Abstract
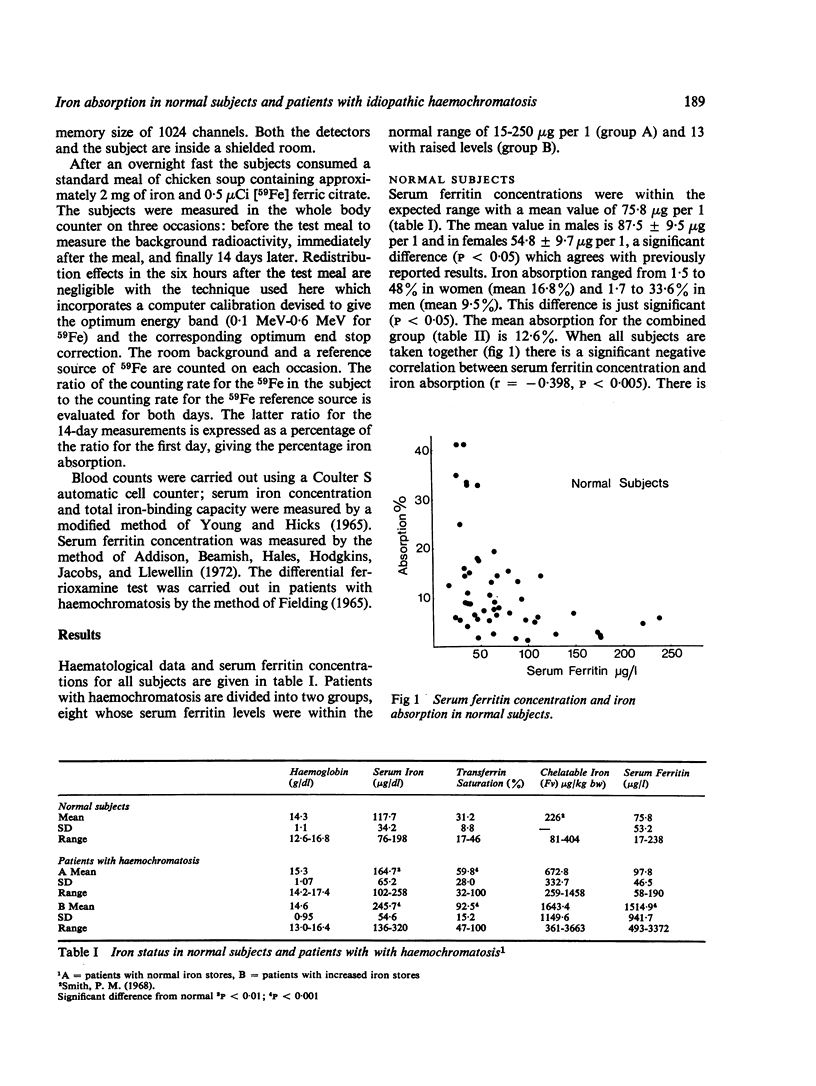
In 52 normal subjects there was an inverse relationship between serum ferritin concentration and iron absorption. In 21 measurements in 15 patients with idiopathic haemochromatosis there was a similar inverse relationship but absorption was higher in relation to iron stores at all levels. Haemochromatotic patients with normal serum ferritin levels had abnormally high values for desferrioxamine chelatable iron and there was no correlation between chelatable iron and iron absorption.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison G. M., Beamish M. R., Hales C. N., Hodgkins M., Jacobs A., Llewellin P. An immunoradiometric assay for ferritin in the serum of normal subjects and patients with iron deficiency and iron overload. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Apr;25(4):326–329. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.4.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTHWELL T. H., PIRZIO-BIROLI G., FINCH C. A. Iron absorption. I. Factors influencing absorption. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Jan;51(1):24–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beamish M. R., Walker R., Miller F., Worwood M., Jacobs A., Williams R., Corrigall A. Transferrin iron, chelatable iron and ferritin in idiopathic haemochromatosis. Br J Haematol. 1974 Jun;27(2):219–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. P., Williams P. Serum ferritin concentration as an index of storage iron in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Oct;27(10):786–788. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.10.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONRAD M. E., CROSBY W. H. The natural history of iron deficiency induced by phlebotomy. Blood. 1962 Aug;20:173–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H. THE CONTROL OF IRON BALANCE BY THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA. Blood. 1963 Oct;22:441–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. E. Humoral regulation of iron absorption. Gastroenterology. 1969 Aug;57(2):225–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELDING J. DIFFERENTIAL FERRIOXAMINE TEST FOR MEASURING CHELATABLE BODY IRON. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jan;18:88–97. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A., Kaye M. D., Trevett D. The chelation of iron during intestinal absorption. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Aug;74(2):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A., Miller F., Worwood M., Beamish M. R., Wardrop C. A. Ferritin in the serum of normal subjects and patients with iron deficiency and iron overload. Br Med J. 1972 Oct 28;4(5834):206–208. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5834.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Miller F. M., Worwood M., Jacobs A. Ferritinaemia in leukaemia and Hodgkin's disease. Br J Cancer. 1973 Mar;27(3):212–217. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letsky E. A., Miller F., Worwood M., Flynn D. M. Serum ferritin in children with thalassaemia regularly transfused. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Aug;27(8):652–655. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.8.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipschitz D. A., Simon M. O., Lynch S. R., Dugard J., Bothwell T. H., Charlton R. W. Some factors affecting the release of iron from reticuloendothelial cells. Br J Haematol. 1971 Sep;21(3):289–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siimes M. A., Addiego J. E., Jr, Dallman P. R. Ferritin in serum: diagnosis of iron deficiency and iron overload in infants and children. Blood. 1974 Apr;43(4):581–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. M., Godfrey B. E., Williams R. Iron absorption in idiopathic haemochromatosis and its measurement using a whole-body counter. Clin Sci. 1969 Oct;37(2):519–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger A., Hershko C. Hepatocellular uptake of ferritin in the rat. Br J Haematol. 1974 Oct;28(2):169–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINTRAUB L. R., CONRAD M. E., CROSBY W. H. THE SIGNIFICANCE OF IRON TURNOVER IN THE CONTROL OF IRON ABSORPTION. Blood. 1964 Jul;24:19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters G. O., Miller F. M., Worwood M. Serum ferritin concentration and iron stores in normal subjects. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Oct;26(10):770–772. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.10.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters G. O., Thompson W., Jacobs A., Wood C. S. Letter: Iron stores and iron absorption. Lancet. 1973 Nov 24;2(7839):1216–1216. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92994-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG D. S., HICKS J. M. METHOD FOR THE AUTOMATIC DETERMINATION OF SERUM IRON. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jan;18:98–102. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


