Abstract
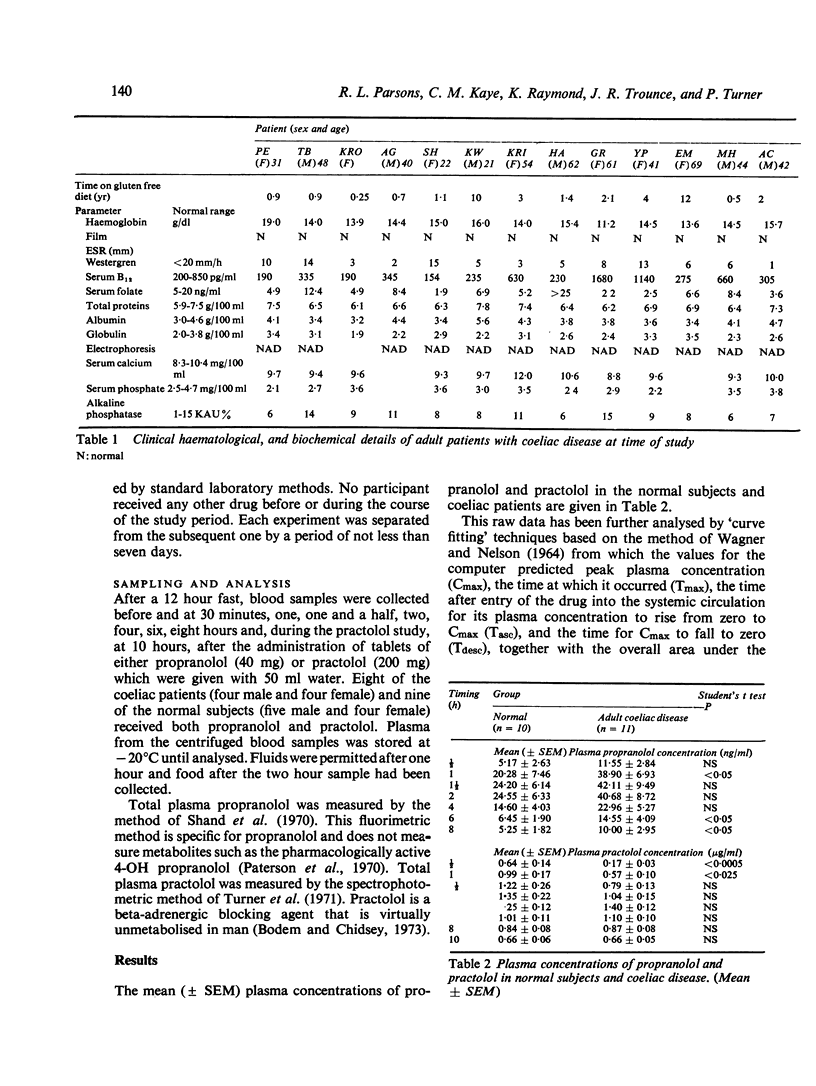
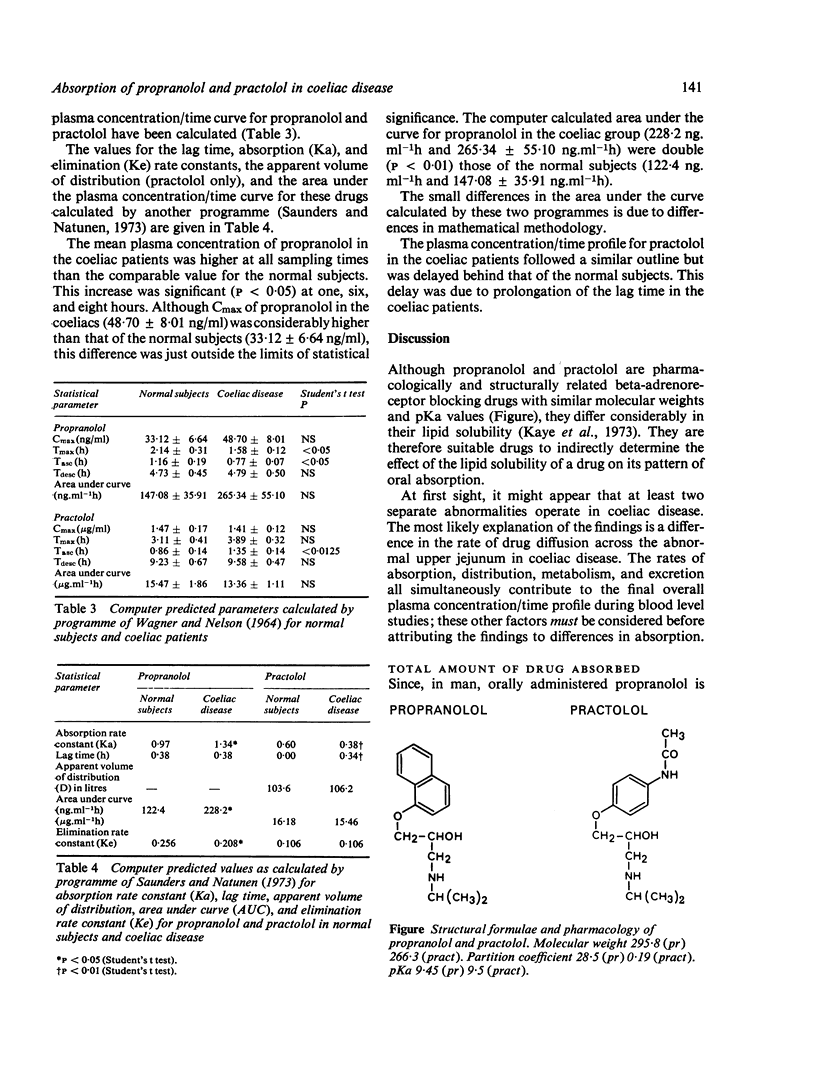
Plasma concentrations of propranolol and practolol were measured in patients with coeliac disease and normal subjects. The mean plasma propranolol concentration in the coeliac patients was higher throughout the period of study, the differences being significant at one, six, and eight hours. The plasma concentration profile of practolol in the coeliacs followed a similar pattern but lagged behind that of the normal subjects. A possible reason for these differences is an alteration in the rate of drug diffusion across the atrophic mucosa of the upper jejunum in coeliac disease. Analysis of the results of the propranolol study suggests that an increase in the rate of absorption combined with saturation of first pass extraction may account for the increased plasma concentrations of unchanged propranolol found in coeliac disease. These abnormalities of drug absorption do not appear to be related to the duration of treatment with a gluten free diet.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benn A., Cooke W. T. Intraluminal pH of duodenum and jejunum in fasting subjects with normal and abnormal gastric or pancreatic function. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1971;6(4):313–317. doi: 10.3109/00365527109181126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodem G., Chidsey C. A. Pharmacokinetic studies of practolol, a beta adrenergic antagonist, in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Jan-Feb;14(1):26–29. doi: 10.1002/cpt197314126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castleden C. M., Kaye C. M., Parsons R. L. The effect of age on plasma levels of propranolol and practolol in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;2(4):303–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1975.tb02774.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGBEN C. A., TOCCO D. J., BRODIE B. B., SCHANKER L. S. On the mechanism of intestinal absorption of drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Apr;125(4):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A., Cooper R. G. Studies on the absorption, distribution and excretion of propranolol in rat, dog and monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Feb;176(2):302–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye C. M., Robinson D. G., Turner P. Proceedings: The influence of urine pH on the renal excretion of practolol and propranolol. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):155P–156P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moberg S., Carlberger G. Gastric emptying in healthy subjects and in patients with various malabsorptive states. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(1):17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Hossack G., Paddock G. The absorption of antibiotics in adult patients with coeliac disease. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Mar;1(1):39–50. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G., Nuckolls E. M., Oates J. A. Plasma propranolol levels in adults with observations in four children. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Jan-Feb;11(1):112–120. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970111112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G. Pharmacokinetic properties of the beta-adrenergic receptor blocking drugs. Drugs. 1974;7(1):39–47. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197407010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G., Rangno R. E. The disposition of propranolol. I. Elimination during oral absorption in man. Pharmacology. 1972;7(3):159–168. doi: 10.1159/000136285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner P., Burman J., Hicks D. C., Cherrington N. K., MacKinnon J., Wallet T., Woolnough M. A comparison of the effects of propranolol and practolol on forced expiratory volume and resting heart rate in normal subjects. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1971 May;191(1):104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER J. G., NELSON E. KINETIC ANALYSIS OF BLOOD LEVELS AND URINARY EXCRETION IN THE ABSORPTIVE PHASE AFTER SINGLE DOSES OF DRUG. J Pharm Sci. 1964 Nov;53:1392–1403. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600531126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


