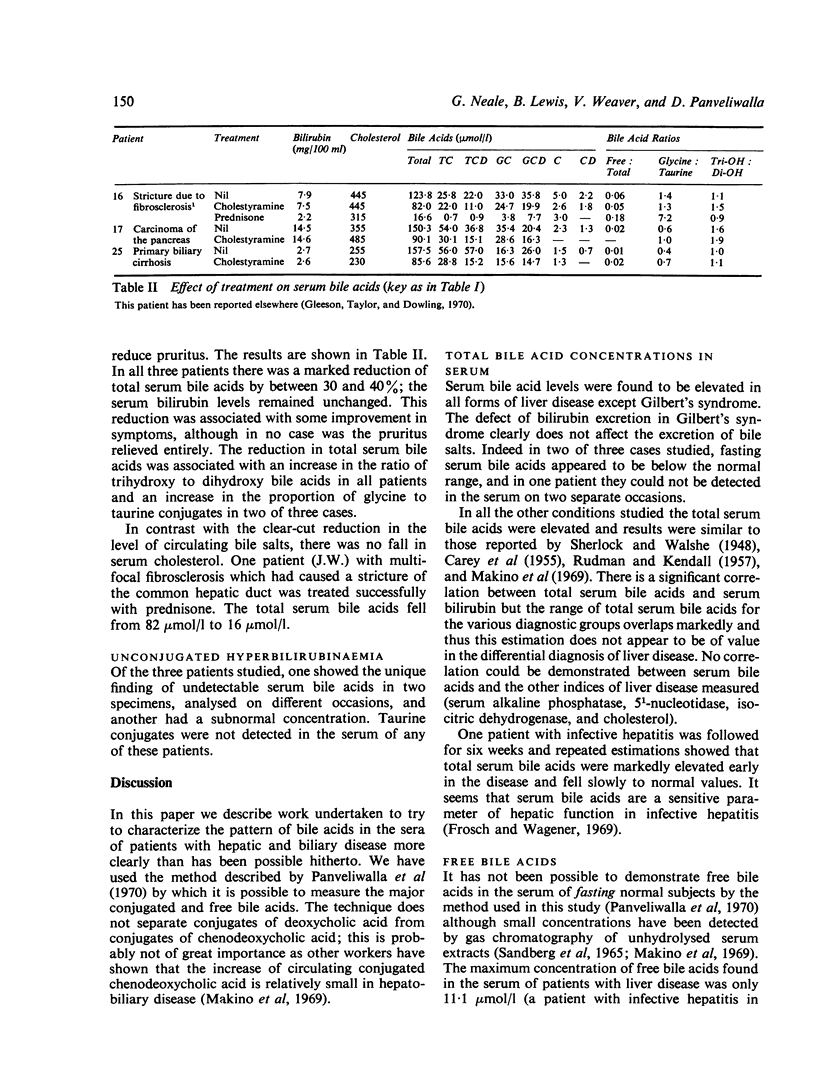
Abstract
Serum bile acids have been measured in patients with a wide variety of liver diseases using a technique which separates the major individual conjugated and free bile acids. Total serum bile acids may be elevated up to 100 times the normal concentration in patients with liver disease and this increase consists largely of conjugated bile acids. The ratio of glycine-conjugated to taurine-conjugated bile salts is low in all types of liver disease and this is found particularly in the serum of patients with obstructive jaundice. There is a decrease in the ratio of trihydroxy:dihydroxy cholanic acid in patients with cirrhosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAREY J. B. BILE ACIDS, CIRRHOSIS, AND HUMAN EVOLUTION. Gastroenterology. 1964 Apr;46:490–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAREY J. B., Jr Bile acids in the serum of jaundiced patients. Gastroenterology. 1961 Sep;41:285–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAREY J. B., Jr The serum trihydroxy-dihydroxy bile acid ratio in liver and biliary tract disease. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1494–1503. doi: 10.1172/JCI103741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKDAHL P. H. On the conjugation and formation of bile acids in the human liver. VI. On the conjugation of cholic acid -2414C in human liver homogenates in various diseases with special reference to patients with jaundice; bile acids and steroids 66. Acta Chir Scand. 1958;115(3):208–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch B., Wagener H. Conjugated bile acids in the serum of patients with acute hepatitis. Ger Med Mon. 1969 Mar;14(3):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson M. H., Taylor S., Dowling R. H. Multifocal fibrosclerosis. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Dec;63(12):1309–1311. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B., Tabaqchali S., Panveliwalla D., Wootton I. D. Serum-bile-acids in the stagnant-loop syndrome. Lancet. 1969 Feb 1;1(7588):219–220. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINI G. A., PHEAR E. A., RUEBNER B., SHERLOCK S. The bacterial content of the small intestine in normal and cirrhotic subjects: relation to methionine toxicity. Clin Sci. 1957 Feb;16(1):35–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino I., Nakagawa S., Mashimo K. Conjugated and unconjugated serum bile acid levels n patients with hepatobiliary diseases. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jun;56(6):1033–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN E. C., WOOTTON I. D., da SILVA L., SHERLOCK S. Serum-bile-acid levels in liver disease. Lancet. 1959 Dec 12;2(7111):1049–1053. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panveliwalla D., Lewis B., Wootton I. D., Tabaqchali S. Determination of individual bile acids in biological fluids by thin-layer chromatography and fluorimetry. J Clin Pathol. 1970 May;23(4):309–314. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.4.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDMAN D., KENDALL F. E. Bile acid content of human serum. I. Serum bile acids in patients with hepatic disease. J Clin Invest. 1957 Apr;36(4):530–537. doi: 10.1172/JCI103450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDBERG D. H., SJOEVALL J., SJOEVALL K., TURNER D. A. MEASUREMENT OF HUMAN SERUM BILE ACIDS BY GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:182–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjövall K., Sjövall J. Serum bile acid levels in pregnancy with pruritus (bile acids and steroids 158). Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Feb;13(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


