Abstract
In guinea-pigs injected intradermally with a small amount of antibody and challenged 2 hours later, by the intravenous route, with a mixture of homologous antigen and aggregated γ-globulin, haemorrhagic reactions of the Arthus type develop at the sites of intradermal sensitization. This effect was obtained with γ-globulins of different species (human, rabbit and horse) by using different techniques for aggregation (heat, mercaptoethanol—urea and bis-diazobenzidine) and was always correlated with the ability of the aggregated globulin to fix complement.
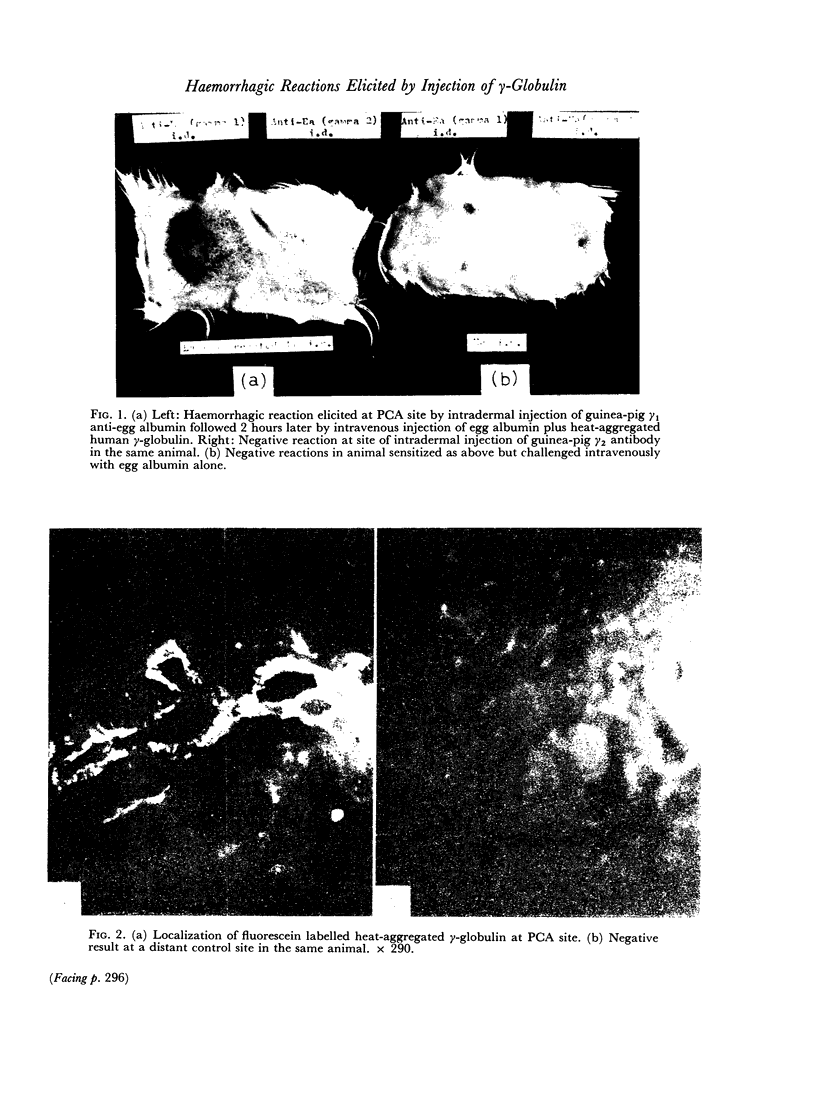
Fluorescein labelled aggregates of γ-globulin were detectable in the wall of vessels at sensitized sites.
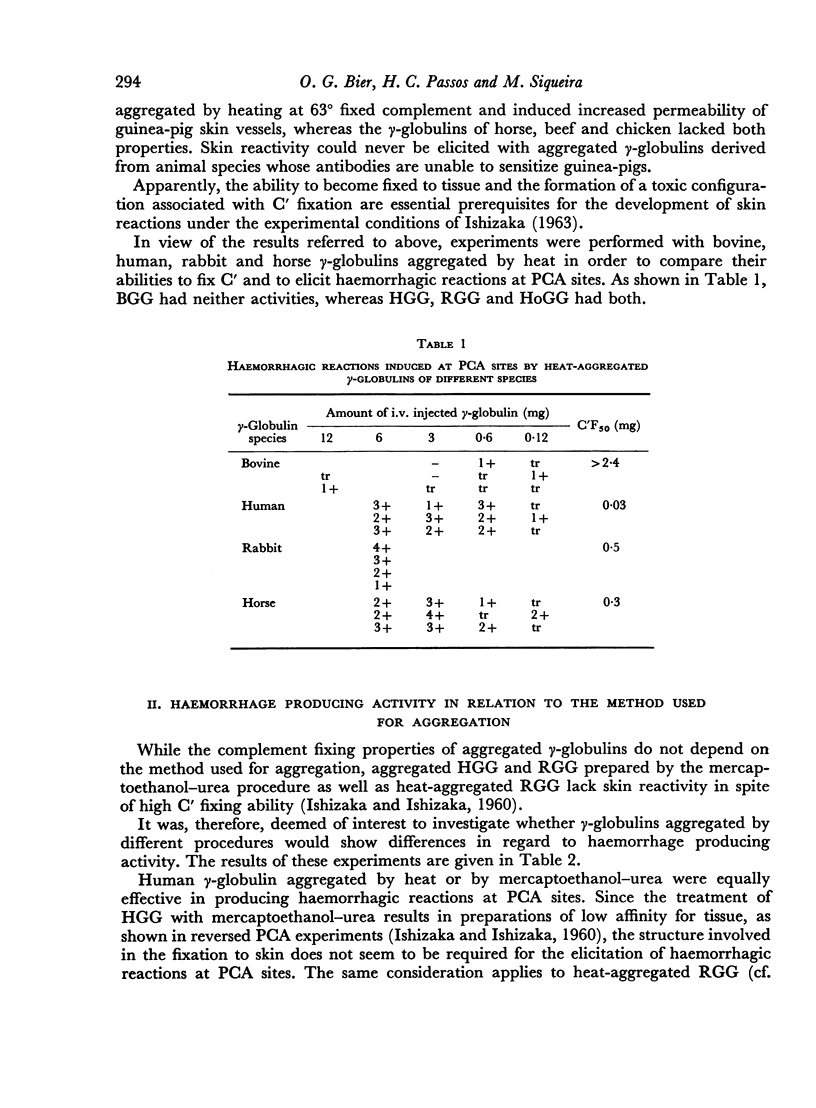
In experiments performed with guinea-pig antibodies, the localizing effect was observed only with γ1, whereas the γ2, Arthus-producing fraction proved completely ineffective.
Histamine and histamine liberators are not sufficient for eliciting the effect obtained with sensitizing antibody plus homologous antigen. It is postulated, therefore, that other effects occurring at the site of specific sensitization may also be responsible for the phenomenon.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENACERRAF B., OVARY Z., BLOCH K. J., FRANKLIN E. C. Properties of guinea pig 7S antibodies. I. Electrophoretic separation of two types of guinea pig 7S antibodies. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:937–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMMHAGEN L. H., FUDENBERG H. The role of aggregated gamma-globulins in the anticomplementary activity of human and animal sera. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:336–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIZAKA K. Gamma globulin and molecular mechanisms in hypersensitivity reactions. Prog Allergy. 1963;7:32–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIZAKA K., ISHIZAKA T. Biologic activity of aggregated gamma-globulin. II. A study of various methods for aggregation and species differences. J Immunol. 1960 Aug;85:163–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIZAKA T., ISHIZAKA K. Biological activities of aggregated gamma globulin. I. Skin reactive and complement-fixing properties of heat denatured gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:845–850. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., BENACERRAF B., BLOCH K. J. Properties of guinea pig 7S antibodies. II. Identification of antibodies involved in passive cutaneous and systemic anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:951–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., TARANTA A. Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis with antibody fragments. Science. 1963 Apr 12;140(3563):193–195. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3563.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIQUEIRA M., BIER O. G. Hemorrhagic reactions at sites of passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in guinea pig after intravenous inoculation of unrelated immune complex. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Aug-Sep;107:779–784. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARANTA A., FRANKLIN E. C. Complement fixation by antibody fragments. Science. 1961 Dec 15;134(3494):1981–1982. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3494.1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. IV. PARTICIPATION OF COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:965–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE A. L., OSLER A. G., MAYER M. M. Quantitative studies of complement fixation. V. Estimation of complement-fixing potency of immune sera and its relation to antibody-nitrogen content. J Immunol. 1950 Dec;65(6):661–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den BERG, OORT J., van RIJSSEL T. Fluorescent proteint tracer studies in allergic reactions. II. The fate of fluorescent antigen in reversed Arthus reactions and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in guinea-pig skin. Immunology. 1962 May;5:389–398. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]