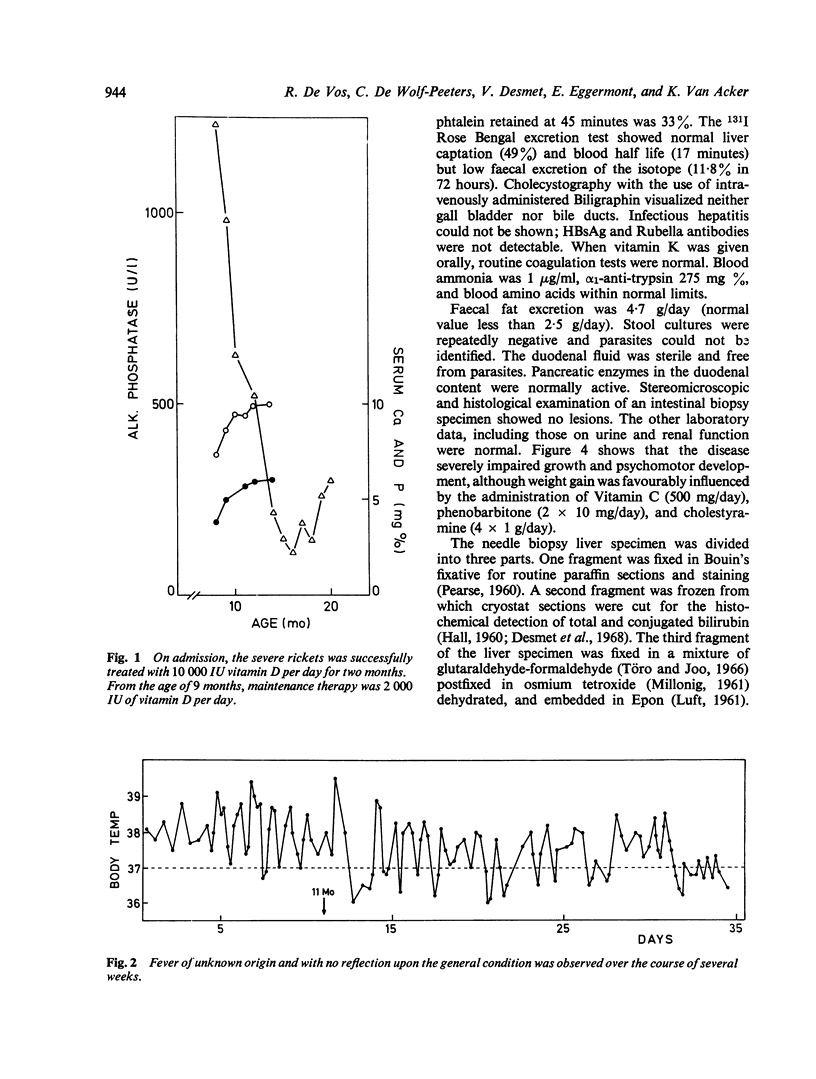
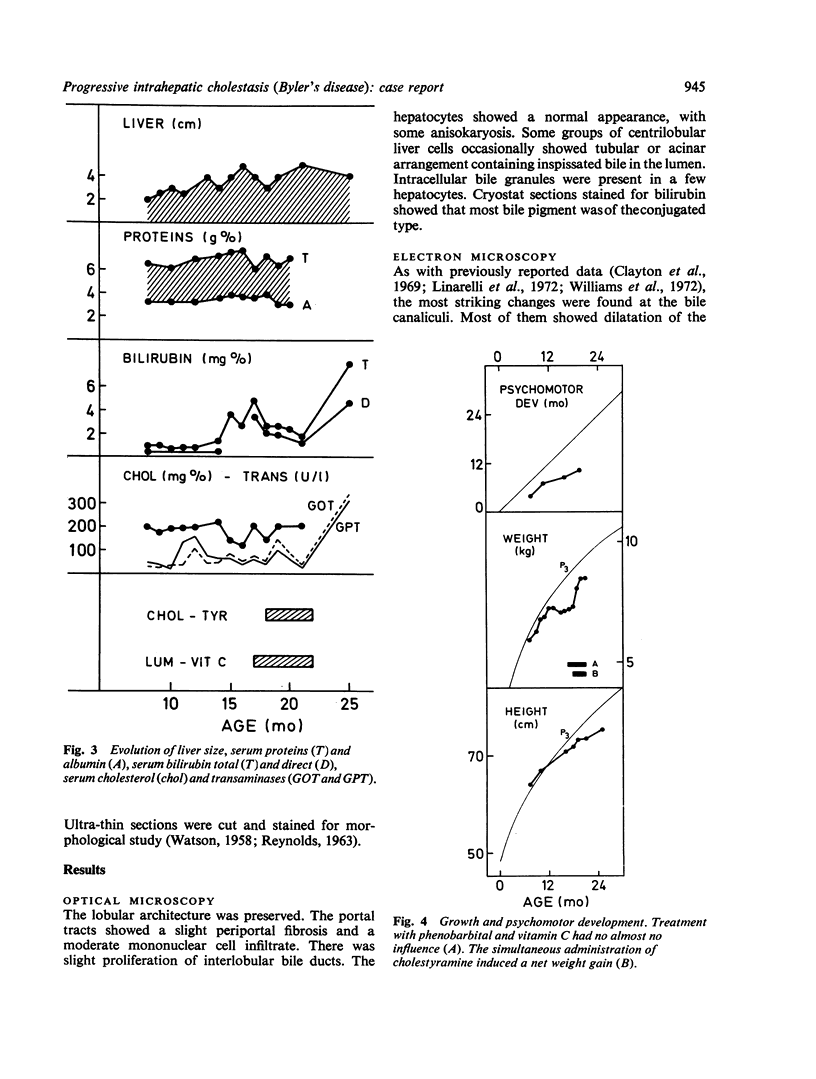
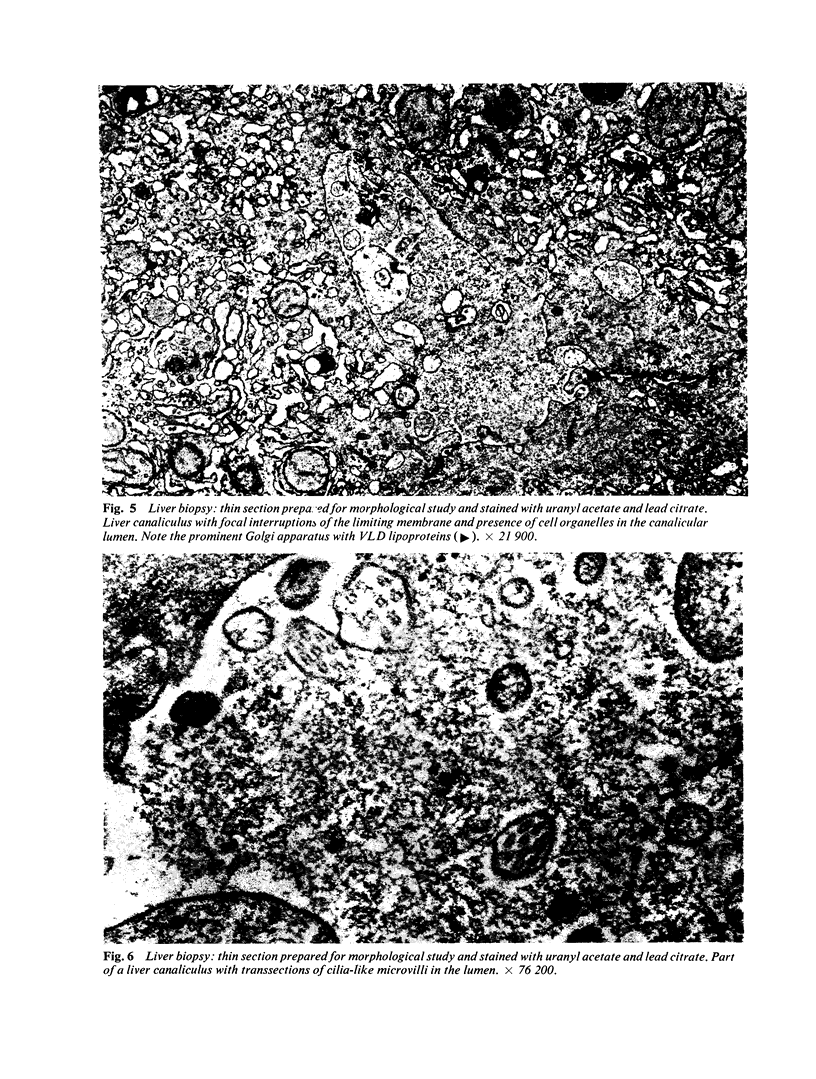
Abstract
This paper reports the case of a child in which the clinical and laboratory data indicate a progressive intrahepatic cholestasis of the type described as Byler's disease. The histological and histochemical findings suggest an intrahepatic cholestasis. Electron microscopy reveals interruptions of the bile canalicular membrane, which have been described as characteristic of this disease. A striking feature in the present case is the remarkable increase of microfilamentous structures in the pericanalicular ectoplasm and in the hepatocytic cytoplasm. The findings suggest a primary disturbance in bile acid secretion as the casue of cholestasis, entailing a hypertrophy of pericanalicular microfilaments which supposedly play a role in the final step of biliary secretion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carr I. The fine structure of microfibrils and microtubules in macrophages and other lymphoreticular cells in relation to cytoplasmic movement. J Anat. 1972 Sep;112(Pt 3):383–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton R. J., Iber F. L., Ruebner B. H., McKusick V. A. Byler disease. Fatal familial intrahepatic cholestasis in an Amish kindred. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jan;117(1):112–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., De Wolf-Peeters C., Desmet V., Bianchi L., Rohr H. P. Significance of liver canalicular changes after experimental bile duct ligation. Exp Mol Pathol. 1975 Aug;23(1):12–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(75)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wolf-Peeters C., De Vos R., Desmet V., Bianchi L., Rohr H. P. Electron microscopy and morphometry of canalicular differentiation in fetal and neonatal rat liver. Exp Mol Pathol. 1974 Dec;21(3):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(74)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J., Bullens A. M., De Groote J., Heirwegh K. P. New diazo reagent for specific staining of conjugated bilirubin in tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Jun;16(6):419–427. doi: 10.1177/16.6.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J. Morphologic and histochemical aspects of cholestasis. Prog Liver Dis. 1972;4:97–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzan H., Okita T., Fujita H., Iijima S. Light and electron microscopic studies on the development of periportal bile ducts of the human embryo. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1974 Jul;24(4):427–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1974.tb00835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Van Damme B., Michiels R., De Groote J., Heirwegh K. P. Bilirubin conjugates in bile of man and rat in the normal state and in liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2482–2492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray O. P., Saunders R. A. Familial intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice in infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Jun;41(217):320–328. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.217.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL M. J. A staining reaction for bilirubin in sections of tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Oct;34:313–316. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/34.4.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirooka M., Ono T. A case of familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1968 Mar;94(3):293–306. doi: 10.1620/tjem.94.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juberg R. C., Holland-Moritz R. M., Henley K. S., Gonzalez C. F. Familial intrahepatic cholestasis with mental and growth retardation. Pediatrics. 1966 Nov;38(5):819–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linarelli L. G., Williams C. N., Phillips M. J. Byler's disease: fatal intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr. 1972 Sep;81(3):484–492. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Van Obberghen E., Devis G., Somers G., Ravazzola M. Dynamics of insulin release and microtubular-microfilamentous system. V. A model for the phasic release of insulin. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;4(5):313–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Price V. M., Fisher M. M., Phillips M. J. Ultrastructure of bile canaliculi, with special reference to the surface coat and the pericanalicular web. Lab Invest. 1974 Oct;31(4):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Schaffner F. Pathophysiology of cholestasis. Hum Pathol. 1970 Mar;1(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherft J. P., Daems W. T. Single cilia in chondrocytes. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Aug 30;19(5):546–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. The subplasmalemmal microfilaments in Kupffer cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Jul;48(1):67–68. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Töro I., Jr, Joó F. An aldehyde-mixture as a fixative for the preservation of both fine structure and acid phosphatase activity. I. Advantage of the method for block incubation. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1966;17(3):265–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. N., Kaye R., Baker L., Hurwitz R., Senior J. R. Progressive familial cholestatic cirrhosis and bile acid metabolism. J Pediatr. 1972 Sep;81(3):493–500. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






