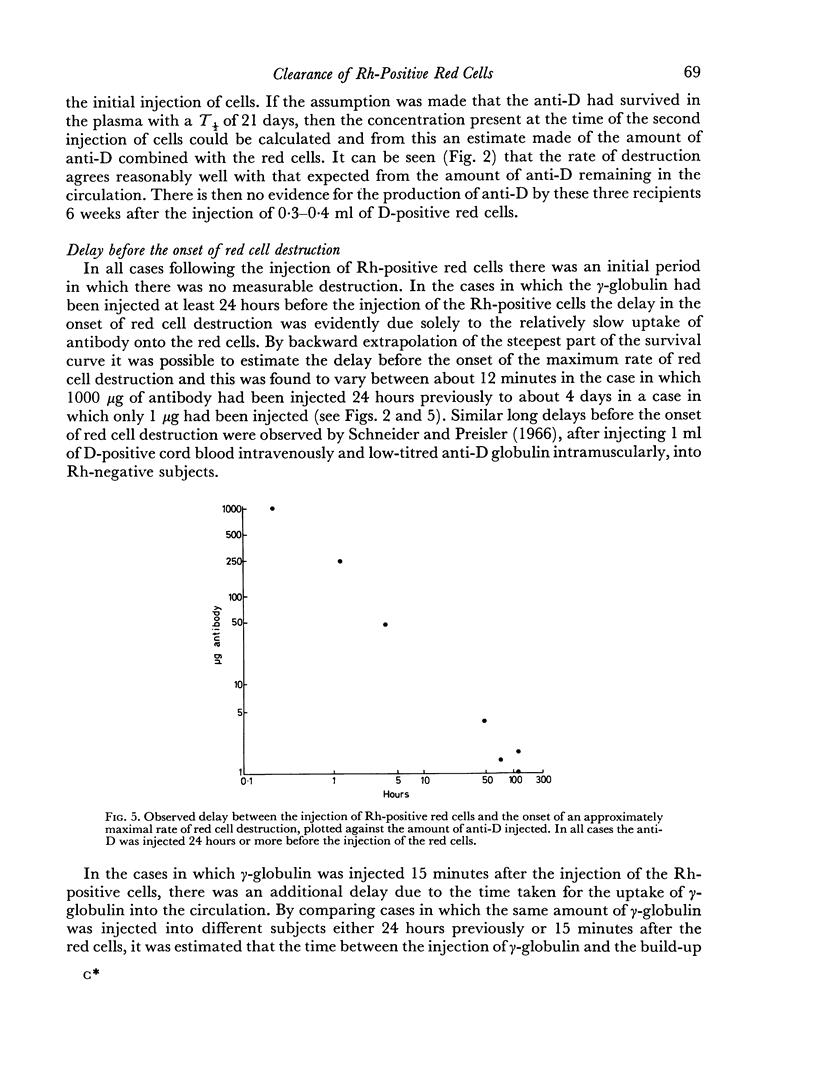
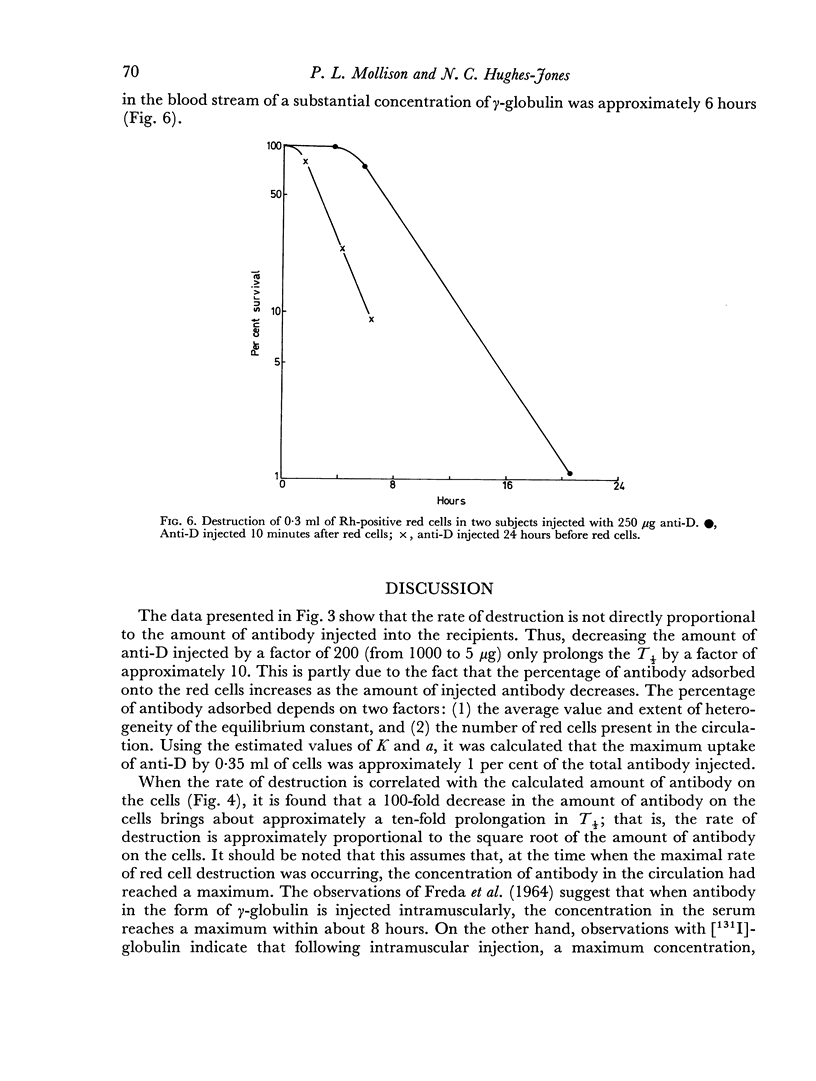
The maximum rate of red cell destruction was calculated to be approximately proportional to the square root of the amount of antibody on the cells. After the injection of the smallest amount of antibody (1 μg) the amount on the red cells was calculated to be about 0.03 μg/ml corresponding to about ten molecules of antibody per cell. This dose produced clearance with a T½ of the order of 100 hours.
The significance of these observations in relation to protection against Rh-immunization is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARKE C. A., DONOHOE W. T., McCONNELL R. B., WOODROW J. C., FINN R., KREVANS J. R., KULKE W., LEHANE D., SHEPPARD P. M. Further experimental studies on the prevention of Rh haemolytic disease. Br Med J. 1963 Apr 13;1(5336):979–984. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5336.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. A., Finn R., Lehane D., McConnell R. B., Sheppard P. M., Woodrow J. C. Dose of anti-D gamma-globulin in prevention of Rh-haemolytic disease of the newborn. Br Med J. 1966 Jan 22;1(5481):213–214. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5481.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DU PAN R. M., WENGER P., KOECHLI S., SCHEIDEGGER J. J., ROUX J. Etude du passage de la gamma-globuline, marquée à travers le placenta humain. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 Jan;4(1):110–115. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N., SISKIND G. W. VARIATIONS IN AFFINITIES OF ANTIBODIES DURING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:996–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDA V. J., GORMAN J. G., POLLACK W. SUCCESSFUL PREVENTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RH SENSITIZATION IN MAN WITH AN ANTI-RH GAMMA2-GLOBULIN ANTIBODY PREPARATION: A PRELIMINARY REPORT. Transfusion. 1964 Jan-Feb;4:26–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1964.tb02824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freda V. J., Gorman J. G., Pollack W. Rh factor: prevention of isoimmunization and clinical trial on mothers. Science. 1966 Feb 18;151(3712):828–830. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3712.828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujio H., Karush F. Antibody affinity. II. Effect of immunization interval on antihapten antibody in the rabbit. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):1856–1863. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES-JONES N. C., GARDNER B., TELFORD R. STUDIES ON THE REACTION BETWEEN THE BLOOD-GROUP ANTIBODY ANTI-D AND ERYTHROCYTES. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:435–440. doi: 10.1042/bj0880435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLISON P. L., CUTBUSH M. Use of isotope-labelled red cells to demonstrate incompatibility in vivo. Lancet. 1955 Jun 25;268(6878):1290–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)92057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., PRESSMAN D. Heterogeneity and average combining constants of antibodies from individual rabbits. J Immunol. 1958 Jun;80(6):417–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochna E., Hughes-Jones N. C. The use of purified 125-I-labelled anti-gamma globulin in the determination of the number of D antigen sites on red cells of different phenotypes. Vox Sang. 1965 Nov-Dec;10(6):675–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1965.tb05179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


