Abstract
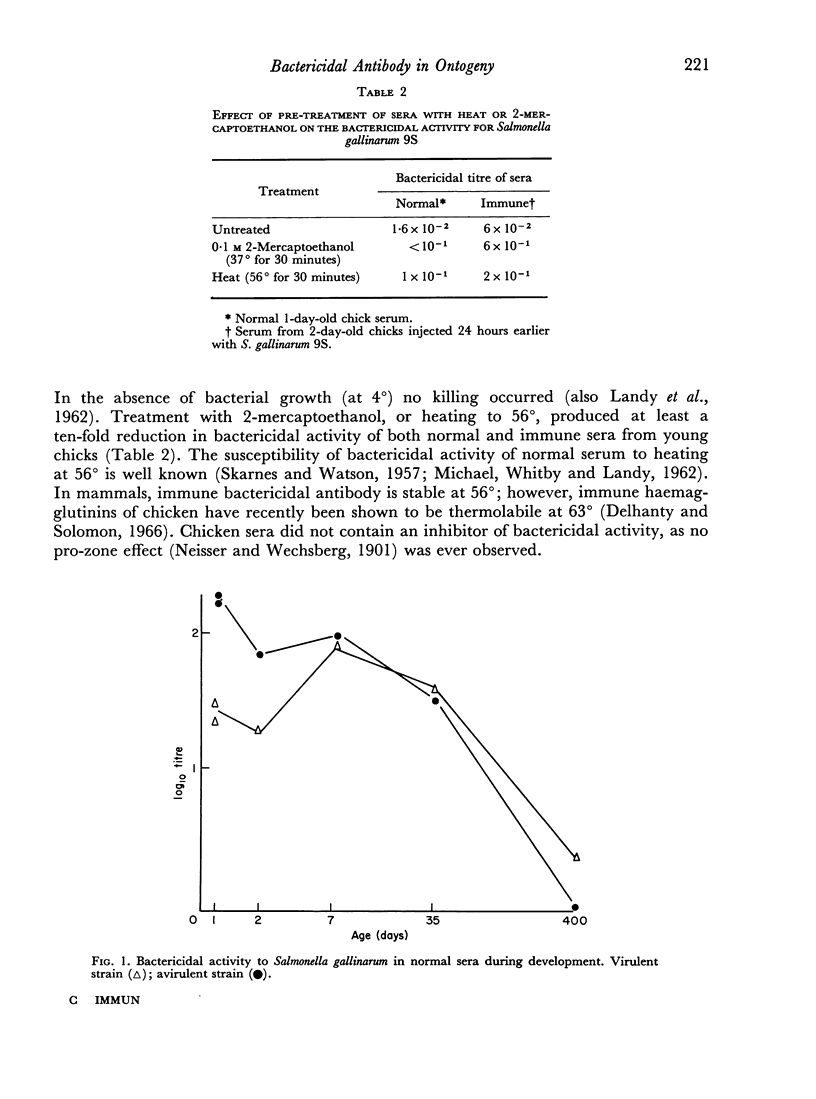
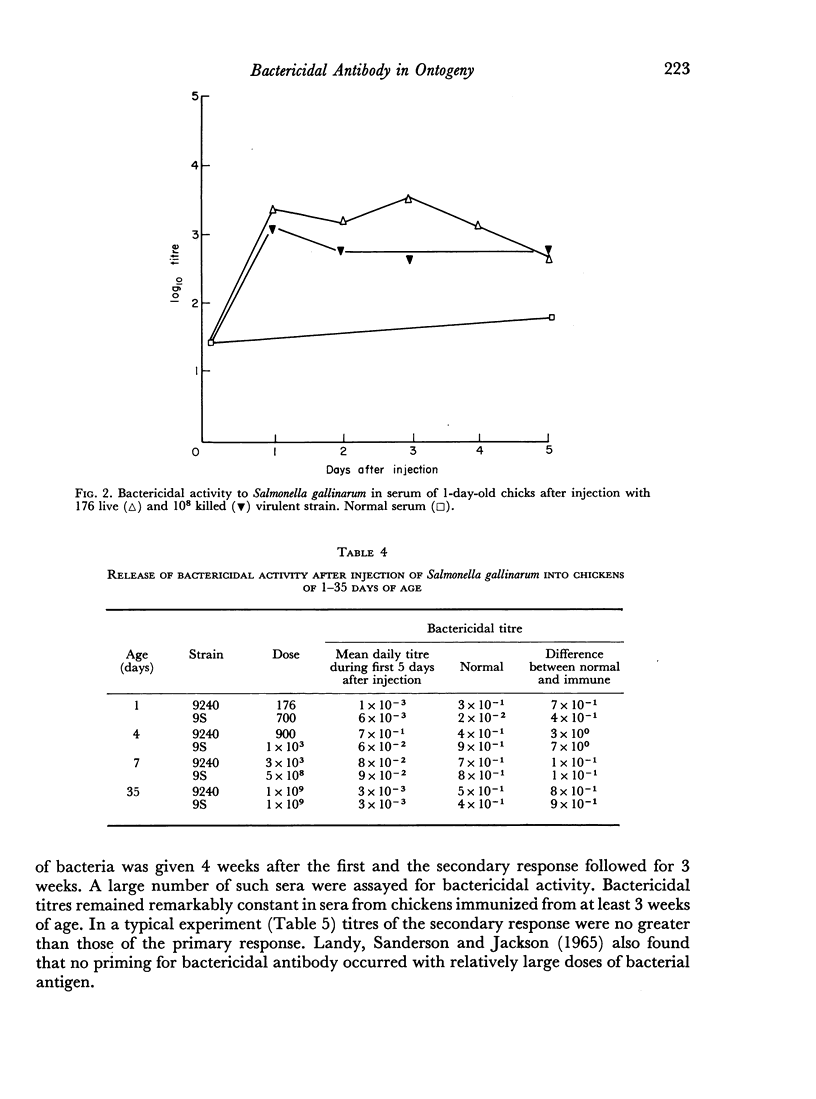
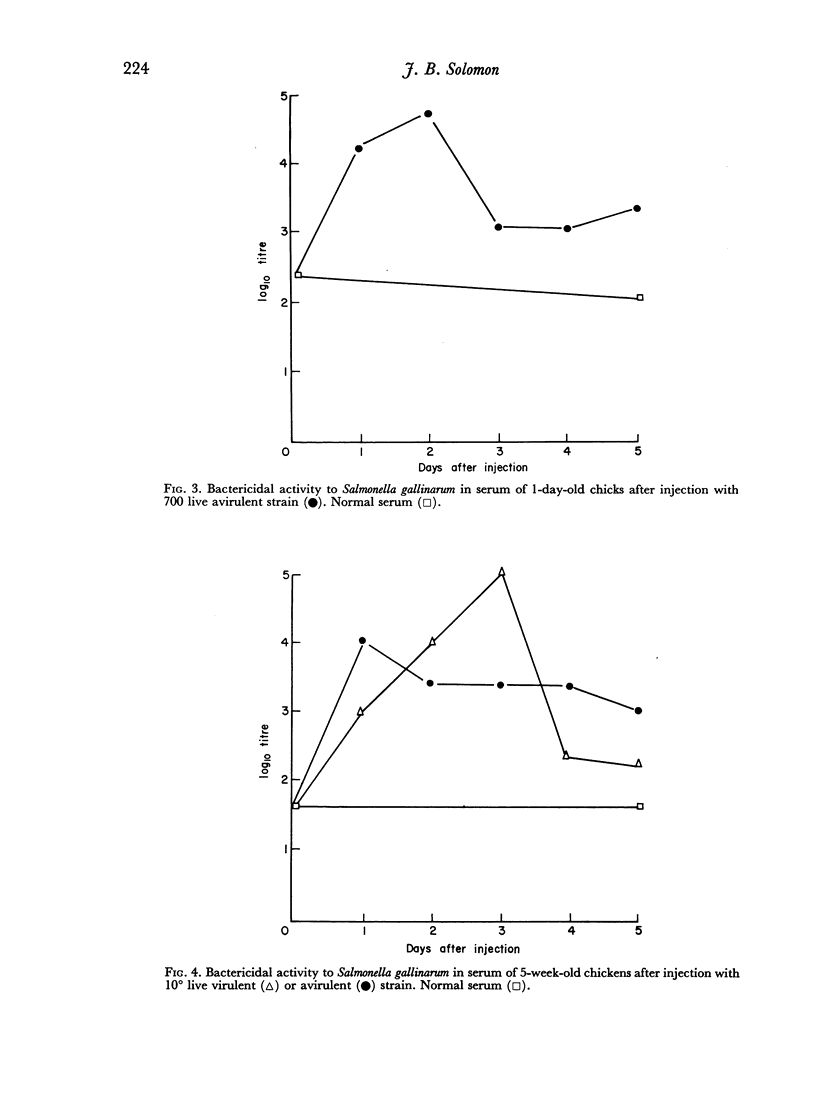
The bactericidal activity of chicken serum before and after injection of 1–35-day-old chickens with Salmonella gallinarum has been studied. The bactericidal action of immune serum is temperature-dependent. Treatment of both normal and immune serum with mercaptoethanol, by heating to 56°, produced a ten-fold reduction in bactericidal activity. The ingested yolk contained bactericidal factors at 1 day of age. Bactericidal activity of normal serum declined very slowly during the first 5 weeks of development. Bactericidal activity released by injection of S. gallinarum, showed some specificity for the somatic-O antigens and a high degree of species specificity. Injection of S. gallinarum into 1-day-old chicks resulted in the rapid release of a high level of bactericidal activity into the circulation. The bactericidal antibody response to an injection of S. gallinarum increased from 4 to 35 days of development. In chickens of 3 weeks of age, or older, induced bactericidal antibody remained at a high level for several weeks.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins F. M. Serum mediated killing of three group D salmonellas. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):247–253. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delhanty J. J., Solomon J. B. The nature of antibodies to goat erythrocytes in the developing chicken. Immunology. 1966 Aug;11(2):103–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., MICHAEL J. G., WHITBY J. L. Bactericidal method for the measurement in normal serum of antibody to gramnegative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:631–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.631-640.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy M., Sanderson R. P., Jackson A. L. Humoral and cellular aspects of the immune response to the somatic antigen of Salmonella enteritidis. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):483–504. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., WHITBY J. L., LANDY M. Increase in specific bactericidal antibodies after administration of endotoxin. Nature. 1961 Jul 15;191:296–297. doi: 10.1038/191296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., WHITBY J. L., LANDY M. Studies on natural antibodies to gram-negative bacteria. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:131–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKARNES R. C., WATSON D. W. Antimicrobial factors of normal tissues and fluids. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Dec;21(4):273–294. doi: 10.1128/br.21.4.273-294.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERZL J., KOSTKA J., LANC A. Development of bactericidal properties against gram-negative organisms in the serum of young animals. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1962 May;7:162–174. doi: 10.1007/BF02928237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B. Immunity to Salmonella gallinarum during ontogeny of the chicken. I. Onset of resistance to infection; the minor role of opsonins. Immunology. 1968 Aug;15(2):197–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B. Immunity to Salmonella gallinarum during ontogeny of the chicken. II. Induction of tolerance or priming by single doses of live or killed bacteria. Immunology. 1968 Aug;15(2):207–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B. Induction of antibody formation to goat erythrocytes in the developing chick embryo and effects of maternal antibody. Immunology. 1966 Aug;11(2):89–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER K. J., JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. THE BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO MOUSE TYPHOID. 2. ANTIBODY FORMATION DURING THE CARRIER STATE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Apr;42:229–236. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


