Abstract
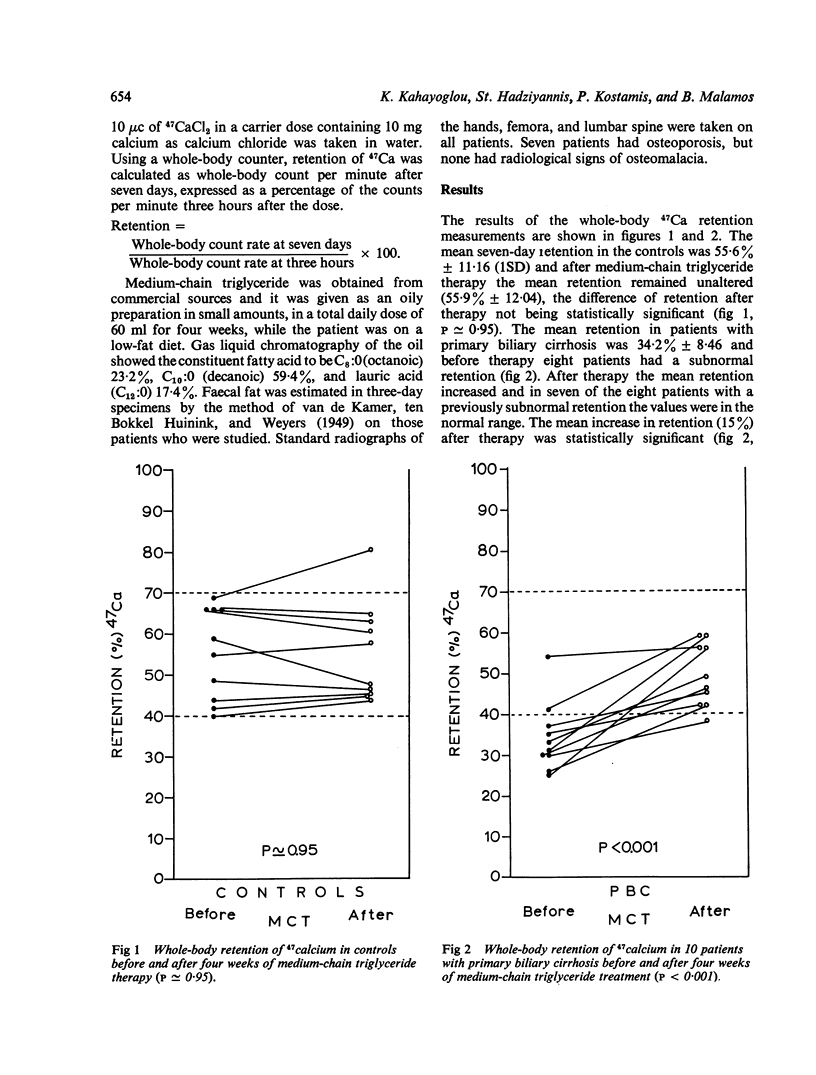
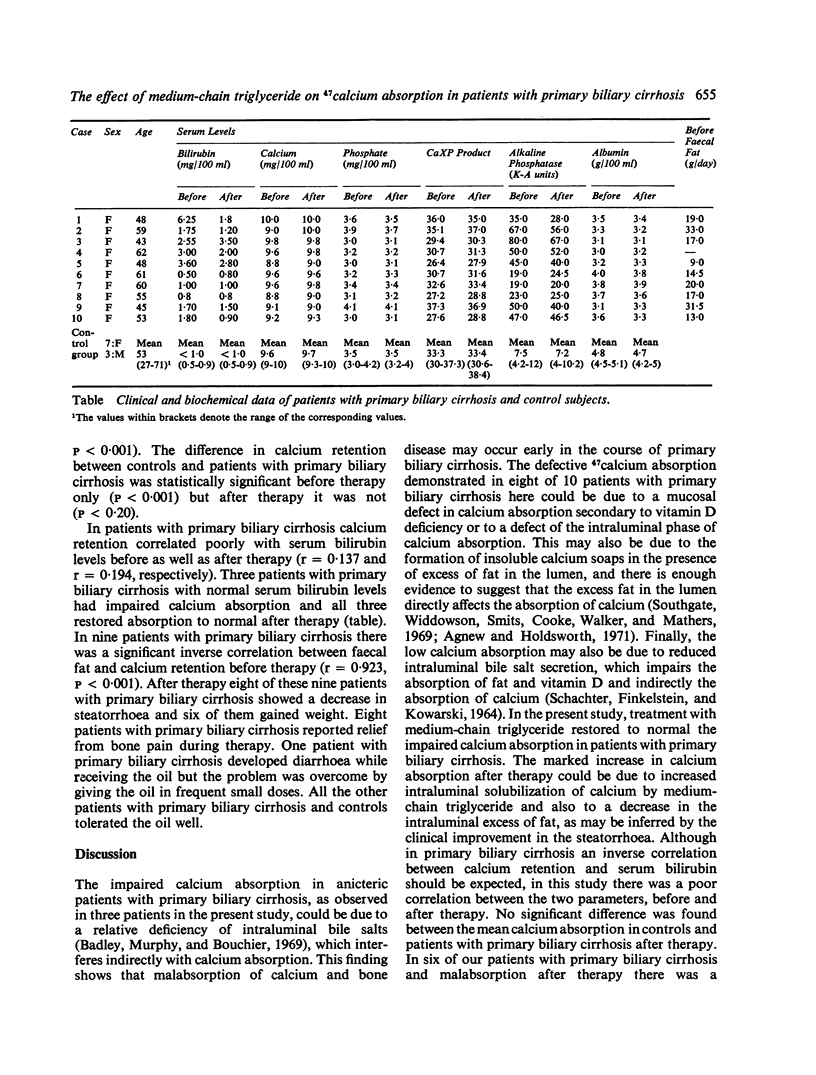
Calcium absorption, as measured by whole-body retention of isotopic 47calcium, was investigated in 10 controls and 10 patients with primary biliary cirrhosis before and after medium-chain triglyceride therapy. Absorption of calcium was impaired in eight patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, three of whom had normal serum bilirubin. Mean absorption was significantly less in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis than in controls. Impaired calcium absorption correlated well with increased faecal fat excretion and less well with the intensity of jaundice. Osteoporosis was diagnosed radiologically in seven patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, and calcium absorption was restored to normal in seven out of eight patients after medium-chain triglyceride therapy. Decrease of steatorrhoea, weight gain, and relief of bone pain have been noted in most patients with primary biliary cirrhosis after therapy. It is concluded that bone disease occurs early in primary biliary cirrhosis, and early medium-chain triglyceride therapy in these patients is suggested.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON M., NORDIN B. E., SHERLOCK S. Malabsorption and bone disease in prolonged obstructive jaundice. Q J Med. 1956 Jul;25(99):299–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnew J. E., Holdsworth C. D. The effect of fat on calcium absorption from a mixed meal in normal subjects, patients with malabsorptive disease, and patients with a partial gastrectomy. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):973–977. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnew J. E., Kehayoglou A. K., Holdsworth C. D. Comparison of three isotopic methods for the study of calcium absorption. Gut. 1969 Jul;10(7):590–597. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.7.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley B. W., Murphy G. M., Bouchier I. A. Intraluminal bile-salt deficiency in the pathogenesis of steatorrhoea. Lancet. 1969 Aug 23;2(7617):400–402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Danks D. M. Medium-chain triglyceride diet: its use in treatment of liver disease. Br Med J. 1966 Oct 29;2(5521):1050–1051. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5521.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELLER D. J., EDWARDS R. G., ADDISON M. CALCIUM METABOLISM AND THE BONES AFTER PARTIAL GASTRECTOMY. II. THE NATURE AND CAUSE OF THE BONE DISORDER. Australas Ann Med. 1963 Nov;12:295–309. doi: 10.1111/imj.1963.12.4.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehayoglou A. K., Holdsworth C. D., Agnew J. E., Whelton M. J., Sherlock S. Bone disease and calcium absorption in primary biliary cirrhosis with special reference to vitamin-D therapy. Lancet. 1968 Apr 6;1(7545):715–718. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehayoglou A. K., Williams H. S., Whimster W. F., Holdsworth C. D. Calcium absorption in the normal, bile-duct ligated, and cirrhotic rat, with observations on the effect of long- and medium-chain triglycerides. Gut. 1968 Oct;9(5):597–603. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.5.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo P. T., Huang N. N. The effect of medium chain triglyceride upon fat absorption and plasma lipid and depot fat of children with cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1924–1933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson C. R., Losowsky M. S. The bones in chronic liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1967;2(4):293–300. doi: 10.3109/00365526709180085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHACHTER D., FINKELSTEIN J. D., KOWARSKI S. METABOLISM OF VITAMIN D. I. PREPARATION OF RADIOACTIVE VITAMIN D AND ITS INTESTINAL ABSORPTION IN THE RAT. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:787–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI104965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMMERSKILL W. H., KELLY P. J. Osteoporosis with fractures in anicteric cirrhosis: observations supplemented by microradiographic evaluation of bone. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1963 Apr 24;38:162–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate D. A., Widdowson E. M., Smits B. J., Cooke W. T., Walker C. H., Mathers N. P. Absorption and excretion of calcium and fat by young infants. Lancet. 1969 Mar 8;1(7593):487–489. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91589-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelton M. J., Kehayoglou A. K., Agnew J. E., Turnberg L. A., Sherlock S. 47 Calcium abosrption in parenchymatous and biliary liver disease. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):978–983. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


