Abstract
In 30 patients with gastrooesophageal reflux, intravenous metoclopramide (Maxolon) has been shown to increase the gastrooesophageal sphincter pressure. The rise is dose-related until a maximum pressure, proportional to the resting sphincter tone, is reached. The effect is reversed by atropine. Peristaltic waves are increased in pressure by metoclopramide.
In 18 patients with gastrooesophageal reflux intravenous metoclopramide diminished the frequency of reflux episodes and increased the rate at which the oesophagus emptied itself of an acid load.
Full text
PDF
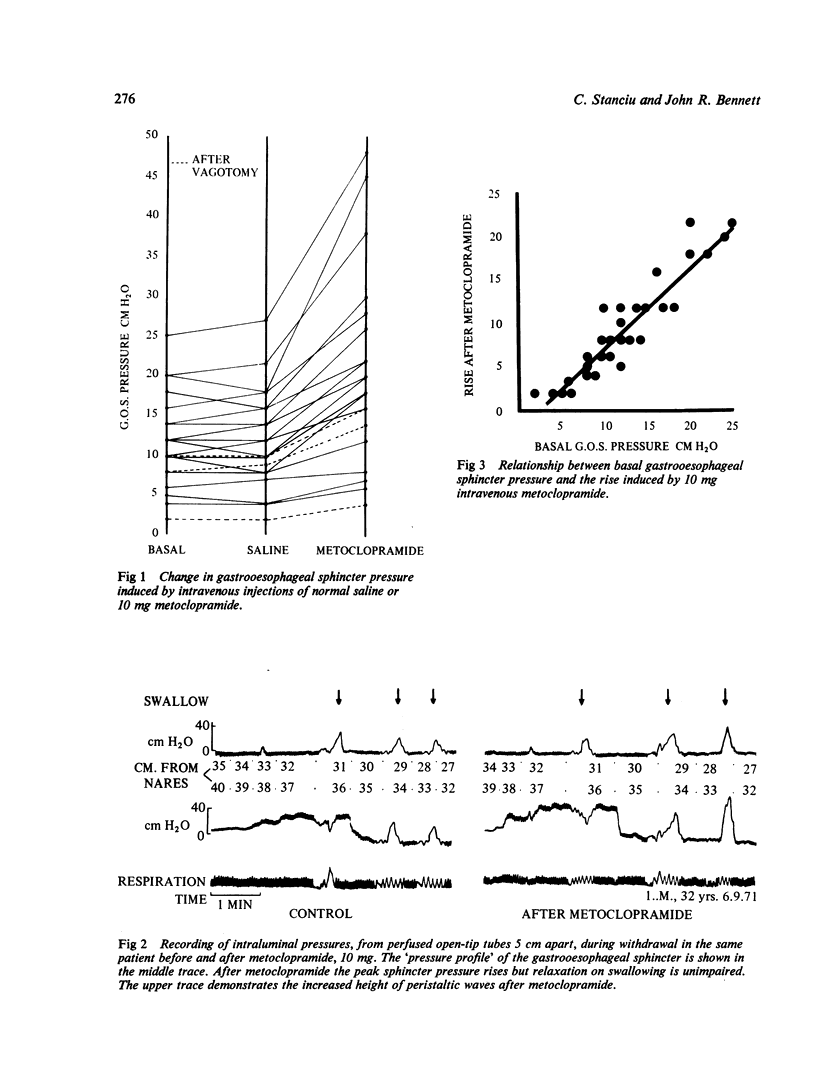
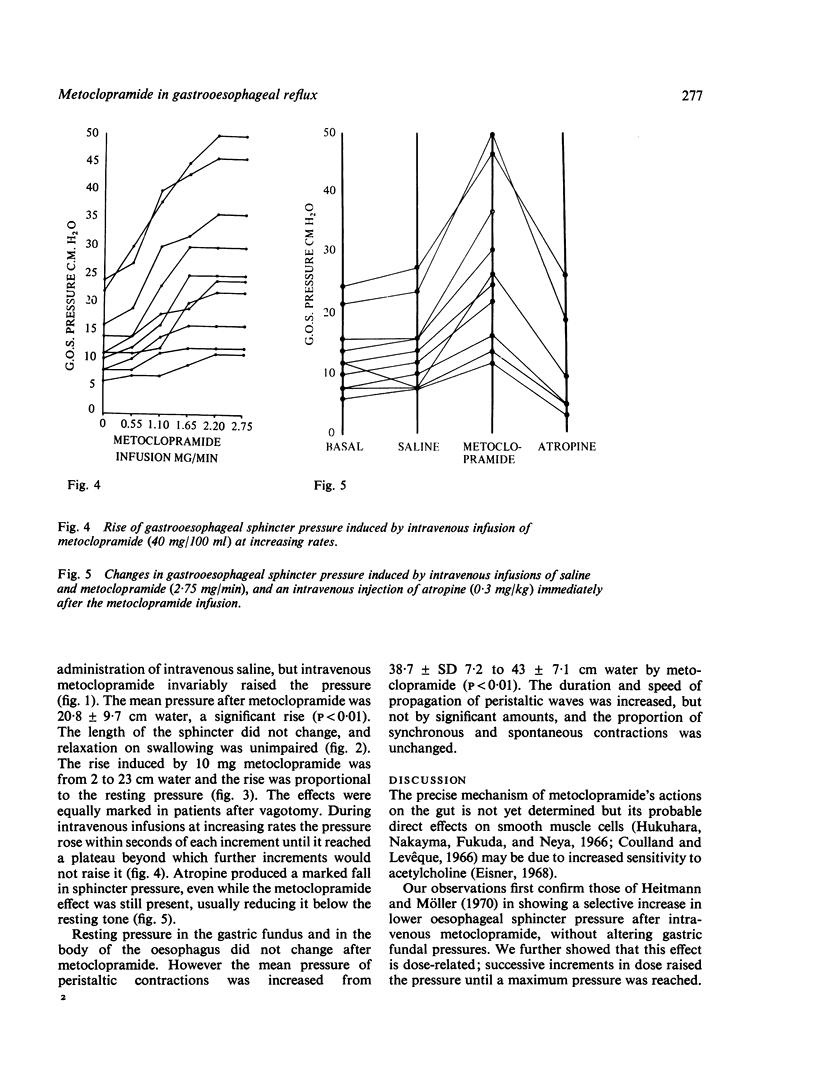
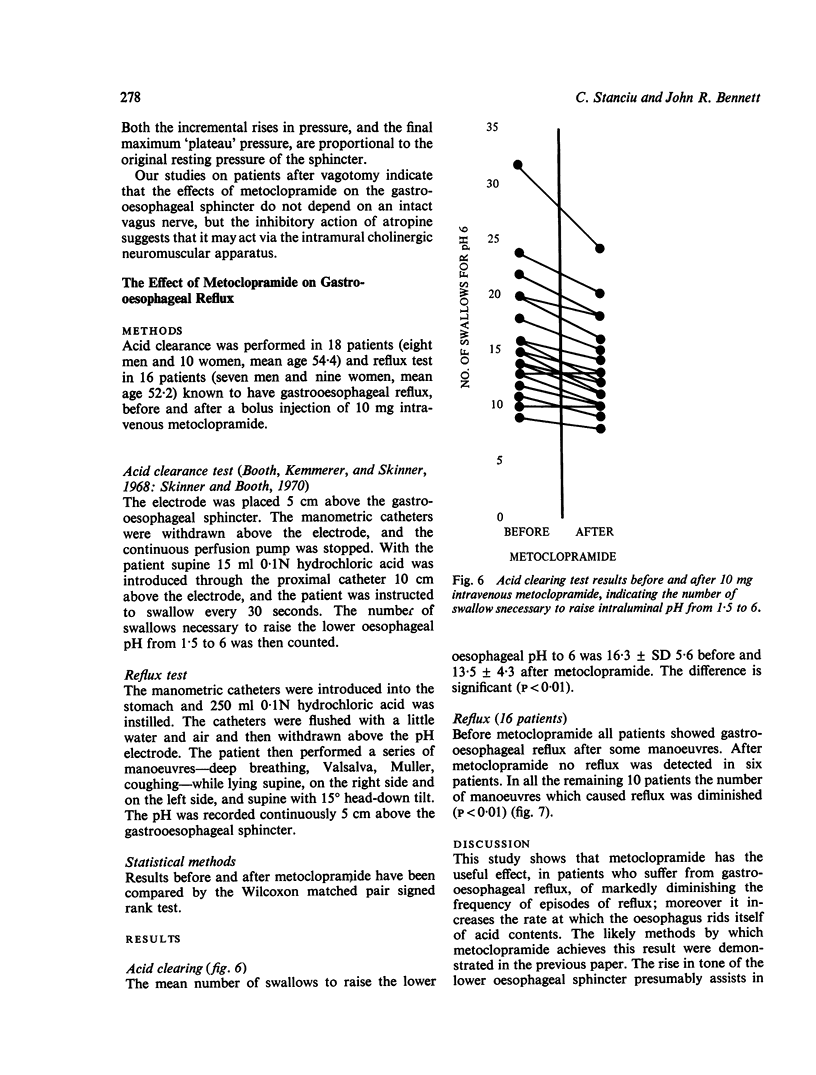
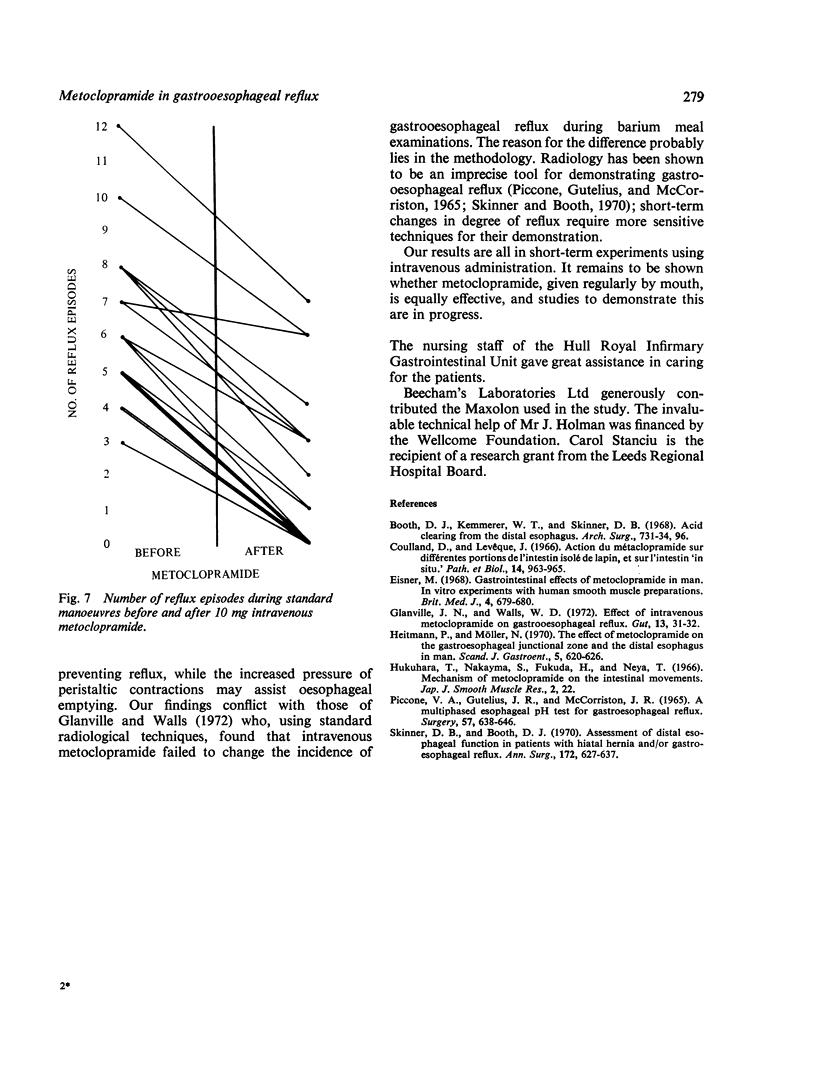
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth D. J., Kemmerer W. T., Skinner D. B. Acid clearing from the distal esophagus. Arch Surg. 1968 May;96(5):731–734. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01330230039006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coullaud D., Lévêque J. Action du métoclopramide sur différentes portions de l'intestin isolé de lapin, et sur l'intestin "in situ". Pathol Biol. 1966 Oct;14(19):963–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner M. Gastrointestinal effects of metoclopramide in man. In vitro experiments with human smooth muscle preparations. Br Med J. 1968 Dec 14;4(5632):679–680. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5632.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville J. N., Walls W. D. Effect of intravenous metoclopramide on gastrooesophageal reflux. Gut. 1972 Jan;13(1):31–32. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitmann P., Möller N. The effect of metoclopramide on the gastroesophageal junctional zone and the distal esophagus in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1970;5(7):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICCONE V. A., GUTELIUS J. R., MCCORRISTON J. R. A MULTIPHASE ESOPHAGEAL PH TEST FOR GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX. Surgery. 1965 May;57:638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B., Booth D. J. Assessment of distal esophageal function in patients with hiatal hernia and-or gastroesophageal reflux. Ann Surg. 1970 Oct;172(4):627–637. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197010000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


