Abstract
Total body potassium (40K) and leucocyte potassium measurements were carried out on 19 patients with stable but decompensated cirrhosis maintained on diuretics for previous ascites. Of 13 patients receiving spironolactone alone none had a total body potassium below the expected lower limit of normal, whereas, of six receiving additional frusemide, two had low values. The results for leucocyte potassium were in agreement and simultaneous measurements of leucocyte magnesium showed a close correlation, those with intracellular potassium depletion also having magnesium depletion. One such patient was treated with magnesium supplements without effect on the potassium, although intracellular magnesium was improved. It is concluded that spironolactone alone is the treatment of choice in the maintenance management of such patients; that additional potassium would be unnecessary; and that additional frusemide should be avoided if possible.
Full text
PDF
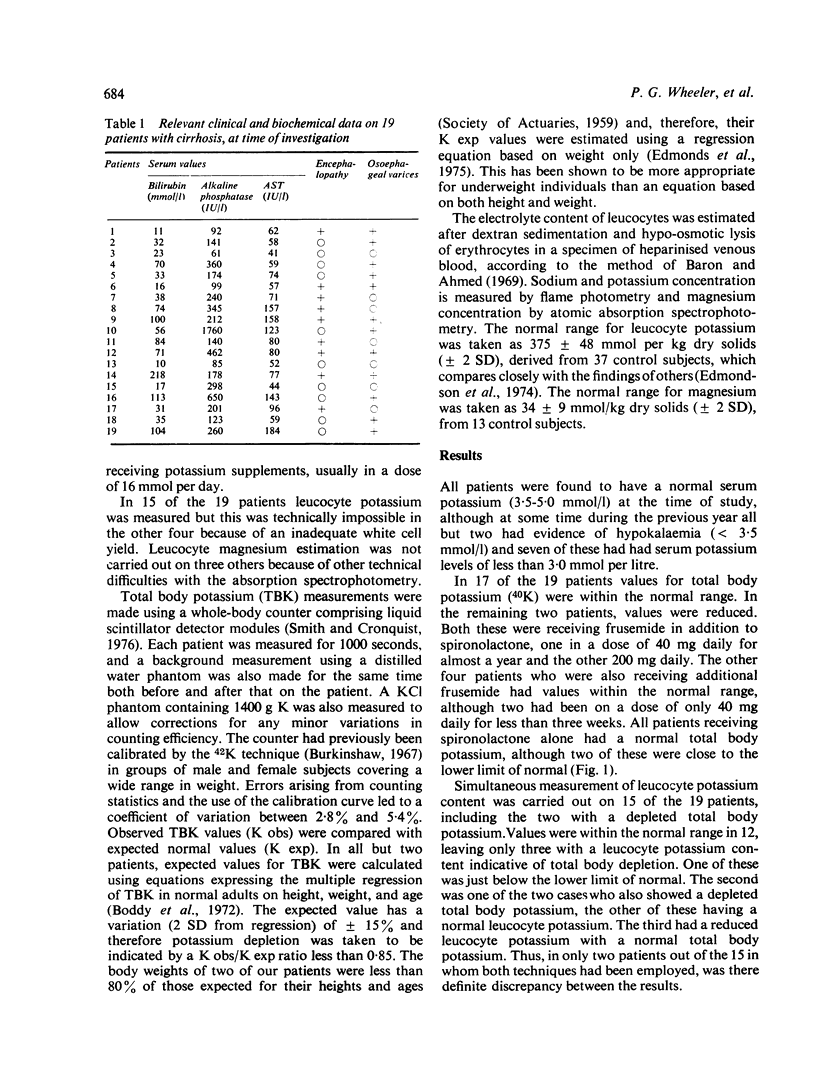
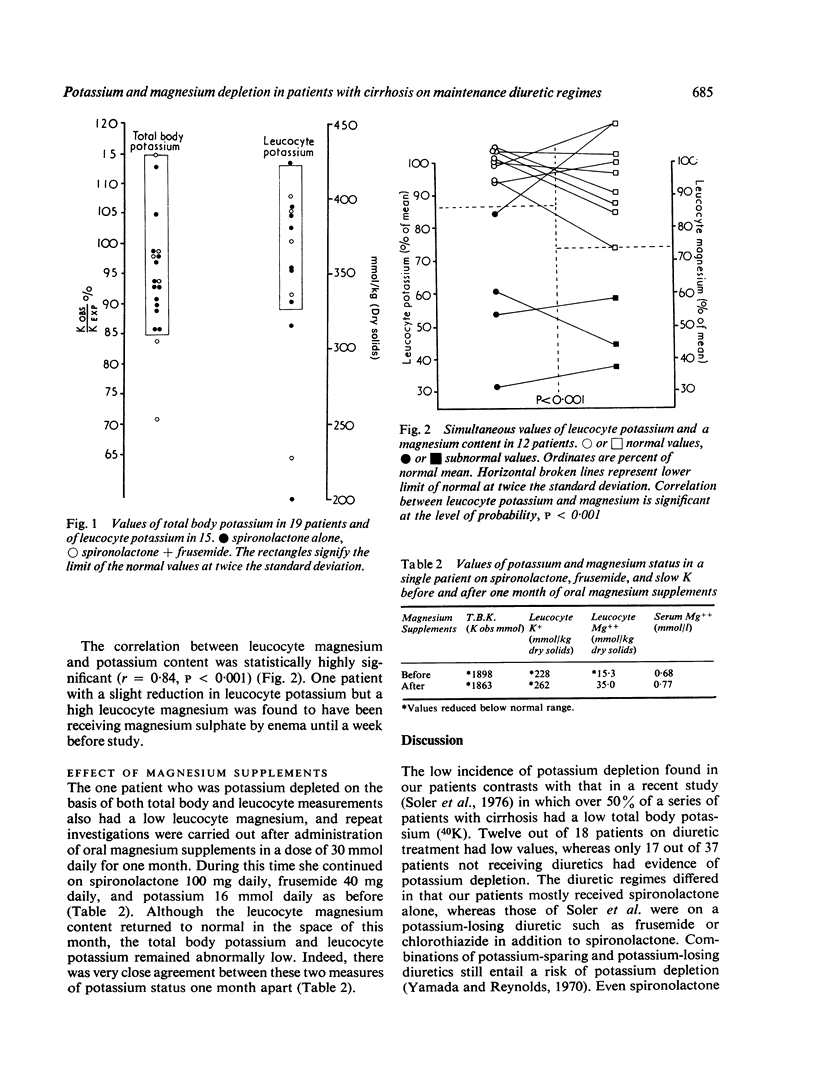


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AIKAWA J. K., FELTS J. H., Jr, HARRELL G. T., Jr Alterations in the body potassium content in cirrhosis of the liver. Gastroenterology. 1953 Jul;24(3):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron D. N., Ahmed S. A. Intracellular concentrations of water and of the principal electrolytes determined by analysis of isolated human leucocytes. Clin Sci. 1969 Aug;37(1):205–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., King P. C., Hume R., Weyers E. The relation of total body potassium to height, weight, and age in normal adults. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jun;25(6):512–517. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.6.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkinshaw L. Measurement of body potassium. Calibration and intercomparison of two whole-body radiation counters. Phys Med Biol. 1967 Oct;12(4):477–488. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/12/4/003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASEY T. H., SUMMERSKILL W. H., ORVIS A. L. BODY AND SERUM POTASSIUM IN LIVER DISEASE. I. RELATIONSHIP TO HEPATIC FUNCTION AND ASSOCIATED FACTORS. Gastroenterology. 1965 Feb;48:198–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J., Jasani B. M., Smith T. Total body potassium and body fat estimation in relationship to height, sex, age, malnutrition and obesity. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 May;48(5):431–440. doi: 10.1042/cs0480431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson R. P., Thomas R. D., Hilton P. J., Patrick J., Jones N. F. Leucocyte electrolytes in cardiac and non-cardiac patients receiving diuretics. Lancet. 1974 Jan 5;1(7845):12–14. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)93001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim P., Jacob E. Magnesium deficiency in liver cirrhosis. Q J Med. 1972 Jul;41(163):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim P., Jacob E. Magnesium deficiency in patients on long-term diuretic therapy for heart failure. Br Med J. 1972 Sep 9;3(5827):620–622. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5827.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy V. G., Lassale B., Del Corso A., Caroli J. Effet de l'aldactone sur le stock potassique chez les cirrhotiques ascitiques. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1970 Feb;121(2):183–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGANT DE DEUXCHAISNES C., COLLET R. A., BUSSET R., MACH R. S. Exchangeable potassium in wasting, amyotrophy, heart-disease, and cirrhosis of the liver. Lancet. 1961 Apr 1;1(7179):681–687. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)91719-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Bradford B. A comparison of leucocyte potassium content with other measurements in potassium-depleted rabbits. Clin Sci. 1972 Apr;42(4):415–421. doi: 10.1042/cs0420415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- READ A. E., LAIDLAW J., HASLAM R. M., SHERLOCK S. Neuropsychiatric complications following chlorothiazide therapy in patients with hepatic cirrhosis: possible relation to hypokalaemia. Clin Sci. 1959 Aug;18:409–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler N. G., Jain S., James H., Paton A. Potassium status of patients with cirrhosis. Gut. 1976 Feb;17(2):152–157. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surveyor I., Hughes D. Discrepancies between whole-body potassium content and exchangeable potassium. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Mar;71(3):464–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverso H. D., Raynaud C., Blanchon P., Roberti A., Vesin P., Viguie R., Kellershohn C. Etude des clearances de l'inuline et du PAH, du débit cardiaque, du Na et du K échangeables et des liquides extracellulaires, au cours de l'évolution de la cirrhose du foie. Rev Int Hepatol. 1966;16(8):1377–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesin P. Potassium metabolism and diuretics administration in liver cirrhosis. Postgrad Med J. 1975 Aug;51(598):545–548. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.51.598.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHANG R., WELT L. G. Observations in experimental magnesium depletion. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42:305–313. doi: 10.1172/JCI104717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker W. E., Parisi A. F. Magnesium metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 28;278(13):712–717. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803282781306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Reynolds T. B. Amiloride (MK-870), a new antikaluretic diuretic. Comparison to other antikaluretic diuretics in patients with liver disease and ascites. Gastroenterology. 1970 Dec;59(6):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


