Abstract
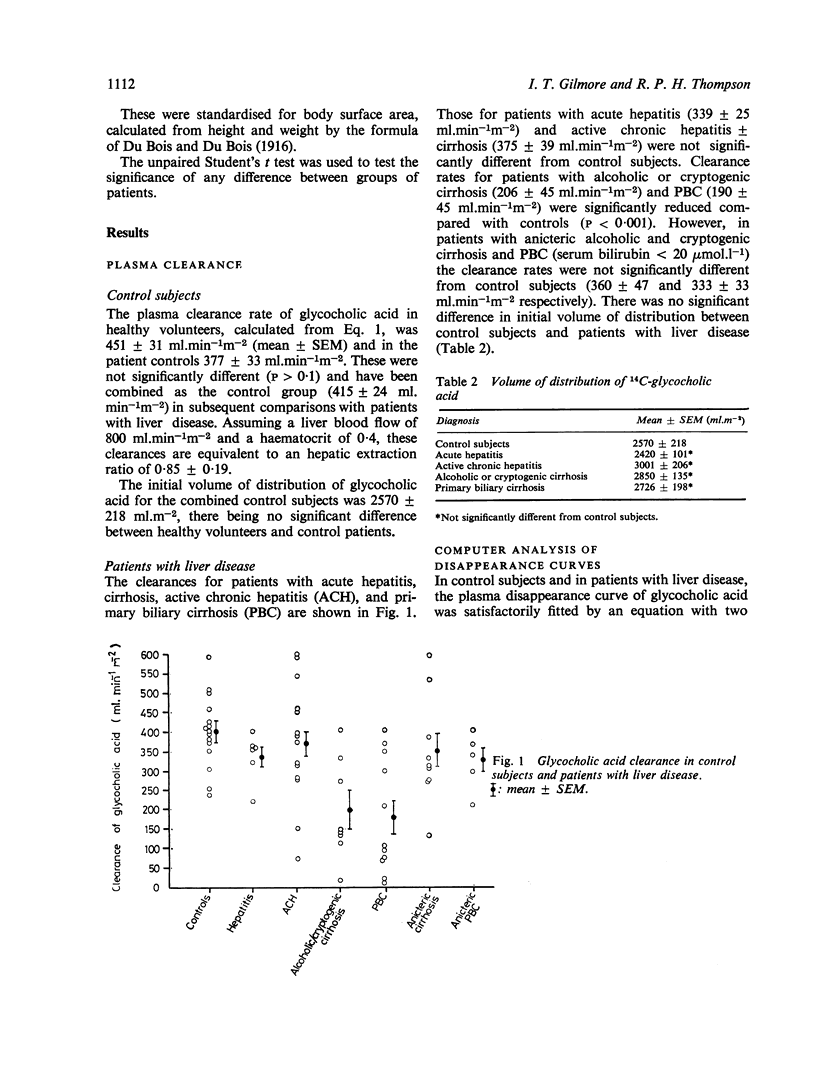
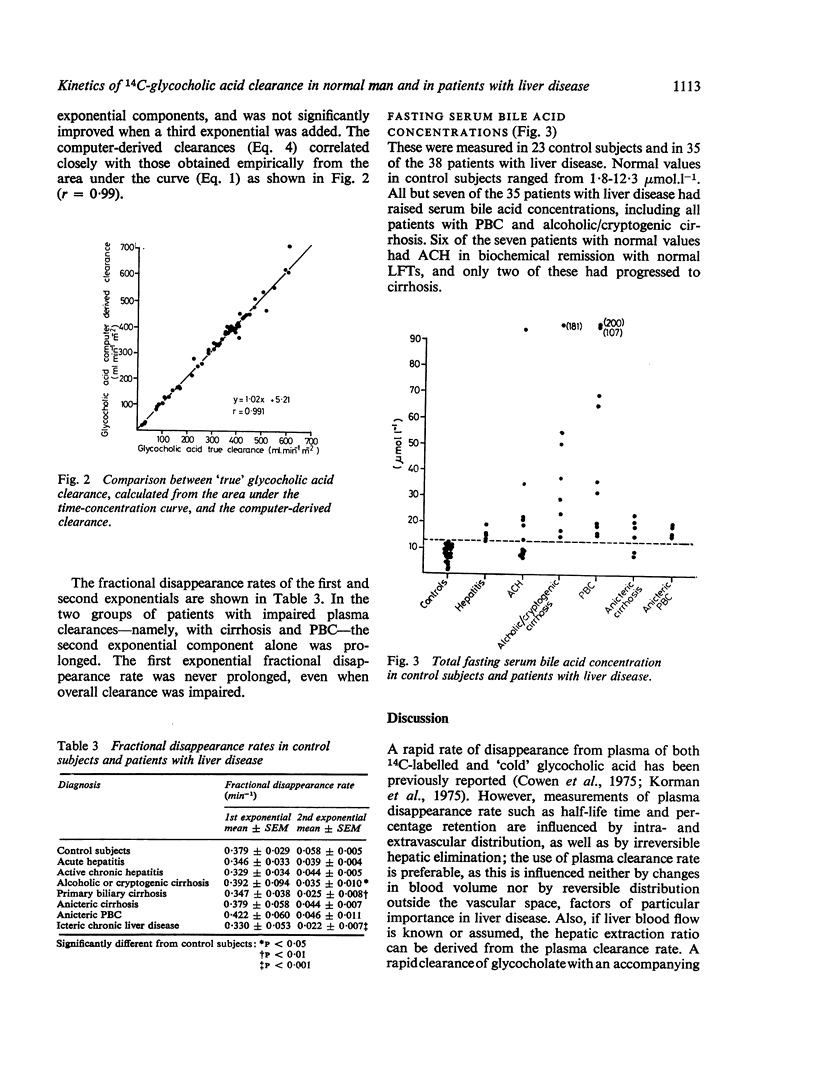
The plasma clearance of a tracer dose of 14C-glycocholic acid, and fasting total serum bile acid concentrations were measured in 14 control subjects and in 38 patients with acute and chronic liver disease. In controls plasma clearance was 415 +/- 24 ml min-1 m-2 (mean +/- SEM), equivalent to a 'first-pass' extraction by the liver of 85%. Clearance was not significantly different from controls in patients with acute hepatitis or active chronic hepatitis, nor in anicteric patients with primary biliary or alcoholic cirrhosis. Thus bile acid clearance was impaired only in icteric chronic liver disease. In contrast, serum bile acid concentrations were abnormal in all but seven patients, six of whom had active chronic hepatitis in complete biochemical remission. The pattern of plasma disappearance of injected 14C-glycocholic acid was biexponential in controls and patients with liver disease, and computer analysis of the curves suggested that there was significant distribution of bile acid outside the vascular space. The preservation of bile acid clearance in anicteric chronic liver disease confirms that it is dependent more on liver blood flow than on liver cell function.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes S., Gallo G. A., Trash D. B., Morris J. S. Diagnositic value of serum bile acid estimations in liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jun;28(6):506–509. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.6.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen A. E., Korman M. G., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Plasma disappearance of radioactivity after intravenous injection of labeled bile acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jun;68(6):1567–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Iser J. H., Smallwood R. A. Hepatic bile acid transport: effect of conjugation and position of hydroxyl groups. Am J Physiol. 1975 Aug;229(2):298–302. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.2.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in man. Clin Gastroenterol. 1977 Jan;6(1):3–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak W., Waldram R., Murray-Lyon I. M., Schuster E., Williams R. Kinetics of [14C]cholic acid in fulminant hepatic failure: a prognostic test. Gastroenterology. 1976 Nov;71(5):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Kok E., Javitt N. B. Postprandial serum bile acid for the detection of hepatobiliary disease. JAMA. 1973 Jul 16;225(3):292–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye M. D., Struthers J. E., Jr, Tidball J. S., DeNiro E., Kern F., Jr Factors affecting plasma clearance of (14C) cholic acid in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Aug;45(2):147–161. doi: 10.1042/cs0450147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiding S. Hepatic elimination kinetics: the influence of hepatic blood flow on clearance determination. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 Mar;36(2):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman M. G., Hofmann A. F., Summerskill W. H. Assessment of activity in chronic active liver disease. Serum bile acids compared with conventional tests and histology. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 20;290(25):1399–1402. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406202902503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman M. G., LaRusso N. F., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F. Development of an intravenous bile acid tolerance test. Plasma disappearance of cholylglycine in health. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jun 5;292(23):1205–1209. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197506052922302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F., Korman M. G. Validity and sensitivity of an intravenous bile acid tolerance test in patients with liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jun 5;292(23):1209–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197506052922303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Korman M. G., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F. Dynamics of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Postprandial serum concentrations of conjugates of cholic acid in health, cholecystectomized patients, and patients with bile acid malabsorption. N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 3;291(14):689–692. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410032911401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. M., Ross A., Billing B. H. Serum bile acids in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gut. 1972 Mar;13(3):201–206. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.3.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Máille E. R., Richards T. G., Short A. H. The influence of conjugation of cholic acid on its uptake and secretion: hepatic extraction of taurocholate and cholate in the dog. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):337–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thjodleifsson B., Barnes S., Chitranukroh A., Billing B. H., Sherlock S. Assessment of the plasma disappearance of cholyl'l14C-glycine as a test of hepatocellular disease. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):697–702. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Berge Henegouwen G. P., Hofmann A. F. A simple batch adsorption procedure for the isolation of sulfated and non-sulfated bile acids from serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Dec;73(3):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Schenker S. Drug disposition and liver disease. Drug Metab Rev. 1975;4(2):139–175. doi: 10.3109/03602537508993754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


