Abstract
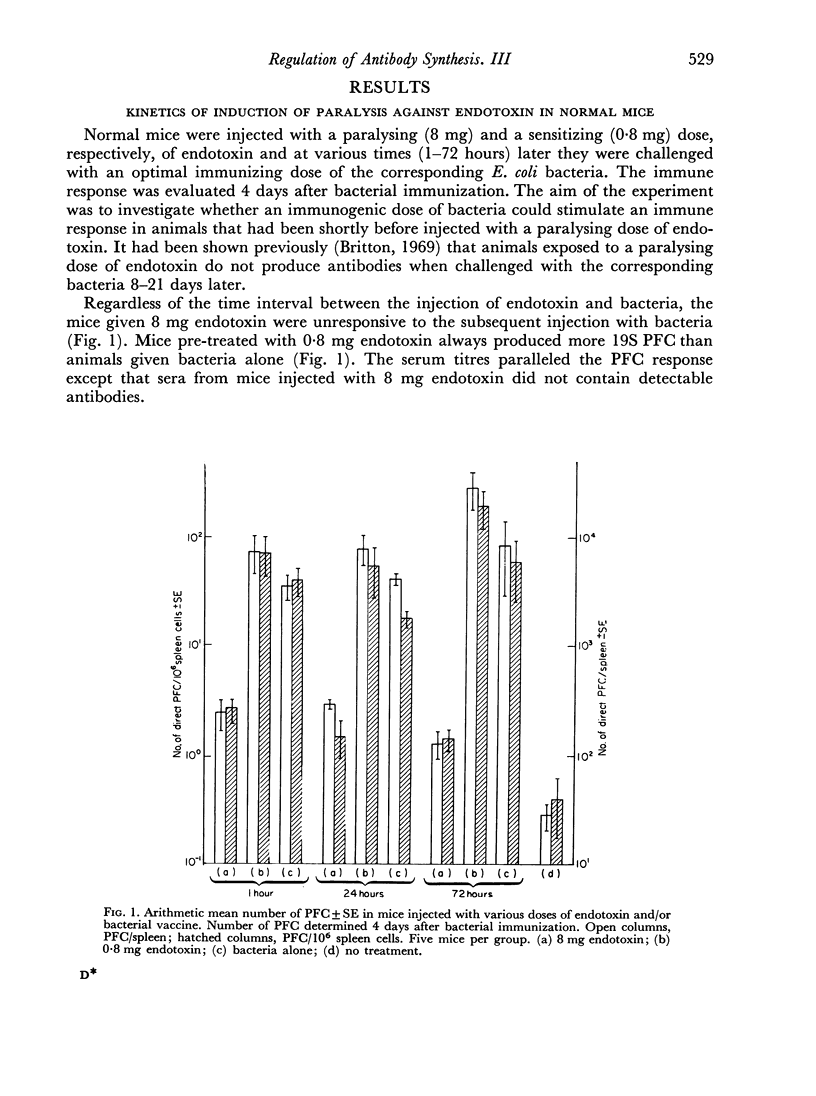
Normal mice injected with a paralysing dose of endotoxin are unresponsive to an immediate subsequent injection of an immunogenic dose of the corresponding bacteria.
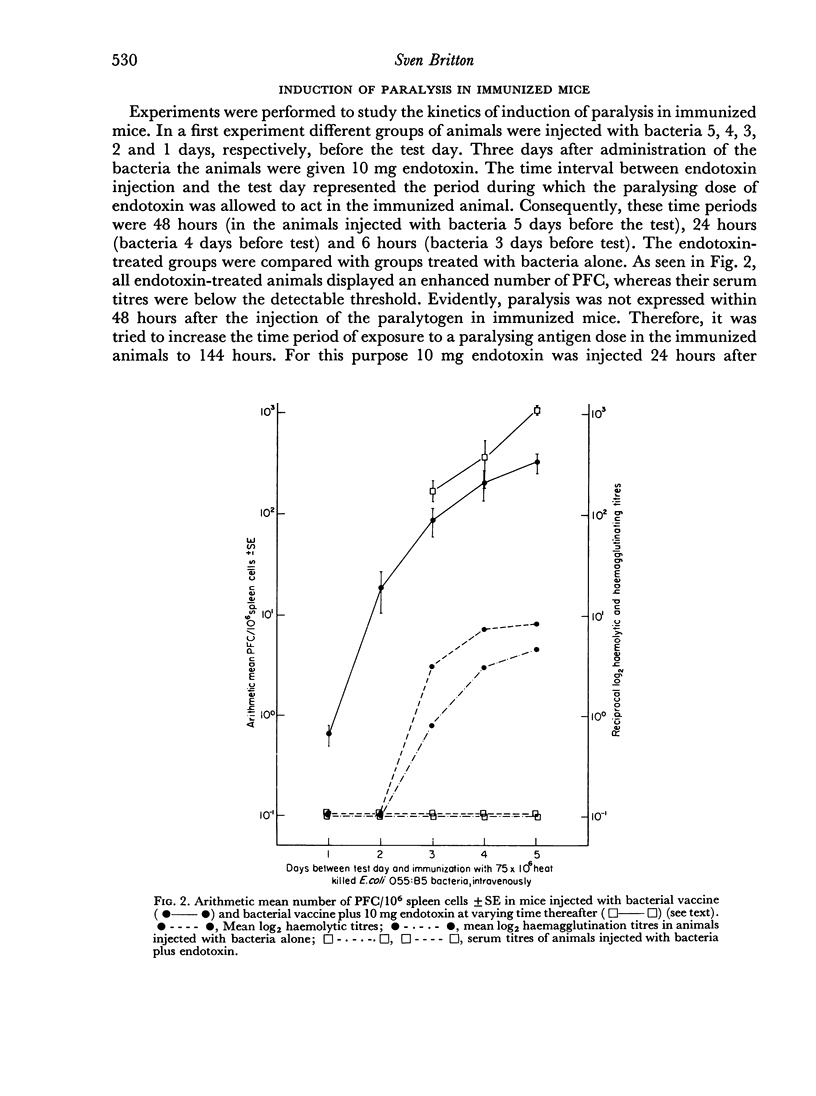
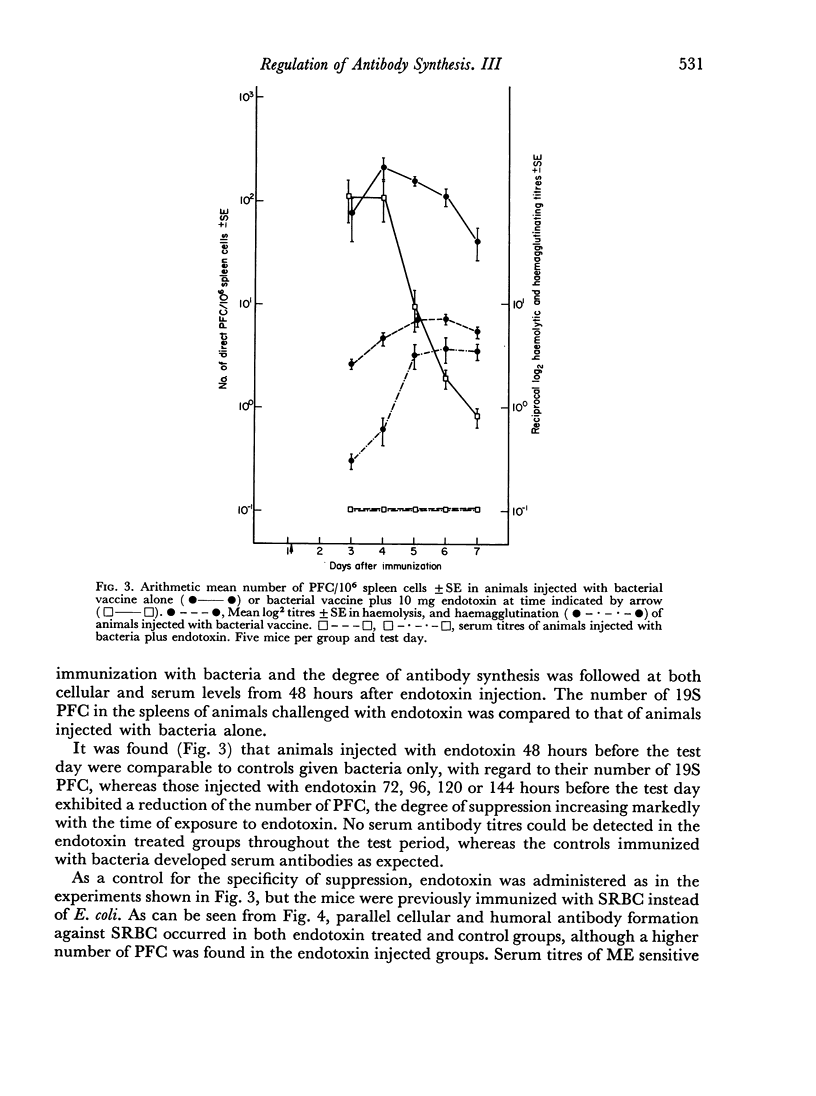
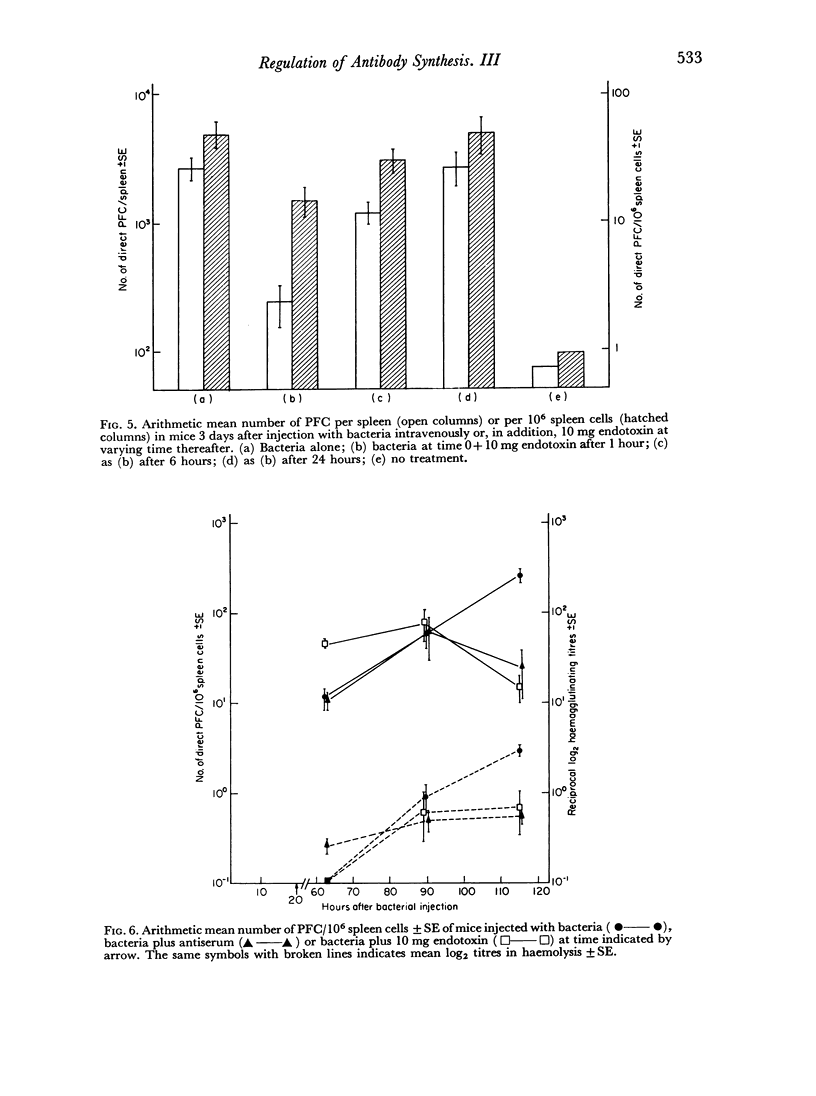
In pre-sensitized mice the injection of a paralysing dose of endotoxin suppresses the immune response after a lag period of 80–90 hours during which the responding cells appear normally. The suggested explanation to this was that antigen-sensitive cells once triggered by the antigen divide and produce antibodies for a certain time period and thereafter disappear. During this period they are unaffected by the paralysing dose of antigen. It is suggested that the cells amenable to suppression are those from which the antibody producing cells are recruited, e.g. the antigen sensitive cells.
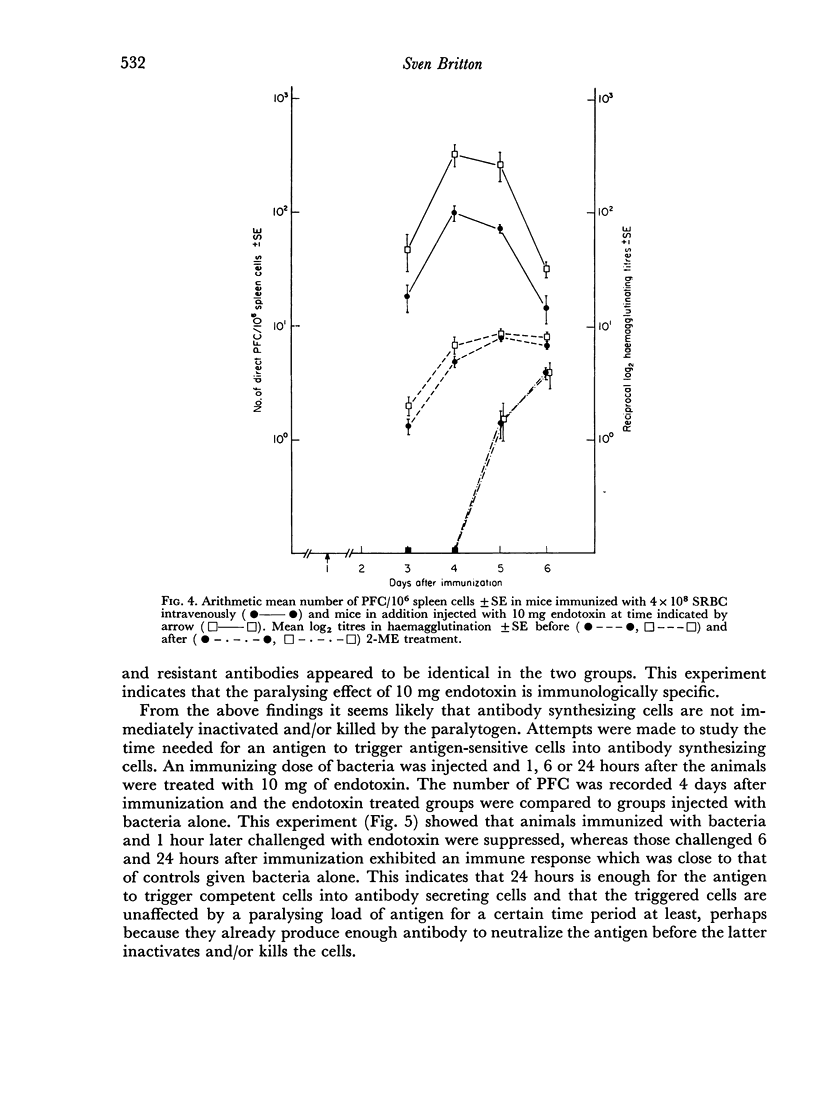
The kinetics of suppression of an active immune response was the same whether antiserum or a paralysing dose of antigen was used as suppressive agent. This finding further supported the conclusion that actively antibody producing cells are antigen independent.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britton S. Regulation of antibody synthesis against Escherichia coli endotoxin. II. Specificity, dose requirements and duration of paralysis induced in adult mice. Immunology. 1969 Apr;16(4):513–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. M., Mäkelä O. Selective inhibition of the secondary response of primed cells by incubation with hapten. Immunology. 1968 Sep;15(3):389–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W., Mitchison N. A. The mechanism of immunological paralysis. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:129–181. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W. Specific inhibition of antibody production. IV. Standardization of the antigen-elimination test; immunological paralysis of mice previously immunized. Immunology. 1965 Sep;9(3):261–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. S., Weigle W. O. Studies on the induction of immunologic unresponsiveness. II. Kinetics. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):624–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Watson D. W. Host-parasite relationships among group A streptococci. IV. Suppression of antibody response by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):14–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.14-21.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIACOPOULOS P., GOODE J. H. TRANSPLANTATION TOLERANCE INDUCED IN ADULT MICE BY PROTEIN OVERLOADING OF DONORS. Science. 1964 Dec 4;146(3649):1305–1307. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3649.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLER G., WIGZELL H. ANTIBODY SYNTHESIS AT THE CELLULAR LEVEL. ANTIBODY-INDUCED SUPPRESSION OF 19S AND 7S ANTIBODY RESPONSE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jun 1;121:969–989. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.6.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makinodan T., Albright J. F., Perkins E. H., Nettesheim P. Suppression of immunologic responses. Med Clin North Am. 1965 Nov;49(6):1569–1596. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)33247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison N. A. Immunological paralysis induced by brief exposure of cells to protein antigens. Immunology. 1968 Oct;15(4):531–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMONSEN M. Graft versus host reactions. Their natural history, and applicability as tools of research. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:349–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALMAGE D. W. Allergy and immunology. Annu Rev Med. 1957;8:239–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.08.020157.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UHR J. W., FINKELSTEIN M. S. Antibody formation. IV. Formation of rapidly and slowly sedimenting antibodies and immunological memory to bacteriophage phi-X 174. J Exp Med. 1963 Mar 1;117:457–477. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


