Abstract
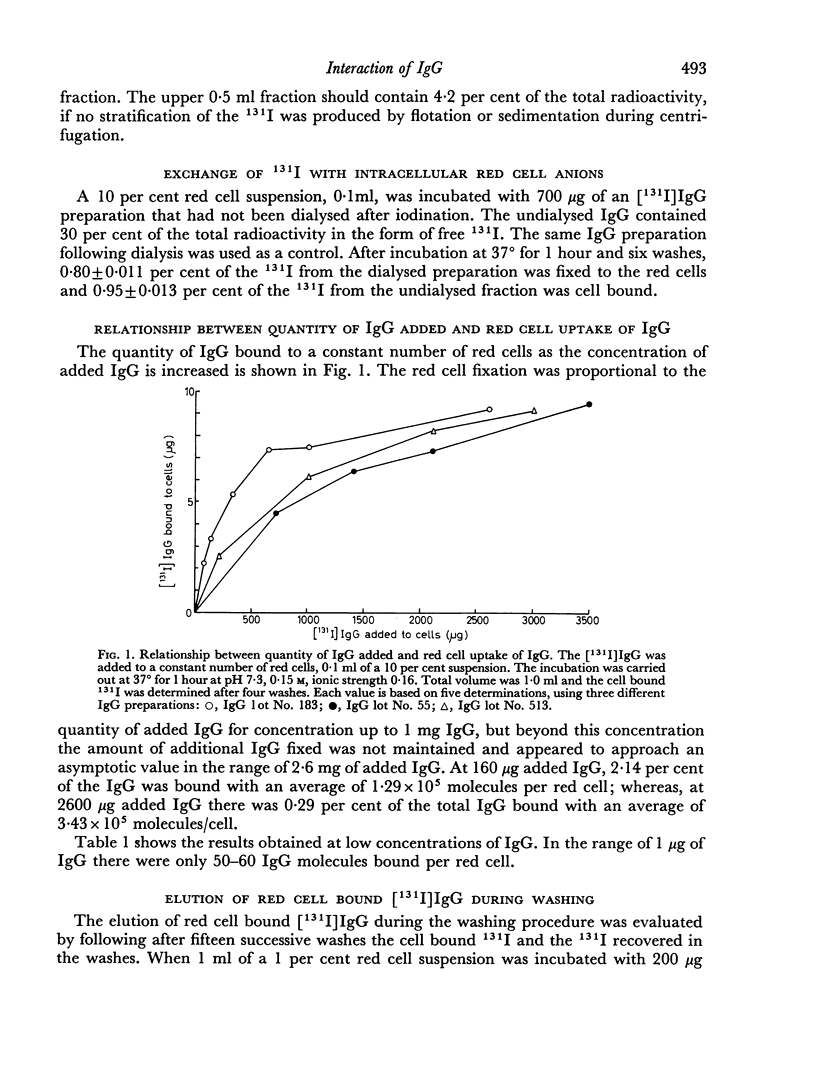
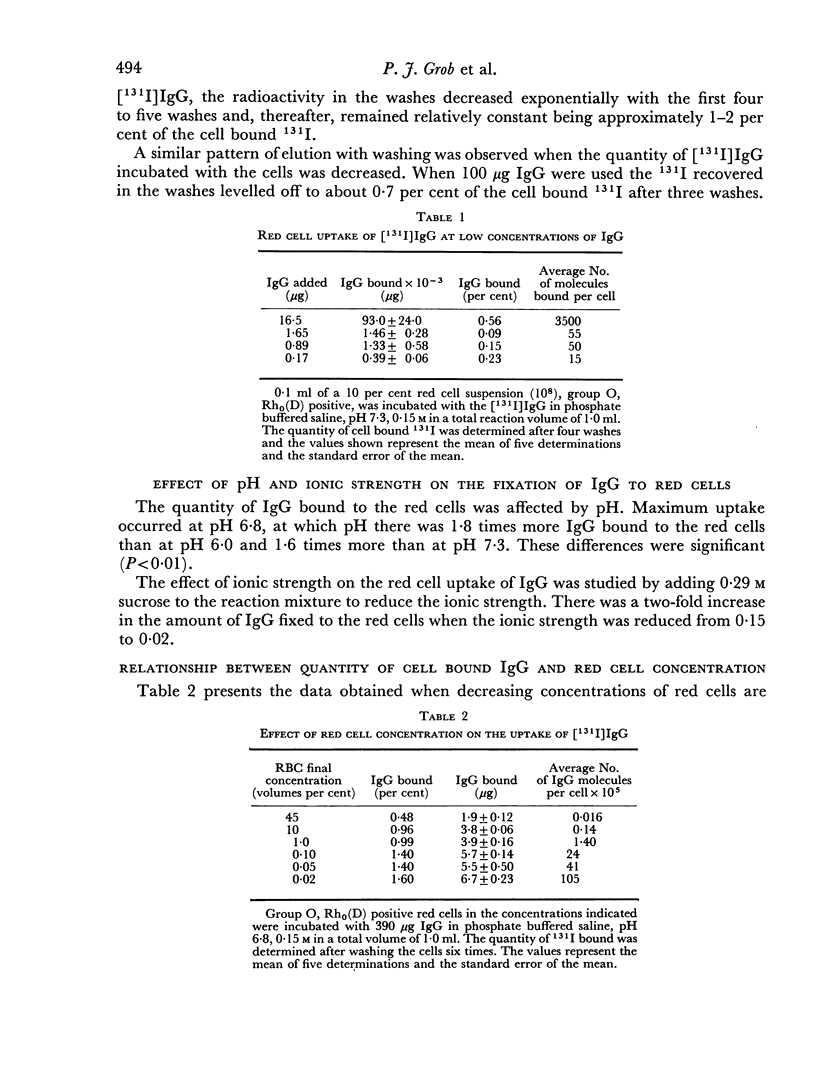
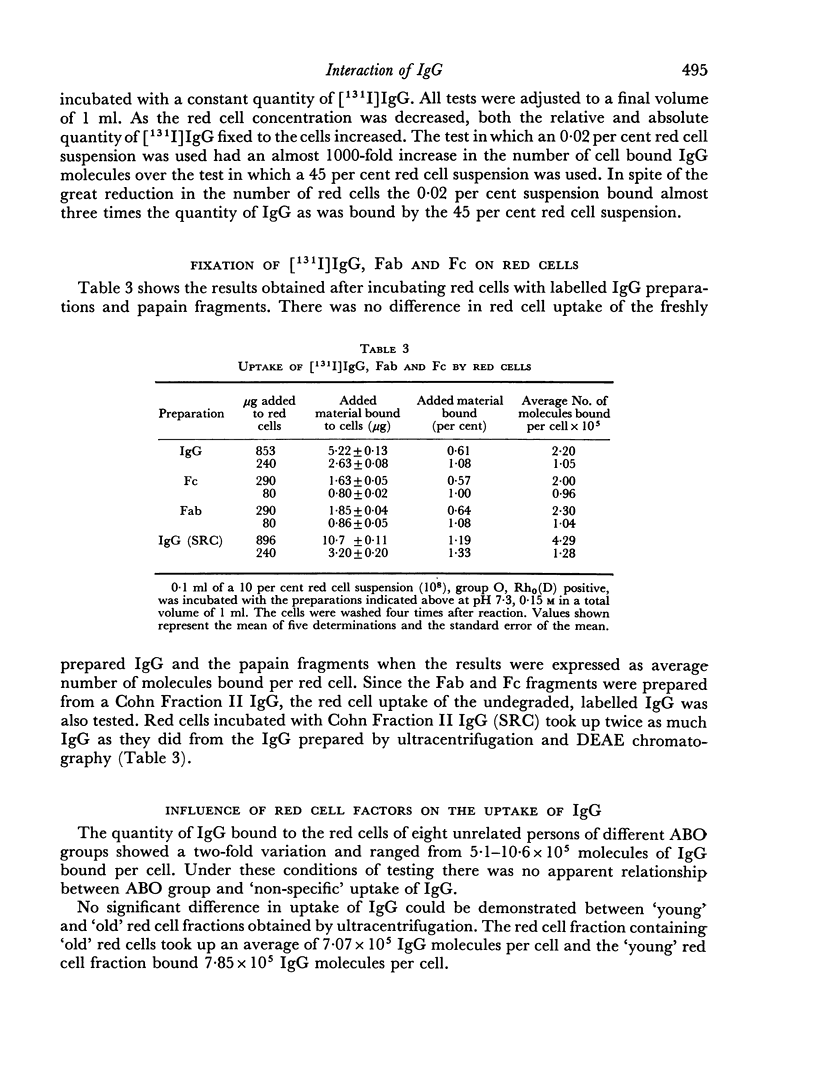
The red cell uptake of 131I following incubation of red cells with [131I] IgG prepared from normal donors was shown to be IgG and not trace contaminants such as transferrin, lipids or iodide. The criteria used were immunodiffusion, DEAE chromatography, gel filtration and exchange with unlabelled lipoproteins and plasma. The uptake of [131I]IgG was pH and ionic strength dependent and was influenced by the proportion of cells to IgG present during the reaction. With constant cell concentration the uptake of [131I]IgG increased progressively as more IgG was added to the cells and approached an asymptotic value suggesting that there was saturation of red cell binding sites. When the IgG concentration was kept constant the uptake of IgG was inversely proportional to the red cell concentration. No difference in the molar binding of IgG, Fab or Fc was found indicating that the non-antibody binding of IgG does not preferentially involve any part of the IgG molecule. The molar quantities of carefully prepared [131I]IgG bound to red cells were similar to those obtained with [131I]BSA. The non-antibody red cell binding of IgG was contrasted with the antibody type of IgG binding.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATCHLEY W. A., BHAGAVAN N. V., MASOUREDIS S. P. INFLUENCE OF IONIC STRENGTH ON THE REACTION BETWEEN ANTI-D AND D POSITIVE RED CELLS. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:701–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOCCI V. EFFICIENT LABELLING OF SERUM PROTEINS WITH I-131 USING CHLORAMINE T. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1964 Aug;15:449–456. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(64)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURSNELL J. C., COOMBS R. R., RIZK V. Studies with marked antisera; quantitative studies with antisera marked with iodine 131isotope and their corresponding red-cell antigens. Biochem J. 1953 Dec;55(5):745–758. doi: 10.1042/bj0550745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTEA N., SCHWARTZ R., CONSTANTOULAKIS M., DAMESHEK W. The use of radioactive antiglobulin for the detection of erythrocyte sensitization. Blood. 1962 Aug;20:214–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUPUY M. E., ELLIOT M., MASOUREDIS S. P. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RED CELL BOUND ANTIBODY AND AGGLUTINATION IN THE ANTIGLOBULIN REACTION. Vox Sang. 1964 Jan-Feb;9:40–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1964.tb03766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C. Structural units of human 7S gamma globulin. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1933–1941. doi: 10.1172/JCI104218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S. W., Masouredis S. P. Physicochemical and immunologic properties of eluates containing I-125 anti-Rho(D). J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):374–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommel D., Grob P. J., Masouredis S. P., Isliker H. C. Studies on the mechanism of immunoglobulin binding to red cells. Immunology. 1967 Nov;13(5):501–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. J., Isliker H. C., Webb T. Inhibition of the anti-globulin reaction by human immunoglobulin G and its fragments. Immunology. 1967 Mar;12(3):275–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES-JONES N. C., GARDNER B., TELFORD R. THE EFFECT OF PH AND IONIC STRENGTH ON THE REACTION BETWEEN ANTI-D AND ERYTHROCYTES. Immunology. 1964 Jan;7:72–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., INMAN J. K., SIMMONS R. L., ALLEN D. W. Transfer of iron from serum iron-binding protein to human reticulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):161–185. doi: 10.1172/JCI103786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., KATZ J. H. The plasma-to-cell cycle of transferrin. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42:314–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI104718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES N. C., GARDNER B. The exchange of 131-I-labelled lipid and 131-I-labelled protein between red cells and serum. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:404–413. doi: 10.1042/bj0830404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASOUREDIS S. P. Reaction of I-131 trace labeled human anti-Rho(D) with red cells. J Clin Invest. 1959 Feb;38(2):279–290. doi: 10.1172/JCI103800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN E. H., LAURELL C. B. STUDIES ON THE EXCHANGE OF IRON BETWEEN TRANSFERRIN AND RETICULOCYTES. Br J Haematol. 1963 Oct;9:471–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb05471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN E. H. THE INTERACTION BETWEEN RABBIT, HUMAN AND RAT TRANSFERRIN AND RETICULOCYTES. Br J Haematol. 1964 Oct;10:442–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIROFSKY B., CORDOVA M. S., IMEL T. L. The nonimmunologic reaction of globulin molecules with the erythrocyte surface. Vox Sang. 1962;7:334–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1962.tb03262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLACK W., HAGER H. J., RECKEL R., TOREN D. A., SINGHER H. A STUDY OF THE FORCES INVOLVED IN THE SECOND STAGE OF HEMAGGLUTINATION. Transfusion. 1965 Mar-Apr;5:158–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1965.tb01152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGAS D. A., KOLER R. D. Ultracentrifugal fractionation of human erythrocytes on the basis of cell age. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Aug;58:242–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAN M., EPSTEIN W. V. Purification of gamma globulin fragments by gel filtration. Science. 1963 Jan 4;139(3549):53–54. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3549.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


