Abstract
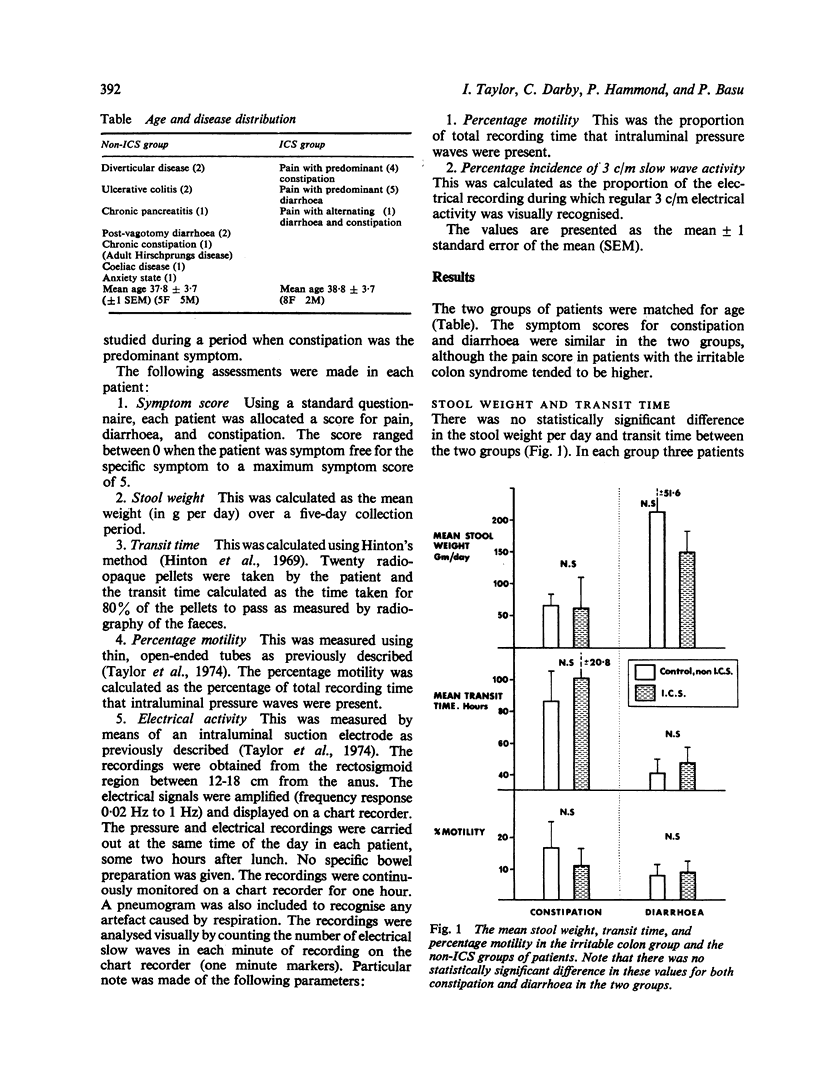
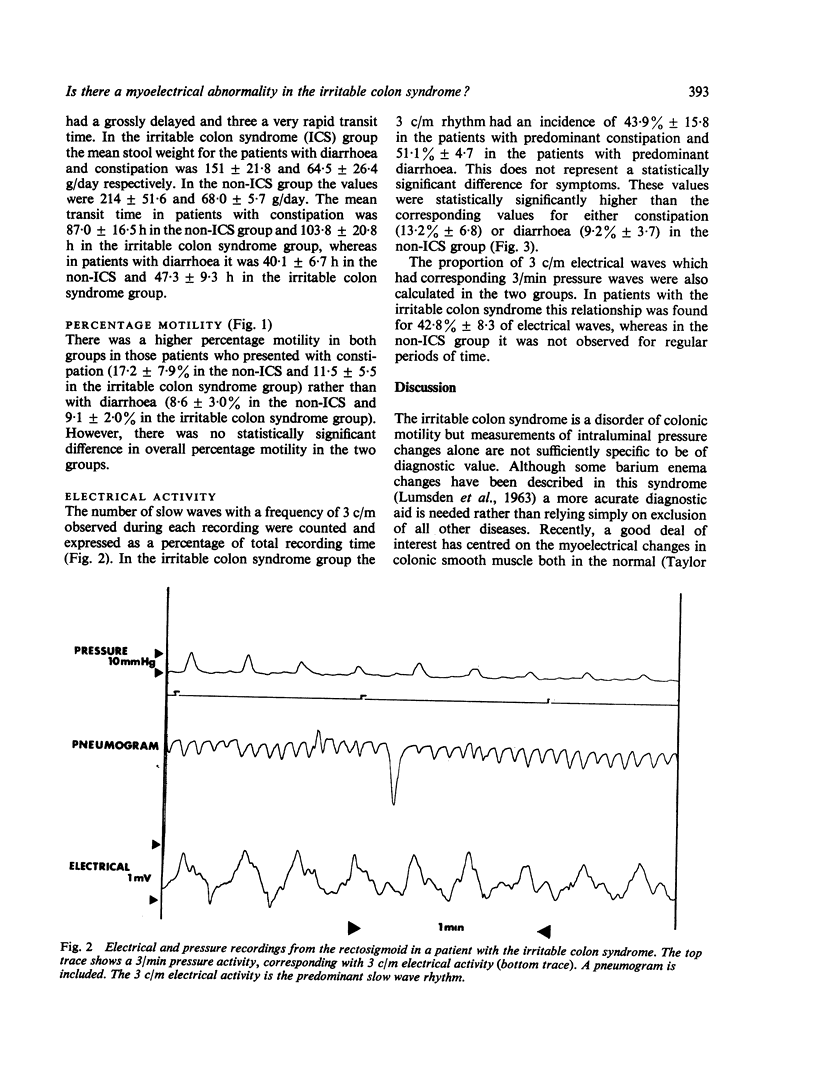
Although recent work has suggested that an abnormality of the 0.05 Hz (3 c/m) slow wave electrical activity exists in the distal colon of patients with the irritable colon syndrome, it is not established whether this is related to altered bowel habit alone, or whether it is specific to the irritable colon syndrome. We have therefore studied 10 patients referred with this disorder and compared their colonic myoelectrical pattern with 10 patients suffering from assorted disorders with similar symptoms--for example, chronic pancreatitis, diverticular disease, ulcerative colitis, etc. Transit time, stool weights, percentage motility, and slow wave electrical activity were measured in each patient. The two groups were well matched for age and patients with similar symptoms in the two groups had similar values for transit time and percentage motility. There was a statistically significant increase in the 3 c/m electrical activity in patients with the irritable colon syndrome unrelated to the degree of diarrhoea or constipation. It would appear, therefore, that the abnormally high incidence of 3 c/m electrical activity in the colon is specific to the irritable colon syndrome and not merely a feature of altered bowel habit.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAUDHARY N. A., TRUELOVE S. C. Human colonic motility: a comparative study of normal subjects, patients with ulcerative colitis, and patients with the irritable colon syndrome. I. Resting patterns of motility. Gastroenterology. 1961 Jan;40:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL A. M., JONES F. A., ROWLANDS E. N. MOTILITY OF THE PELVIC COLON. IV. ABDOMINAL PAIN ASSOCIATED WITH COLONIC HYPERMOTILITY AFTER MEALS. Gut. 1965 Apr;6:105–112. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Read A. E. Effect of cholecystokinin on colonic motility and symptoms in patients with the irritable-bowel syndrome. Lancet. 1973 Jan 6;1(7793):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton J. M., Lennard-Jones J. E., Young A. C. A ne method for studying gut transit times using radioopaque markers. Gut. 1969 Oct;10(10):842–847. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.10.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSNER J. B., PALMER W. L. The irritable colon. Gastroenterology. 1958 Mar;34(3):491–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUMSDEN K., CHAUDHARY N. A., TRUELOVE S. C. The irritable colon syndrome. Clin Radiol. 1963 Jan;14:54–63. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(63)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Carlson G. M., Matarazzo S. A., Cohen S. Evidence that abnormal myoelectrical activity produces colonic motor dysfunction in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I., Duthie H. L. Bran tablets and diverticular disease. Br Med J. 1976 Apr 24;1(6016):988–990. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6016.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I., Duthie H. L., Cumberland D. C., Smallwood R. Glucagon and the colon. Gut. 1975 Dec;16(12):973–978. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.12.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I., Duthie H. L., Smallwood R., Brown B. H., Linkens D. The effect of stimulation on the myoelectrical activity of the rectosigmoid in man. Gut. 1974 Aug;15(8):599–607. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.8.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I., Duthie H. L., Smallwood R., Linkens D. Large bowel myoelectrical activity in man. Gut. 1975 Oct;16(10):808–814. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.10.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANGEL A. G., DELLER D. J. INTESTINAL MOTILITY IN MAN. 3. MECHANISMS OF CONSTIPATION AND DIARRHEA WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE IRRITABLE COLON SYNDROME. Gastroenterology. 1965 Jan;48:69–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller S. L., Misiewicz J. J. Colonic motility in constipation or diarrhoea. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7(1):93–96. doi: 10.3109/00365527209180743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


