Abstract
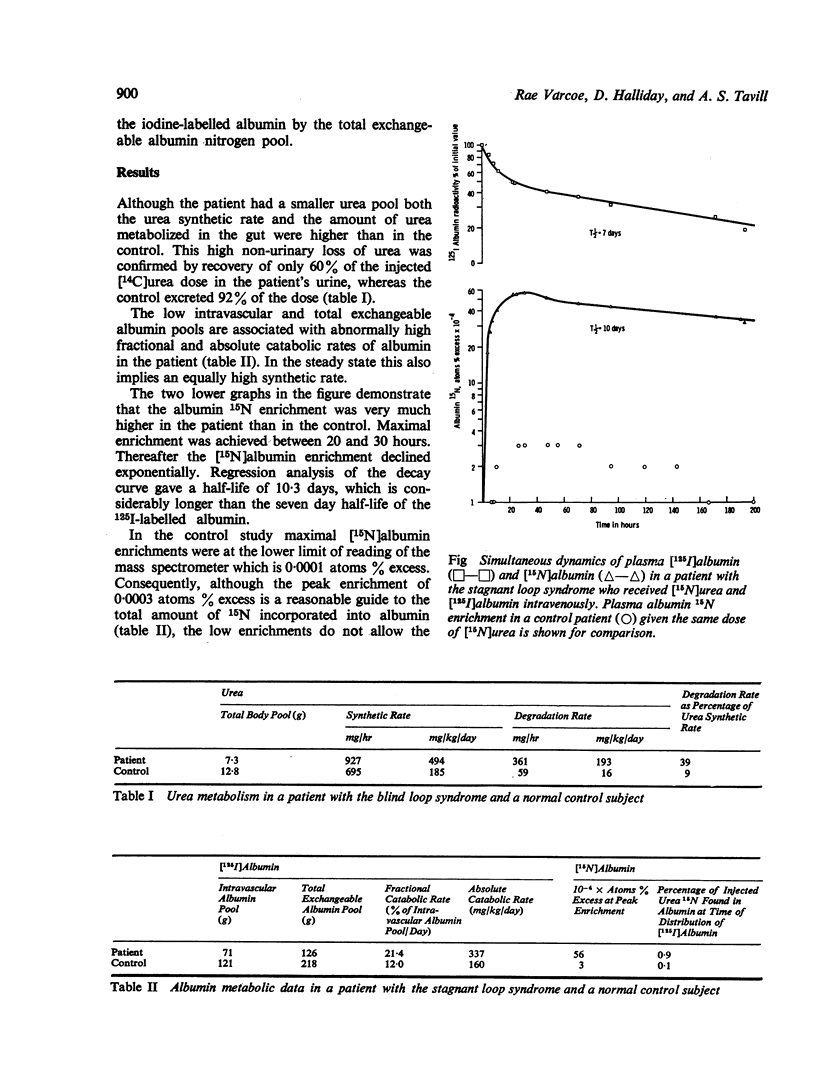
A study of urea and albumin metabolism was carried out in a patient with the stagnant loop syndrome and in a control subject using radioisotopic and stable isotopic techniques. The patient had a higher rate of urea synthesis, urea hydrolysis in the gut, and of incorporation of recycled urea nitrogen into albumin. Although only a small proportion (0·4%) of the urea nitrogen available was used for albumin synthesis and this constituted only 0·8% of the daily nitrogen requirement for this purpose, the reutilization of nitrogen was relatively much greater than was observed in the control study.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DEBRO J. R., KORNER A. Solubility of albumin in alcohol after precipitation by trichloroacetic acid: a simplified procedure for separation of albumin. Nature. 1956 Nov 10;178(4541):1067–1067. doi: 10.1038/1781067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Hofmann A. F. Breath test for altered bile-acid metabolism. Lancet. 1971 Sep 18;2(7725):621–625. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. A., Craigie A., Tavill A. S., Franglen G., Rosenoer V. M. Protein metabolism in the intestinal stagnant loop syndrome. Gut. 1968 Aug;9(4):466–469. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.4.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIKLER D. M., SCHRIRE V. Kwashiorkor in an adult due to an intestinal blind loop. Lancet. 1958 Mar 8;1(7019):510–511. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90815-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale G., Antcliff A. C., Welbourn R. B., Mollin D. L., Booth C. C. Protein malnutrition after partial gastrectomy. Q J Med. 1967 Oct;36(144):469–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T. Studies on factors affecting the levels of urea cycle enzymes in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:1012–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. H., Hill H. Z., Hoagland M. B. Physiology of rat-liver polysomes. Protein synthesis by stable polysomes. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):567–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1030567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tongeren J. H., Reichert W. J. Demonstration of protein-losing gastroenteropathy. The quantitative estimation of gastrointestinal protein loss, using 51Cr-labelled plasma proteins. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Jul;14(1):42–48. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


