Abstract
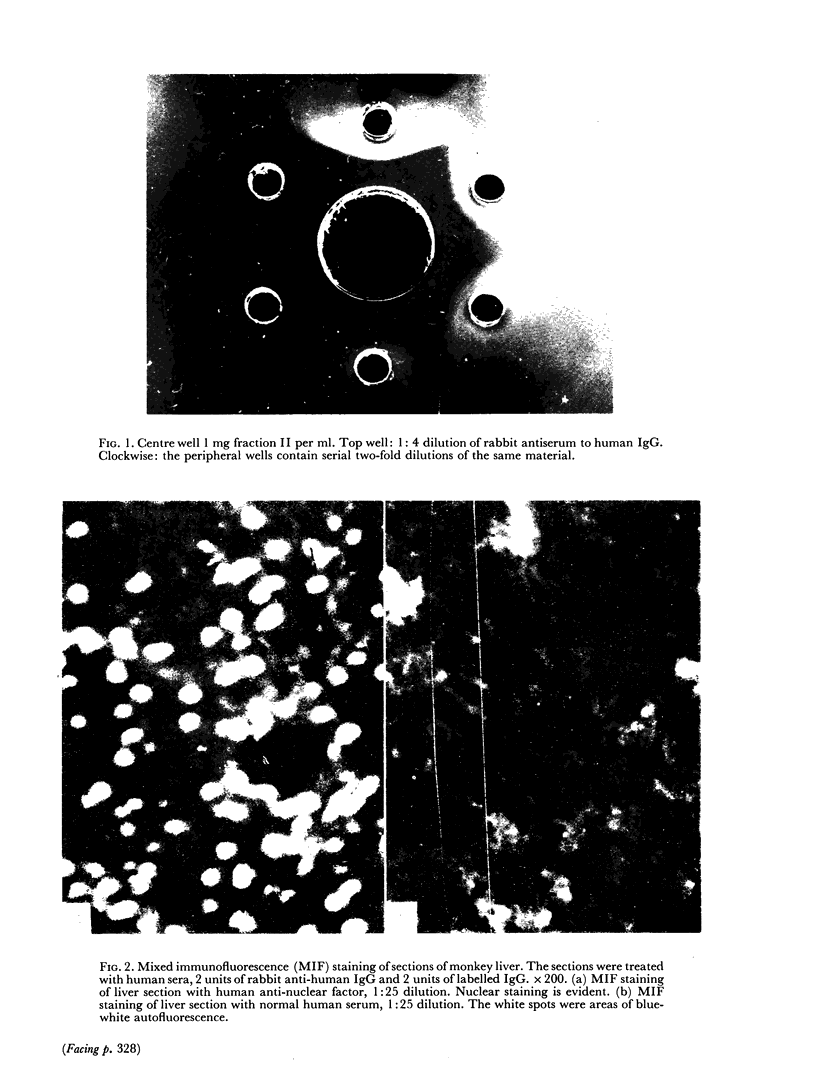
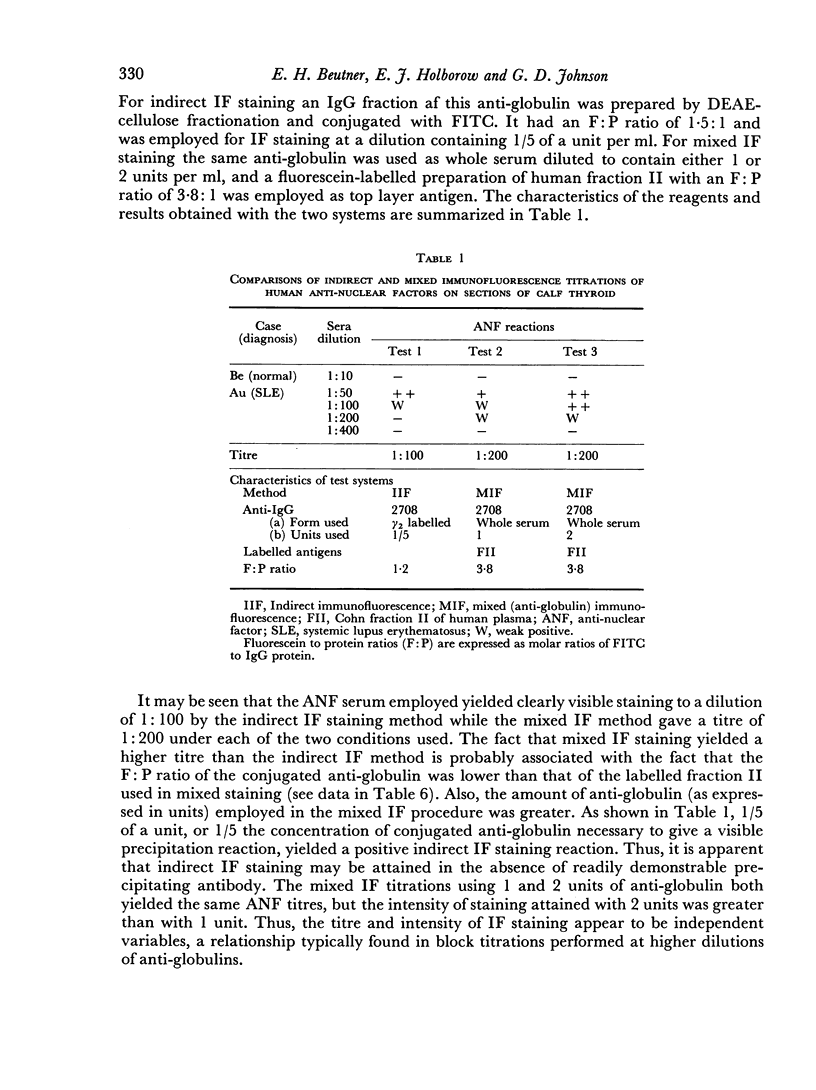
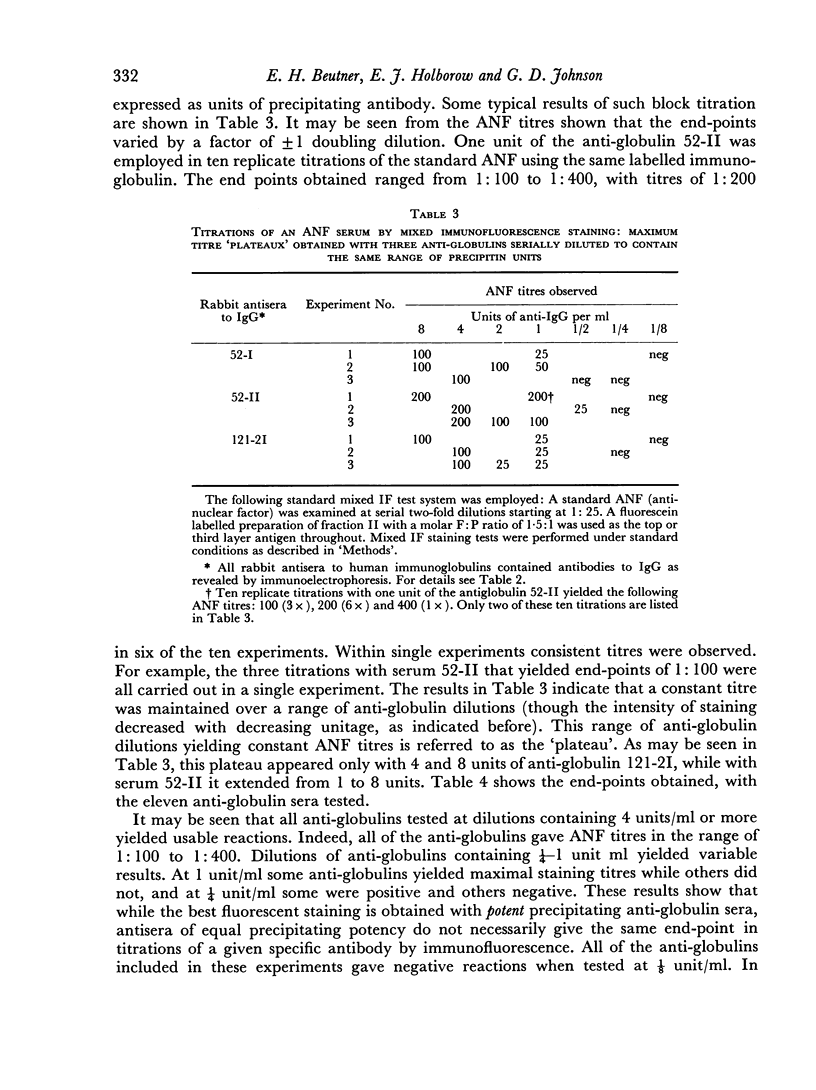
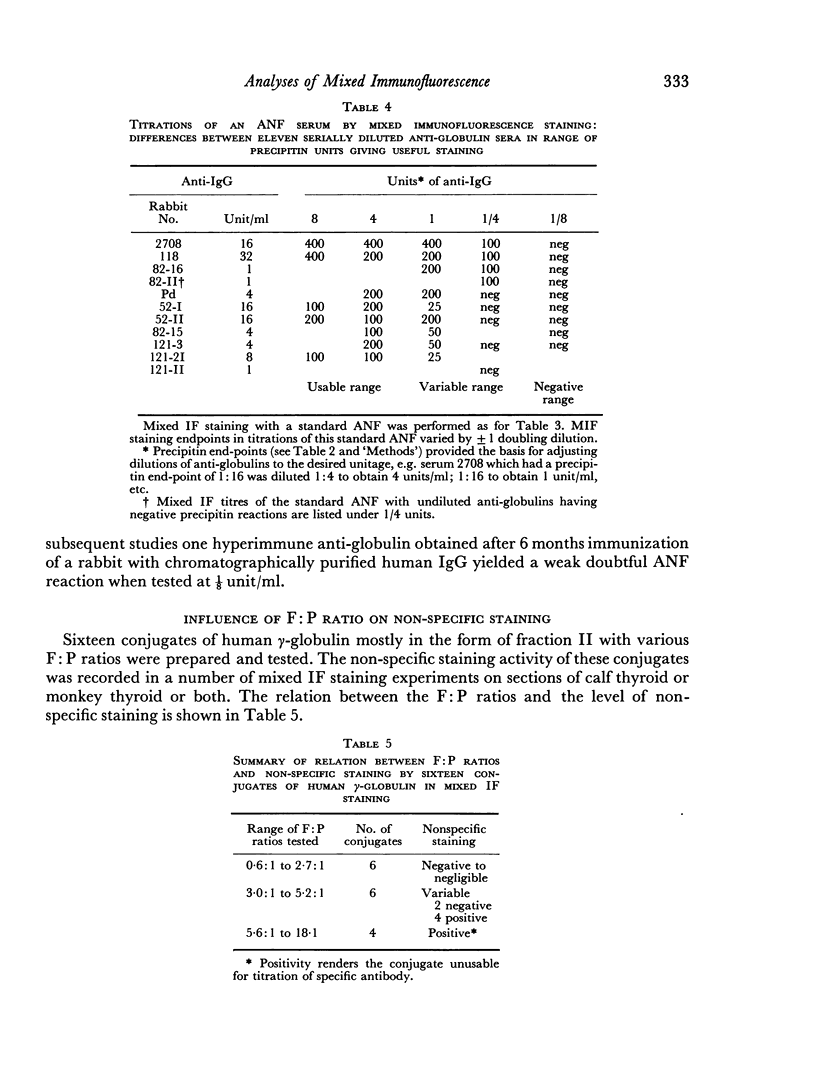
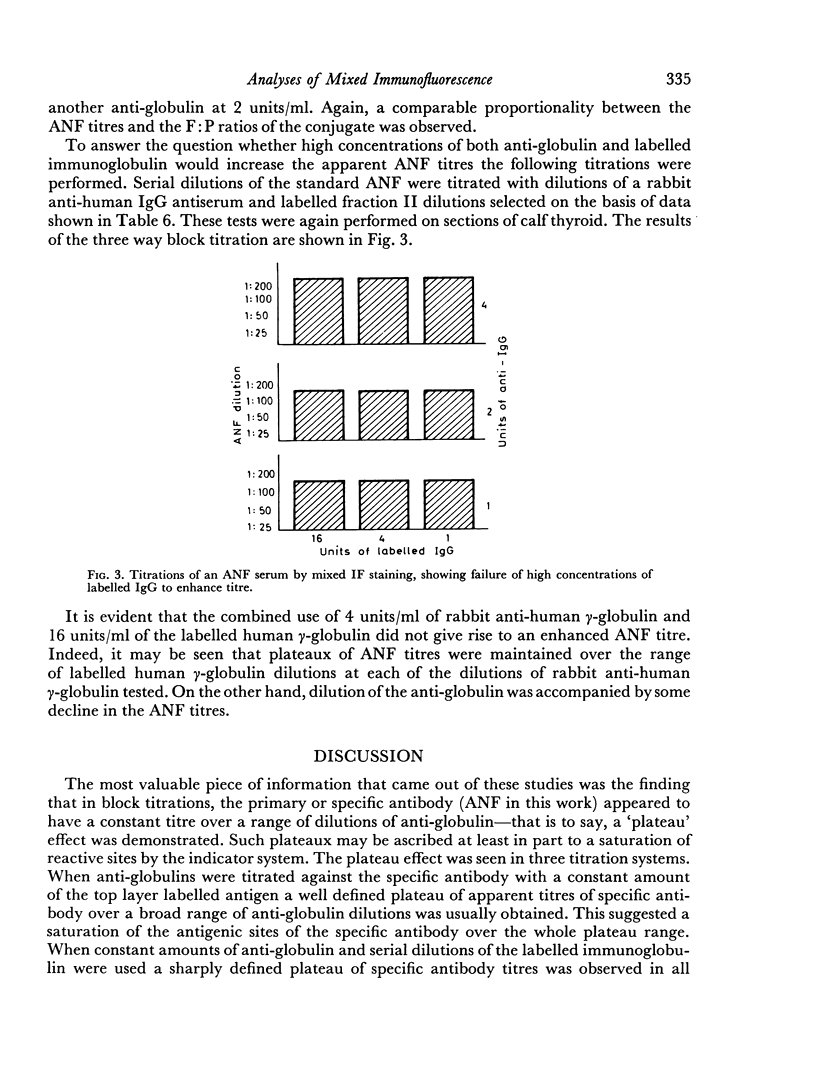
Mixed anti-globulin immunofluorescence (or mixed IF) was analysed using the following model system: calf thyroid sections, human anti-nuclear factor (ANF), rabbit antisera to human IgG and fluorescein-labelled human IgG. This system was characterized on the basis of: (1) the immunoelectrophoretic demonstration of antibodies to human IgG in anti-globulins; (2) titration of the antiglobulins and labelled globulins; and (3) determination of molar fluorescein to protein (F:P) ratios. Titration of anti-globulins (rabbit anti-human IgG) by gel precipitation afforded an assay of `units' of antibody activity. Similarly, `units' of labelled globulin antigen were determined by a gel precipitation titration. Block titrations of these components of the indicator system against ANF serum yielded constant titres or `plateaux' of nuclear staining over a range of units of anti-globulin and of labelled immunoglobulin. Thus, the following predictions can be made. Optimal mixed IF staining may be attained with 4 units or more of an anti-globulin (anti-human IgG) and with 1 unit or more of a fluorescein-labelled human immunoglobulin if the latter has an F:P ratio in the range of about 1:1 to 3:1. The titre of the ANF appears to be proportional to the F:P ratio over this range.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutner E. H., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D. A new fluorescent antibody method: mixed antiglobulin immunofluorescence or labelled antigen indirect immunofluorescence staining. Nature. 1965 Oct 23;208(5008):353–355. doi: 10.1038/208353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK H. F., SHEPARD C. C. A DIALYSIS TECHNIQUE FOR PREPARING FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:642–644. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBISKI S., MILGROM F., WOZNICZKO G. A simple method of Rh determination. Nature. 1956 Sep 8;178(4532):539–539. doi: 10.1038/178539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommhagen L. H. The solubility and other physicochemical properties of human gamma-globulin labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate. J Immunol. 1965 Sep;95(3):442–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN G., SLIZYS I. S., CHASE M. W. Studies on fluorescent antibody staining. I. Non-specific fluorescence with fluorescein-coupled sheep anti-rabbit globulins. J Exp Med. 1961 Jul 1;114:89–110. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDWASSER R. A., SHEPARD C. C. Staining of complement and modification of fluorescent antibody procedures. J Immunol. 1958 Feb;80(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKINNEY R. M., SPILLANE J. T., PEARCE G. W. FLUORESCEIN DIACETATE AS A REFERENCE COLOR STANDARD IN FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY STUDIES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Dec;9:474–476. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., NILSSON U., ARONSSON T. Isolation and characterization of two beta1-glycoproteins of human serum. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:201–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS J. L., LOH P. C., EVELAND W. C. A simple fractionation method for preparation of fluorescein-labeled gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Dec;105:655–658. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody studies with agents of varicella and herpes zoster propagated in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Aug-Sep;86(4):789–794. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]