Abstract
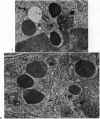
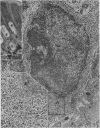
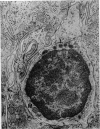
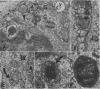
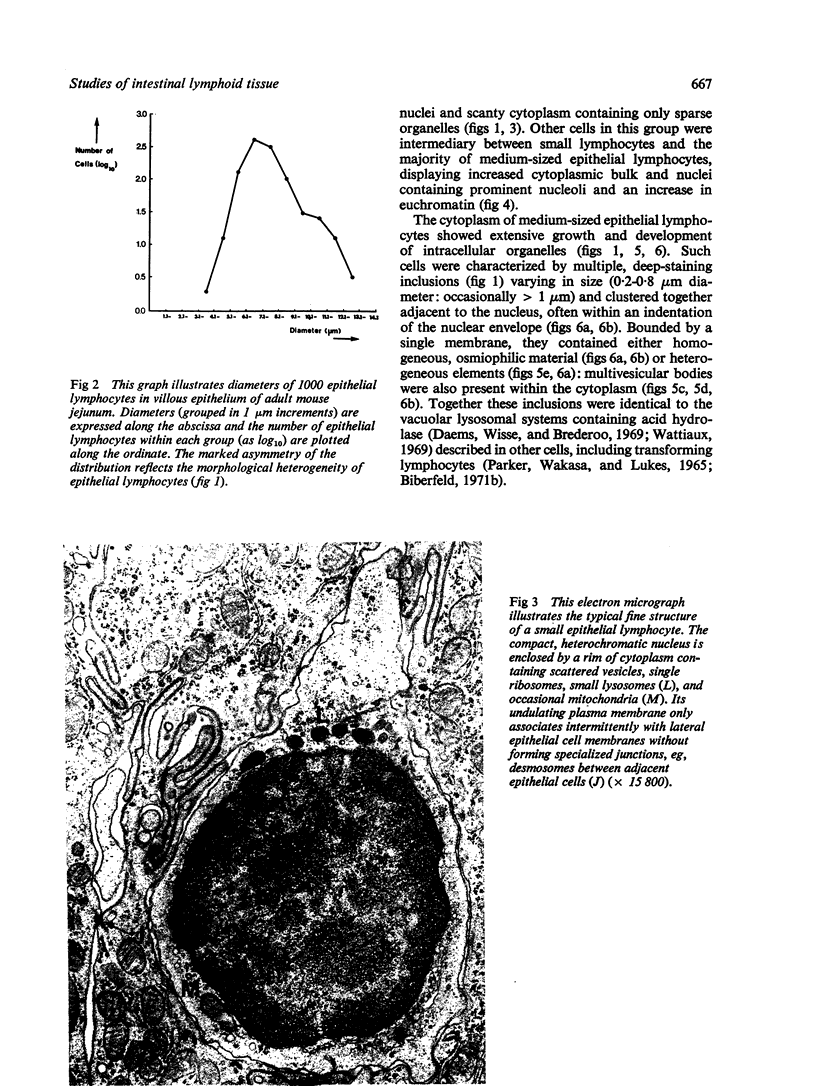
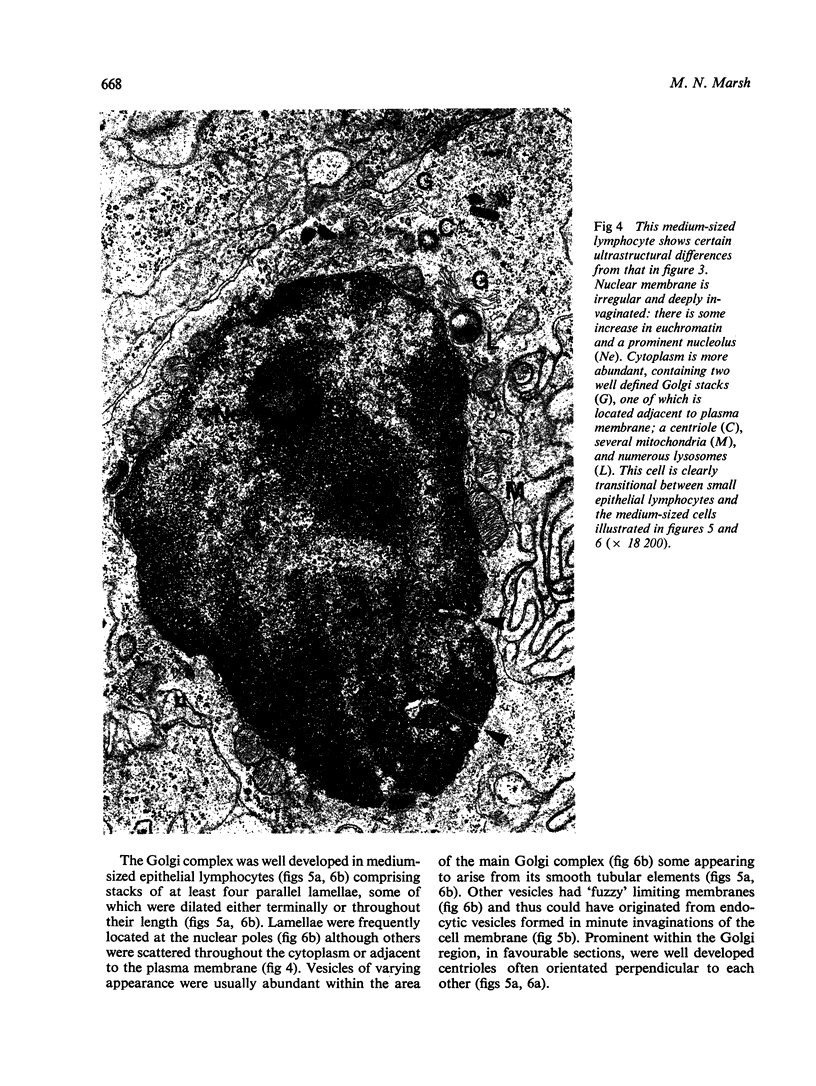
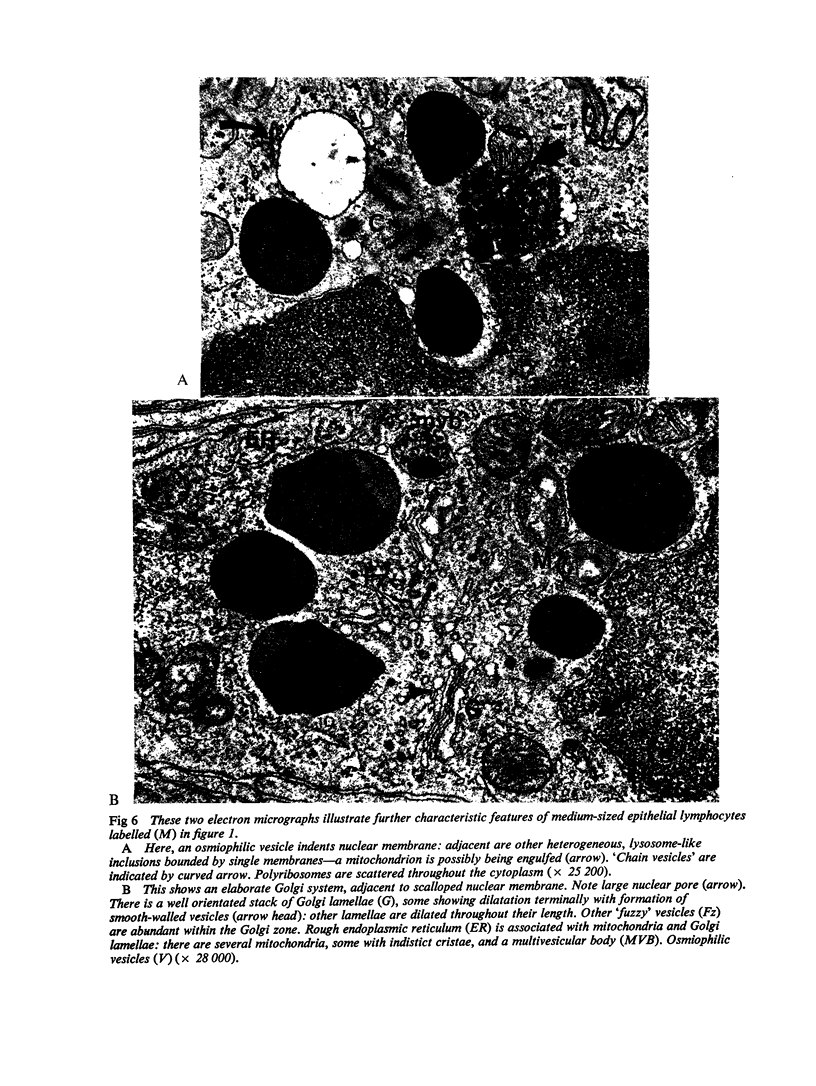
The morphology of epithelial lymphocytes in osmium-fixed, Epon-embedded jejunum of adult mice was studied by light and electron microscopy. Toluidine blue-stained 1 mum 'thick' plastic sections were compared with adjacent thin sections, thereby permitting precise ultrastructural identification and description of selected epithelial lymphocytes. Their size and appearances varied considerably, ranging from typical small lymphocytes through medium-sized lymphocytes to large immunoblasts. A high proportion of medium-sized epithelial lymphocytes (mean diameter 6-9 +/- 1-1 mum) contained several lysosomes, extensive Golgi complexes, prominent centrioles and abundant ribosomes. Their appearances, therefore, corresponded directly to mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes. In contrast, immunoblasts were big cells (mean diameter 11-0 +/- 0-8 mum) with large, euchromatic nuclei and prominent nucleoli. The majority had pale-staining, ribosome-studded cytoplasm and thus resembled type I, or T blasts. Very rarely, densely staining blasts containing ribosomes and well developed rough endoplasmic reticulum were observed; these corresponded to type II or B blasts. These observations indicate that transformation of lymphocytes occurs within the interepithelial cell spaces of the small intestinal mucosa, suggesting that epithelial lymphocytes are immunocompetent cells which may be responsive to local antigenic stimulation.
Full text
PDF
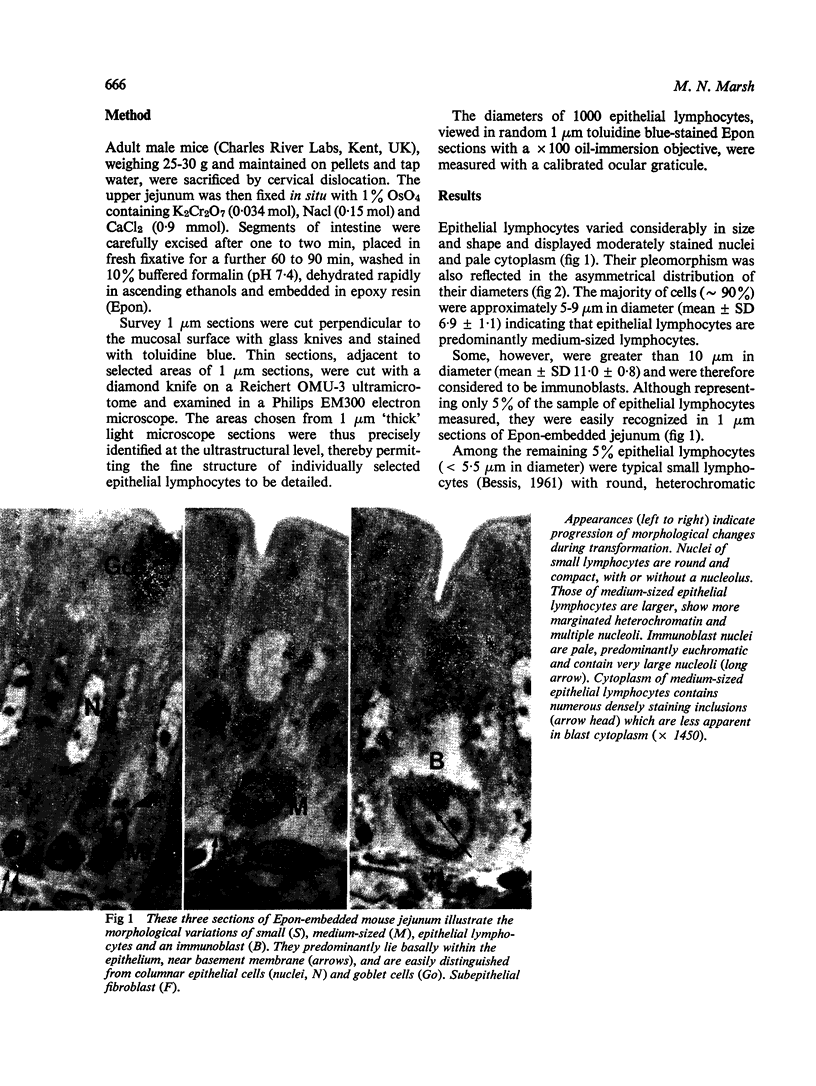

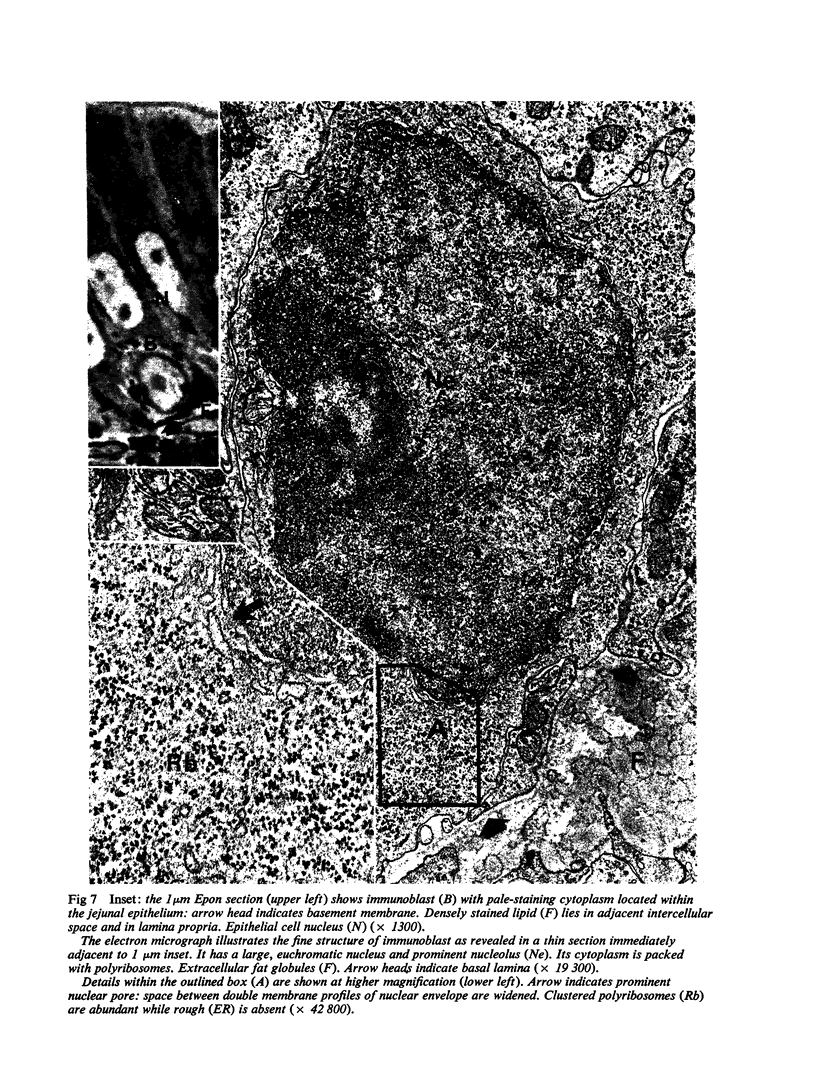
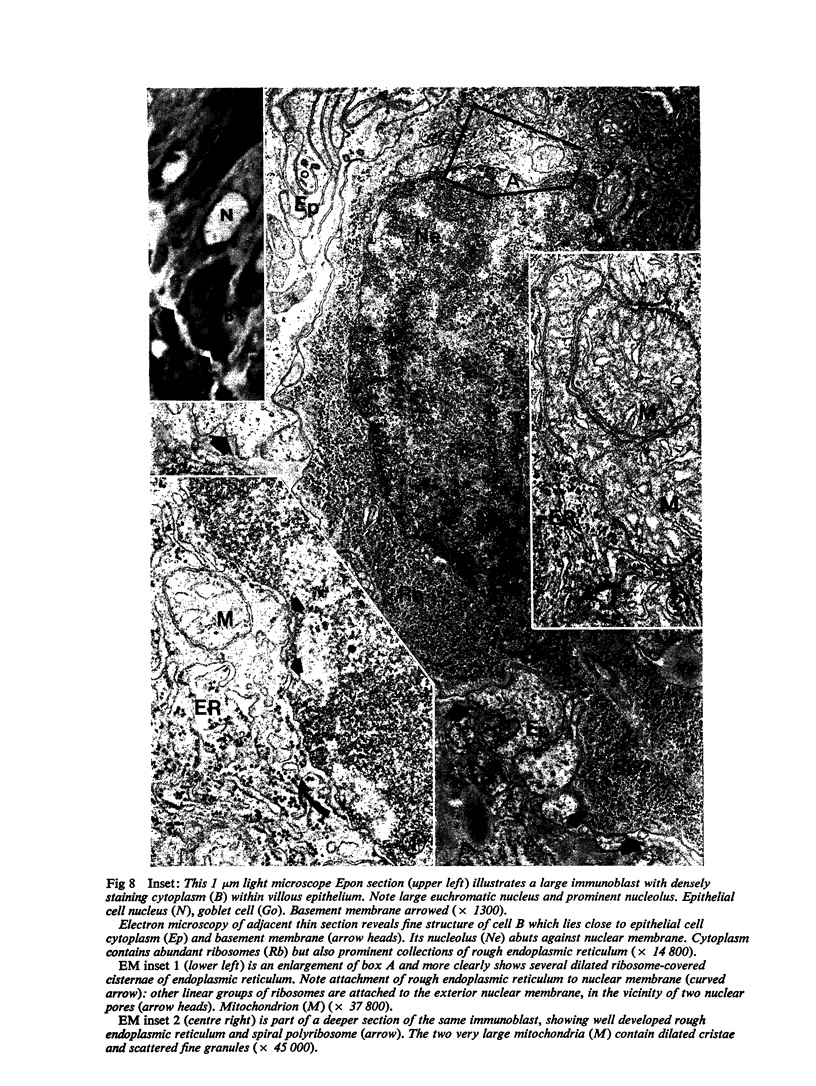


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew W. Lymphocyte transformation in epithelium. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Jul;35(1):113–137. doi: 10.1093/jnci/35.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSIS M. C. Ultrastructure of lymphoid and plasma cells in realtion to globulin and antibody formation. Lab Invest. 1961 Nov-Dec;10:1040–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld P. Endocytosis and lysosome formation in blood lymphocytes transformed by phytohemagglutinin. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Oct;37(1):41–68. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diengdoh J. V., Turk J. L. Immunological significance of lysosomes with lymphocytes in vivo. Nature. 1965 Sep 25;207(5004):1405–1406. doi: 10.1038/2071405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D. Electron microscopic and functional aspects of human lymphocyte response to mitogens. Transplant Rev. 1972;11:39–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Hoffman P. F., Borjeson J., Chessin L. N. Studies on human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. 3. Fine structural features of lymphocyte transformation by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):17–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D. Human lymphocyte growth in vitro: morphologic, biochemical, and immunologic significance. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1971;10:41–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Parrott D. M. The effect of antigen deprivation on thymus-dependent and thymus-independent lymphocytes in the small intestine of the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Dec;12(4):477–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Janossy G. Elicitation of selective T and B lymphocyte responses by cell surface binding ligands. Transplant Rev. 1972;11:87–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudat F. G., Harris T. N., Harris S., Hummeler K. Studies on antibody-producing cells. I. Ultrastructure of 19S and 7S antibody-producing cells. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):448–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The gut-associated lymphoid system: nature and properties of the large dividing cells. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jun;4(6):435–443. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Brittinger G., Hirschhorn K., Weissmann G. Studies on lysosomes. XII. Redistribution of acid hydrolases in human lymphocytes stimulated by phytohemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):412–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummeler K., Harris T. N., Harris S., Farber M. B. Studies on antibody-producing cells. IV. Ultrastructue of plaque-forming cells of rabbit lymph. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):491–502. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Shohat M., Greaves M. F., Dourmashkin R. R. Lymphocyte activation. IV. The ultrastructural pattern of the response of mouse T and B cells to mitogenic stimulation in vitro. Immunology. 1973 Feb;24(2):211–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S., Ling N. R., Sell S., Oxnard C. E. The transformation in vitro of peripheral lymphocytes of some laboratory animals. Immunology. 1965 Dec;9(6):565–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOVAT H. Z., FERNANDO N. V. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE LYMPHOID TISSUE DURING ANTIBODY FORMATION. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Apr;28:155–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meader R. D., Landers D. F. Electron and light microscopic observations on relationships between lymphocytes and intestinal epithelium. Am J Anat. 1967 Nov;121(3):763–773. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. W., Wakasa H., Lukes R. J. The morphologic and cytochemical demonstration of lysosomes in lymphocytes incubated with phytohemagglutinin by electron microscopy. Lab Invest. 1965 Oct;14(10):1736–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. M., Ferguson A. Selective migration of lymphocytes within the mouse small intestine. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):571–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzik O., Bienenstock J. Isolation and characteristics of gut mucosal lymphocytes. Lab Invest. 1974 Mar;30(3):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields J. W., Touchon R. C., Dickson D. R. Quantitativ studies on small lymphocyte disposition in epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1969 Jan;54(1):129–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordat B., Sordat M., Hess M. W., Stoner R. D., Cottier H. Specific antibody within lymphoid germinal center cells of mice after primary immunization with horseradish peroxidase: a light and electron microscopic study. J Exp Med. 1970 Jan 1;131(1):77–91. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Chambers V., Storb R., Weiser R. S. Antibody-carrying cells in the immune response II. Ultrastructure of "rosette"-forming cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1967 Jan;4(1):69–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toner P. G., Ferguson A. Intraepithelial cells in the human intestinal mucosa. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Feb;34(3):329–344. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowell O. A. Ultrastructural changes in lymphocytes exposed to noxious agents in vitro. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1966 Jul;51(3):207–220. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1966.sp001850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]