Abstract
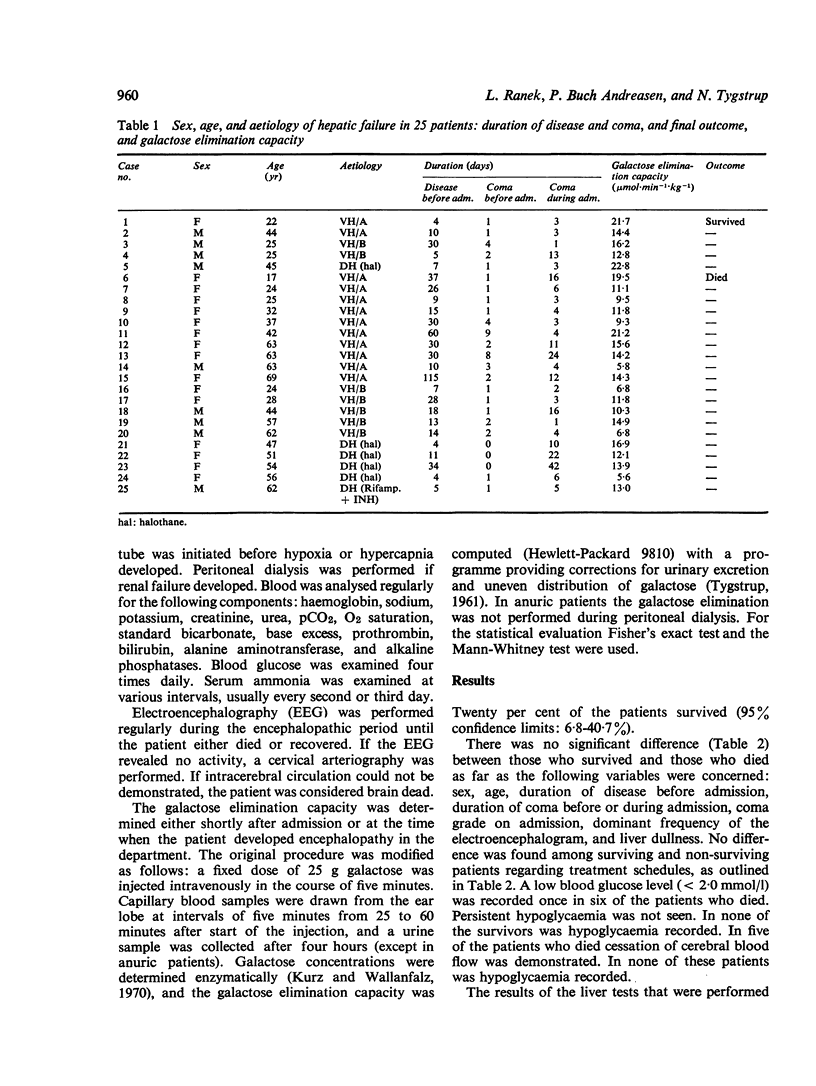
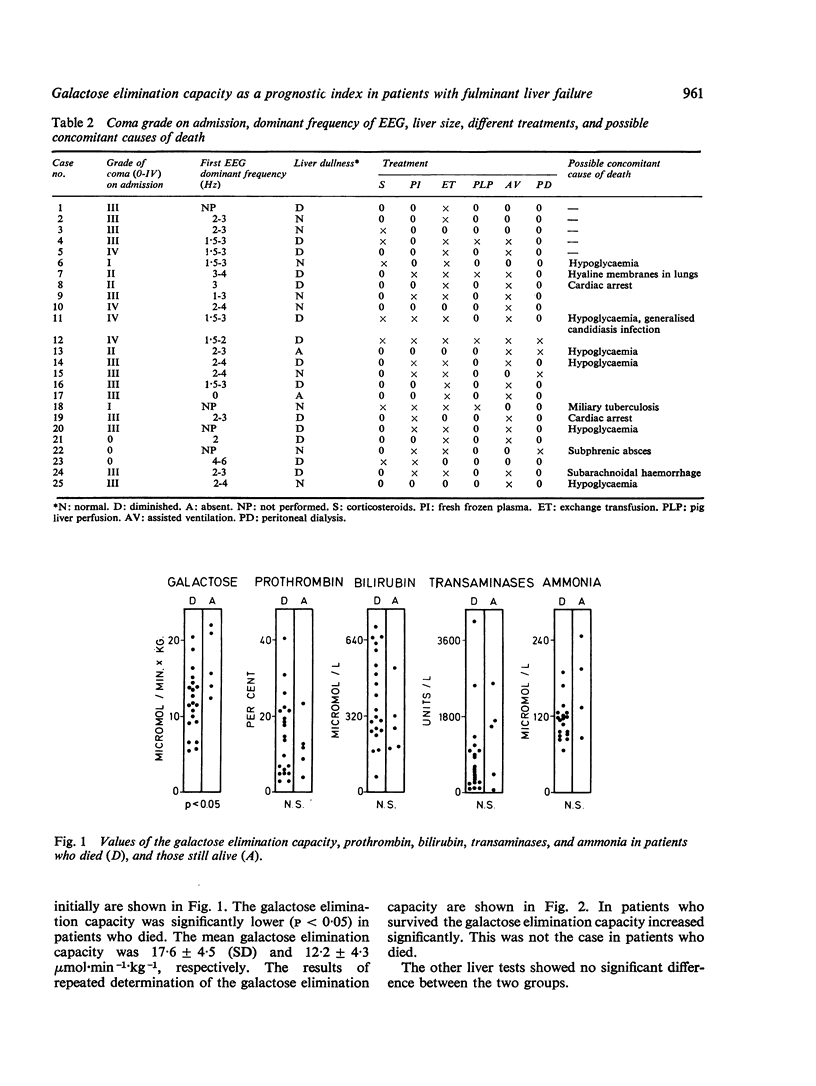
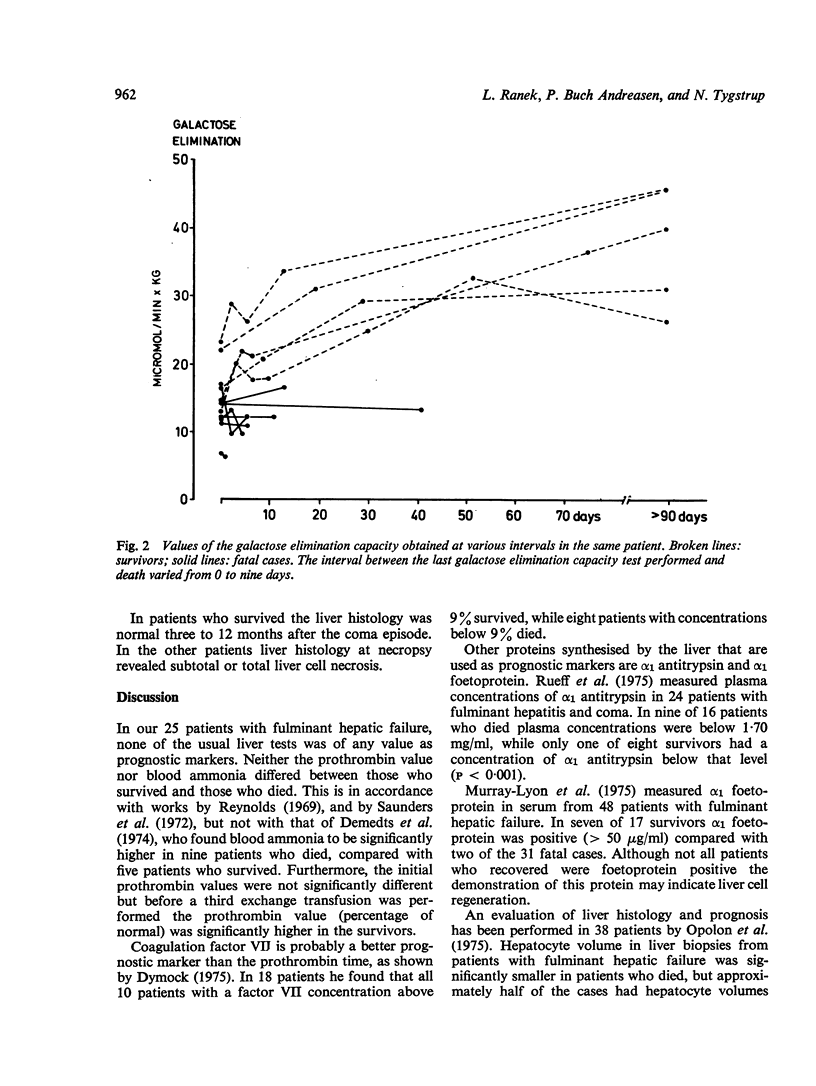
In 25 patients with fulminant hepatic failure the prognostic value of a quantitative liver function test, the galactose elimination capacity, was assessed and comapred with routine liver function tests and clinical features. The galactose elimination capacity was significantly higher (P less than 0-05) in the five patients who survived than in the 20 patients who died. None of the other liver function tests, was significantly different. The values of the galactose elimination capacity overlapped considerably between survivors and non-survivors, but all patients with a galactose elimination capacity below 12-8 mumol galactose/min and kg body weight died. The disease among most patients who died having a galactose elimination capacity greater than 13 mumol ran a subacute course. It is suggested that quantitative liver function tests be included when new treatments of fulminant hepatic failure are investigated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. B., Ranek L. Liver failure and drug metabolism. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(3):293–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnell J. M., Runge C., Saunders F. C., Thomas E. D., Volwiler W. Acute hepatic failure treated by cross circulation. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Oct;132(4):493–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demedts M., De Groote J., Vandamme B., Desmet V. J. Discriminative and prognostic signs in acute hepatic coma, treated by exchange transfusions. Digestion. 1974;11(1-2):105–114. doi: 10.1159/000197573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiseman B., Liem D. S., Raffucci F. Heterologous liver perfusion in treatment of hepatic failure. Ann Surg. 1965 Sep;162(3):329–345. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196509000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzard B. G., Weston M. J., Murray-Lyon I. M., Flax H., Record C. O., Williams R., Portmann B., Langley P. G., Dunlop E. H., Mellon P. J. Charcoal haemoperfusion in the treatment of fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet. 1974 Jun 29;1(7870):1301–1307. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90678-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karvountzis G. G., Redeker A. G., Peters R. L. Long term follow-up studies of patients surviving fluminant viral hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1974 Nov;67(5):870–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Roscoe P., Wright N., Brown S. S. Plasma-paracetamol half-life and hepatic necrosis in patients with paracetamol overdosage. Lancet. 1971 Mar 13;1(7698):519–522. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranek L., Hansen R. I., Hilden M., Ramsöe K., Schmidt A., Winkler K., Tygstrup N. Pig liver perfusion in the treatment of acute hepatic failure. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1971;9:161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds T. B. Exchange transfusion in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):170–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S. J., Hickman R., Macdonald R., Terblanche J. The treatment of acute liver failure. Prog Liver Dis. 1972;4:333–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYGSTRUP N. The urinary excretion of galactose and its significance in clinical intravenous galactose tolerance tests. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Feb-Mar;51:263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trey C., Burns D. G., Saunders S. J. Treatment of hepatic coma by exchange blood transfusion. N Engl J Med. 1966 Mar 3;274(9):473–481. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196603032740901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tygstrup N. Determination of the hepatic elimination capacity (Lm) of galactose by single injection. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1966;18:118–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


