Abstract
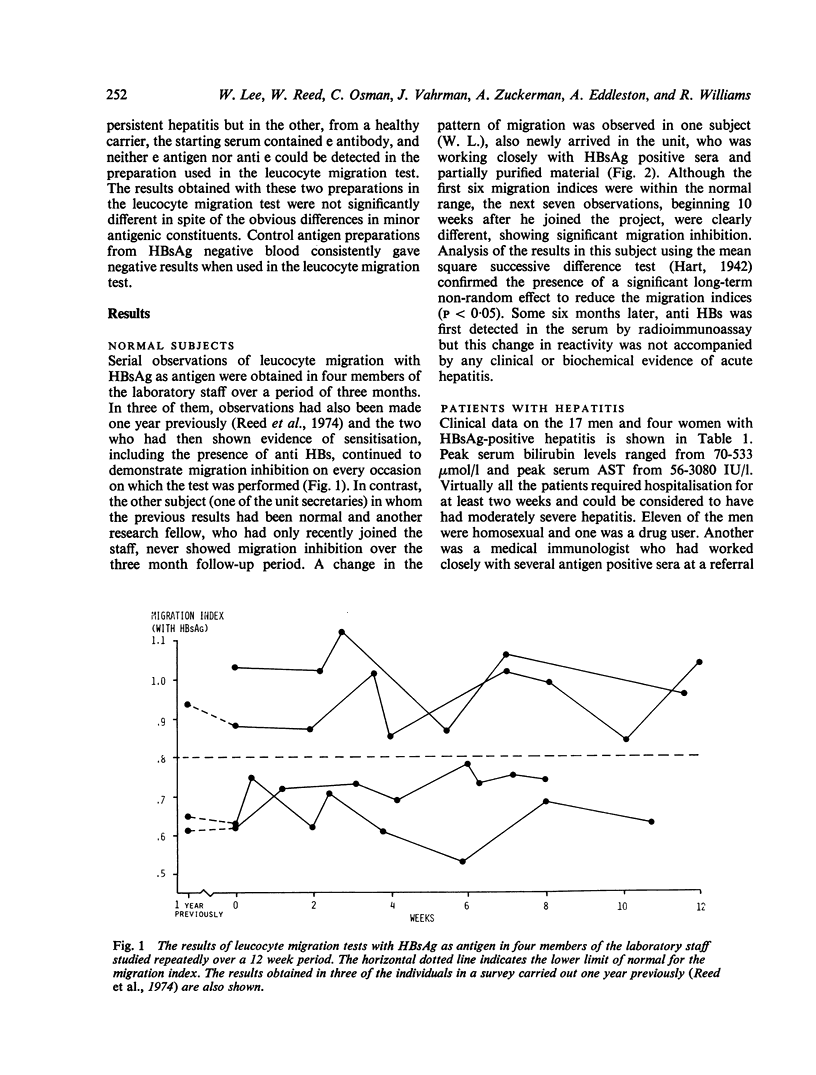
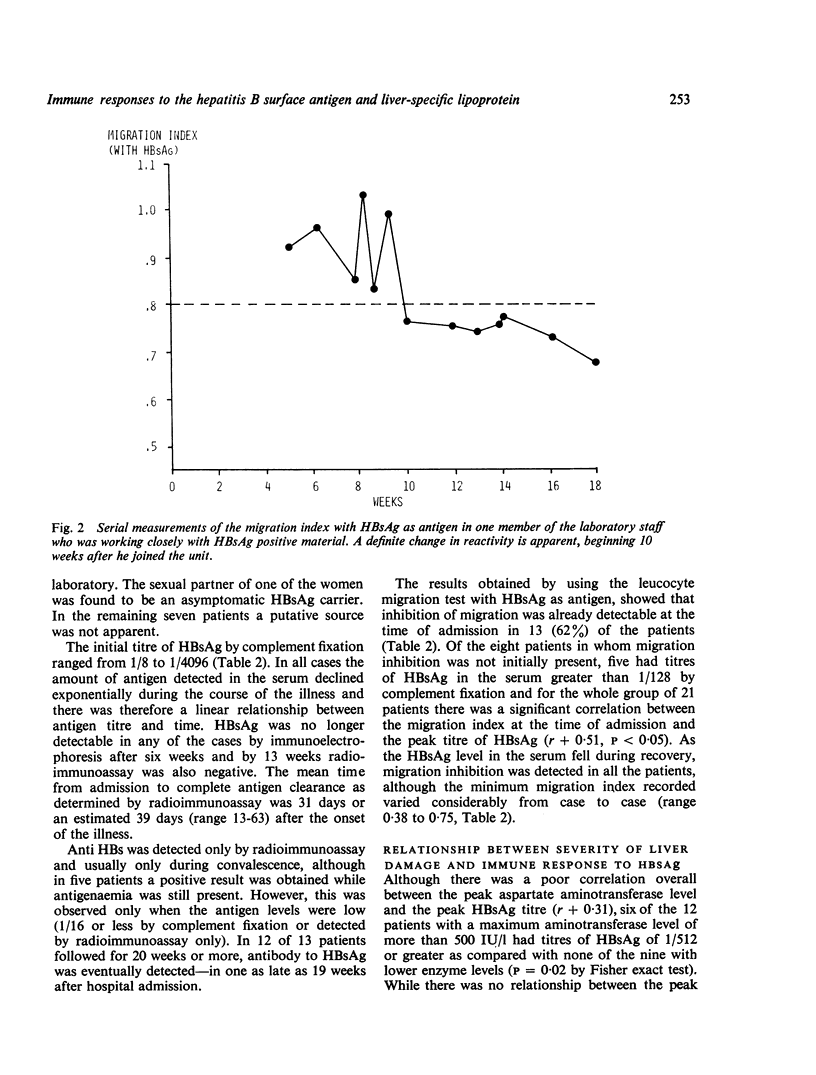
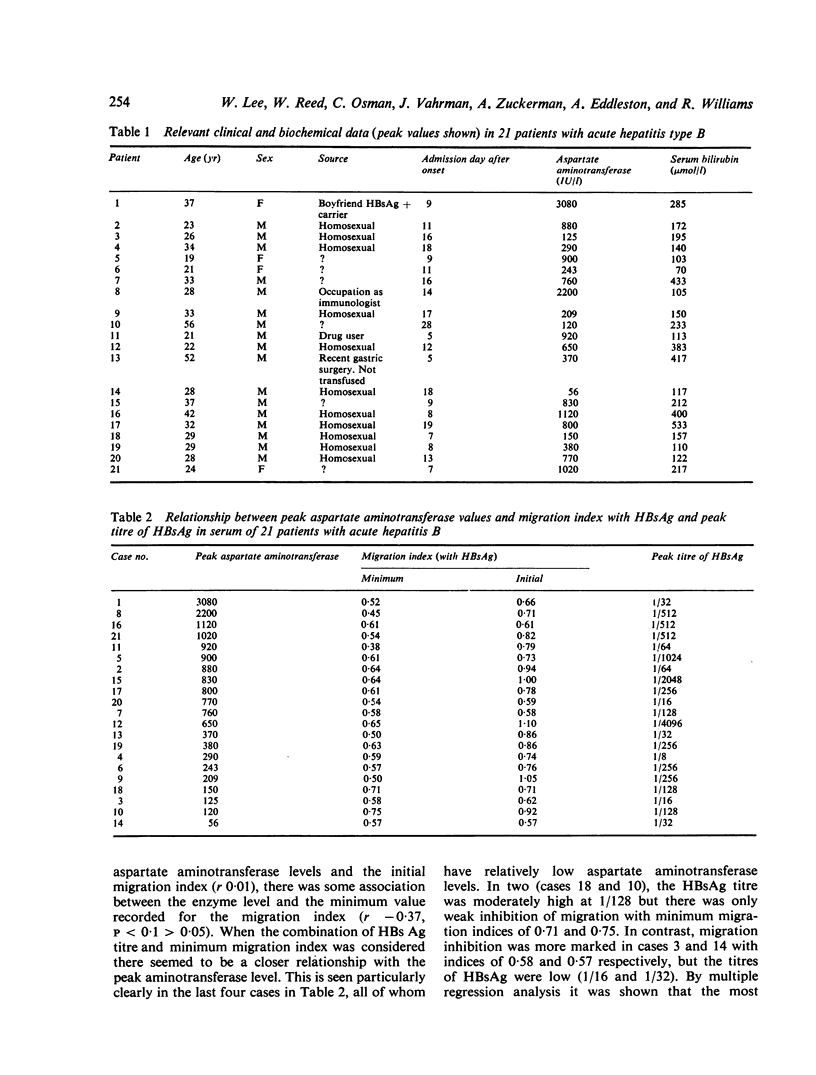
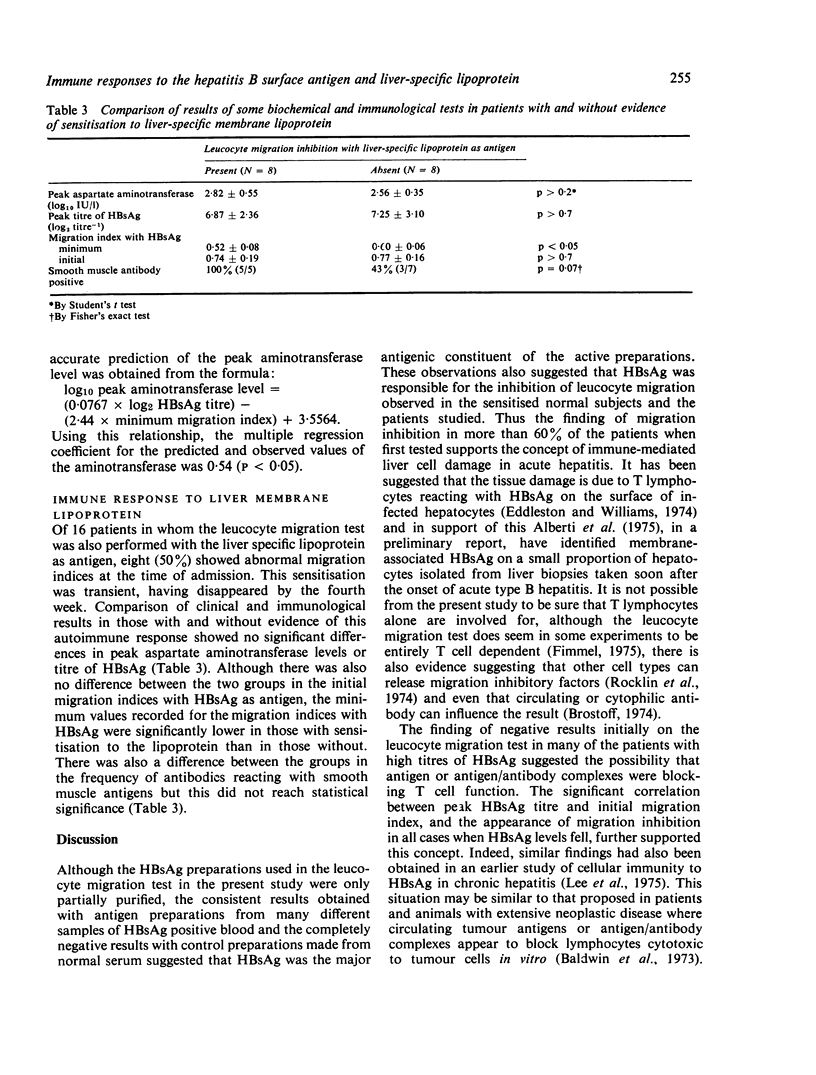
A serial prospective study of cellular immunity to HBsAg and liver-specific membrane lipoprotein was undertaken in 21 adults with acute hepatitis type B. Cellular immunity to HBsAg as determined by leucocyte migration inhibition with partially purified HBsAg as antigen was detected in all the patients during the recovery phase of the illness and was already detectable at the time of admission in 13 (62%) of the cases. In five of the remaining eight the titre of HBsAg in the serum at this time was high and in the whole series there was an inverse correlation between the degree of migration inhibition on admission and the peak HBsAg titre suggesting that antigen or possibly antigen/antibody complexes might be interfering with the demonstration of cellular immunity in vitro. Using a combination of minimum migration index recorded during the recovery period peak HBsAg titre, it was possible to compute the peak aspartate aminotransferase level with reasonable accuracy, a finding consistent with the hypothesis that the severity of the illness is related to both the number of infected hepatocytes and the vigour of the immune response to HBsAg. Evidence of an immune response to the liver-specific hepatocyte membrane lipoprotein was present in 50% of the patients tested at the time of admission, but was transient, having disappeared in every case by four weeks. The minimum migration index recorded with HBsAg as antigen was significantly lower in those with detectable sensitisation to the lipoprotein and it is possible that this autoimmune reaction is also generated by the interaction of T cells with viral antigenic determinants on the liver cell surface.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti A., Realdi G., Tremolada F., Cadrobbi P. Letter: HBAg on liver-cell surface in viral hepatitis. Lancet. 1975 Feb 8;1(7902):346–346. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91267-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADSTREET C. M., TAYLOR C. E. Technique of complementfixation test applicable to the diagnosis of virus diseases. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1962 May;21:96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin R. W., Price M. R., Robins R. A. Inhibition of hepatoma-immune lymph-node cell cytotoxicity by tumour-bearer serum, and solubilized hepatoma antigen. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):527–535. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff J. Critique of present in vitro methods for the detection of cell-mediated immunity. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 Jun;67(6 Pt 1):514–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Smith A., Thomson A. D., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Autoimmune reaction to a liver specific membrane antigen during acute viral hepatitis. Gut. 1976 Sep;17(9):714–718. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.9.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie G. A., Basham C. Serum mediated inhibition of the immunological reactions of the patient to his own tumour: a possible role for circulating antigen. Br J Cancer. 1972 Dec;26(6):427–438. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach D., Roitt I. M., Walker J. G., Sherlock S. Tissue antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis, active chronic (lupoid) hepatitis, cryptogenic cirrhosis and other liver diseases and their clinical implications. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jul;1(3):237–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Fox R. A., Sherlock S. Cellular immunity and hepatitis-associated, Australia antigen liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Apr 1;1(7753):723–726. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Giustino V., Sherlock S. Cell-mediated immunity in patients positive for hepatitis-associated antigen. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 30;4(5843):754–756. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5843.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston A. L., McFarlane I. G., Mitchell C. G., Reed W. D., Williams R. Cell-mediated immune response in primary biliary cirrhosis to a protein fraction from human bile. Br Med J. 1973 Nov 3;4(5887):274–276. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5887.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Inadequate antibody response to hBAg or suppressor T-cell defect in development of active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1543–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Sheikh N., Woolf I. L., Galbraith R. M., Eddleston A. L., Dymock I. W., Williams R. e Antigen-antibody system as indicator of liver damage in patients with hepatitis-B antigen. Br Med J. 1975 Nov 1;4(5991):252–253. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5991.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fimmel P. J. Studies on leukocyte migration inhibiton: the role of E rosette-forming cells in specific antigen-induced inhibition of migration. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):135–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei P. C., Erard P., Zinkernagel R. Cell-mediated immunity to hepatitis-associated antigen (HAA) demonstrated by leucocyte migration test during and after acute B hepatitis. Biomedicine. 1973 Sep 20;19(9):379–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim A. B., Vyas G. N., Perkins H. A. Immune response to hepatitis B surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):137–141. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.137-141.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin G. R., Jr, Hierholzer W. J., Jr, Cimis R., McCollum R. W. Delayed hypersensitivity in hepatitis B: clinical correlates of in vitro production of migration inhibition factor. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):580–587. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiwah A. A., Chaudhuri A. K., Anderson J. R. Lymphocyte transformation and leucocyte migration-inhibition by Australia antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Sep;15(1):27–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Reed W. D., Mitchell C. G., Galbraith R. M., Eddleston A. L., Zuckerman A. J., Williams R. Cellular and humoral immunity to hepatitis-B surface antigen in active chronic hepatitis. Br Med J. 1975 Mar 29;1(5960):705–708. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5960.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Smith M. G., Mitchell C. G., Reed W. D., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Cell-mediated immunity to a human liver-specific antigen in patients with active chronic hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1972 Aug 12;2(7772):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92904-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. G., Eddleston A. L. The importance of selecting suitable foetal calf serum for use in the leucocyte migration test. Transplantation. 1973 Dec;16(6):689–691. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197312000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. G., Smith M. G., Golding P. L., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Evaluation of the leucocyte migration test as a measure of delayed hypersensitivty in man. Suppression of migration inhibition by puromycin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Aug;11(4):535–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portmann B., Galbraith R. M., Eddleston A. L., Zuckerman A. J., Williams R. Detection of HBSAG in fixed liver tissue - use of a modified immunofluorescent technique and comparison with histochemical methods. Gut. 1976 Jan;17(1):1–9. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. D., Mitchell C. G., Eddleston A. L., Lee W. M., Williams R., Zuckerman A. J. Exposure and immunity to hepatitis-B virus in a liver unit. Lancet. 1974 Apr 6;1(7858):581–583. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92646-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. D., Stern R. B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R., Zuckerman A. J., Bowes A., Earl P. M. Detection of hepatitis-B antigen by radioimmunoassay in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in Great Britain. Lancet. 1973 Sep 29;2(7831):690–694. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soborg M. In vitro detection of cellular hypersensitivity in man. Specific migration inhibition of white blood cells from brucella-positive persons. Acta Med Scand. 1967 Aug;182(2):167–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


