Abstract
The ability to respond selectively to particular frequency components of sensory inputs is fundamental to signal processing in the ear. The frog (Rana pipiens) sacculus, which is used for social communication and escape behaviors, is an exquisitely sensitive detector of sounds and ground-borne vibrations in the 5- to 200-Hz range, with most afferent axons having best frequencies between 40 and 60 Hz. We monitored the synaptic output of saccular sensory receptors (hair cells) by measuring the increase in membrane capacitance (ΔCm) that occurs when synaptic vesicles fuse with the plasmalemma. Strong stepwise depolarization evoked an exocytic burst that lasted 10 ms and corresponded to the predicted capacitance of all docked vesicles at synapses, followed by a 20-ms delay before additional vesicle fusion. Experiments using weak stimuli, within the normal physiological range for these cells, revealed a sensitivity to the temporal pattern of membrane potential changes. Interrupting a weak depolarization with a properly timed hyperpolarization increased ΔCm. Small sinusoidal voltage oscillations (±5 mV centered at −60 mV) evoked a ΔCm that corresponded to 95 vesicles per s at each synapse at 50 Hz but only 26 vesicles per s at 5 Hz and 27 vesicles per s at 200 Hz (perforated patch recordings). This frequency selectivity was absent for larger sinusoidal oscillations (±10 mV centered at −55 mV) and was largest for hair cells with the smallest sinusoidal-stimuli-evoked Ca2+ currents. We conclude that frog saccular hair cells possess an intrinsic synaptic frequency selectivity that is saturated by strong stimuli.
Keywords: afferent, synaptic vesicle pool, ribbon synapse, capacitance, tuning
The auditory and vestibular systems in the ear and the related mechanosensory and electrosensory organs of the lateral line employ a remarkable variety of mechanical and neural mechanisms to distinguish frequency components of sensory signals from <10 Hz to nearly 100 kHz (1, 2). In each of these organs, a sensory stimulus passes through one or more stages of mechanical or electrical filtering (3), leading to graded changes in the sensory receptor cell’s membrane potential, Vm. Oscillatory sensory stimuli usually produce oscillations in Vm, with the greatest amplitude occurring at a preferred frequency. Hair cells in the frog sacculus possess a broadly tuned electrical filter that causes Vm to oscillate preferentially at frequencies between 35 and 75 Hz (4), as well as spontaneous oscillations of the mechanosensory apparatus at frequencies between 5 and 50 Hz (5).
At the hair cells’ output synapses, the information contained in Vm is transmitted by a chemical neurotransmitter (glutamate) to postsynaptic terminals and encoded as a train of action potentials that travel to the brain. Each of these afferent synapses contains a presynaptic dense body [also known as the synaptic body (SB) or synaptic ribbon] (Fig. 1a) similar to ribbon synapses in the retina. As at other chemical synapses, Vm controls calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels, which in turn controls neurotransmitter release. Ribbon-class synapses differ from conventional chemical synapses in that transmitter release is controlled by small, graded changes in Vm rather than large action potentials.
Fig. 1.
SV pools and ΔCm in whole-cell recordings from frog saccular hair cells. In these and all other whole-cell experiments, the intracellular Ca2+ buffer was 1 mM EGTA. (a) The SB is surrounded by docked (green) and nondocked (purple) SVs. “Afferent” labels a postsynaptic terminal. (Scale bar, 200 nm.) (b) Representative Cm traces for depolarizations to −20 mV lasting 10 ms (small response) or 200 ms (large response). We did not attempt to interpret Cm measurements during the depolarization-induced changes in membrane conductance, which have been blanked during the interval from the onset of the depolarization until 30 ms after Vm was returned to −80 mV (dashed lines). (c) Boxed region from b. Cm(t) was averaged in 100-ms windows (red) surrounding the blanked interval, and the difference was used to compute ΔCm. (d) ΔCm plotted as a function of step duration. Each point is the average ΔCm for the first depolarization applied to each cell (mean ± SEM; n shown in parentheses; each cell contributed one ΔCm value at one duration only; total, n = 66 cells). There was no significant difference for any pairwise comparison of means at 10, 25, 30, and 50 ms (see Table 2, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site). Green and purple dashed lines indicate estimated numbers of docked SVs and docked plus undocked SVs, respectively, that are associated with synaptic ribbons. (e) Mean Ca2+ influx during the stimuli in d. Data are for whole-cell, voltage-clamp recordings. Evidence for the Ca2+ dependence of ΔCm and the ensemble-averaged Cm(t) traces for the data in d are shown in Figs. 8, 9b, and 10, which are published as supporting information on the PNAS web site.
We now demonstrate that the afferent synapses in frog saccular hair cells possess an intrinsic frequency selectivity that enhances exocytosis of neurotransmitter in the middle of the sacculus preferred frequency range (50 Hz). Similar to many tuning mechanisms (6), this frequency selectivity is saturated by large stimuli. Because the SB is intimately associated with synaptic vesicles (SVs) and is likely to be involved in timing their availability for release, our results raise the possibility that the SB plays a previously unknown role in frequency selectivity.
Results
We used whole-cell and perforated-patch voltage clamp recordings from frog saccular hair cells to measure the ΔCm associated with the increase in cell surface area that accompanies fusion of SVs with the plasmalemma. To avoid using proteases, which are known to shift the voltage dependence of the Ca2+ current and alter other ion channels in these cells, we used a semiintact epithelial preparation (4) rather than dissociated cells. Stepwise depolarizations from −80 mV caused rapid exocytosis followed by compensatory endocytosis (Fig. 1 b and c). In contrast with a previous study (7) that did not include GTP or glutathione in the pipette solution, we consistently observed 50–100% compensatory endocytosis within 30 s after stimuli that evoked ΔCm > 50 fF; noise and slow baseline drift obscured the extent of the ΔCm recovery after smaller responses.
The Pool of Docked SVs Accounts for the Fastest Exocytic Component.
Our initial experiments were designed to test the hypothesis that there are two kinetically distinct “pools” of SVs tethered to the SB (Fig. 1a): a small pool of docked SVs in contact with the cell plasmalemma that are immediately available for exocytosis, and a larger pool of nondocked SVs that become available more slowly (8, 9). Steps to −20 mV were used to maximally stimulate exocytosis for durations between 0.5 and 500 ms. The resulting multicomponent ΔCm waveform (Fig. 1d) is strikingly different from the linear relationship between stimulus duration and total Ca2+ influx (Fig. 1e). A positive ΔCm was apparent by 2 ms, reached a plateau at 10 ms, and did not increase further for steps lasting up to 30 ms. A second rise began after 30 ms and reached 160 fF at 100 ms. This rise was followed by a third, sustained secretory component that continued for at least several seconds (e.g., Fig. 7b, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site) (7, 8).
We estimated the size of the first kinetic component by averaging ΔCm over all steps lasting between 10 and 30 ms (n = 25). The result (44 ± 8 fF) corresponds to 59 SVs per synapse [calculated by assuming 20 synapses per hair cell (10) and 37 aF per SV (11)], comparable with the results of a previous electron tomographic study (12) that reported 43 docked SVs associated with the SB at inhibited synapses in these hair cells. The agreement is improved if all docked SVs within 300 nm of the center of the active zone are included, which raises the count to 66 docked SVs per synapse.
The correspondence between the second kinetic component and the rest of the SVs tethered to the SB is less clear. The total pool of 400 docked and nondocked SVs on the SB (12) can contribute ≈300 fF, sufficient to account for ΔCm during steps lasting up to 500 ms (Fig. 1d), but stimuli of longer duration elicit much larger responses (see Fig. 7b) (7). The lack of a plateau in ΔCm for long depolarizations is consistent with the morphological result that the pool of nondocked SVs on the SB is depleted by <50% during maintained stimulation (12). The simplest explanation is that the SB is continuously resupplied with SVs from the cytoplasm. Alternatively, prolonged depolarization may evoke exocytosis of extrasynaptic, outlying docked SVs (12).
Interrupting a Depolarization Can Increase Exocytosis.
When the frog sacculus is stimulated in vivo by sounds or substrate vibrations at frequencies ≤50 Hz, many postsynaptic axons fire at most one phase-locked action potential during each stimulus cycle (13, 14). To account for this observation, we hypothesized that the depolarizing phase of each cycle triggers a brief burst of transmitter release and that the hyperpolarizing phase reenables the synapse to release transmitter during the next depolarization. This hypothesis predicts that periodic weak stimuli in which depolarizations are interrupted by hyperpolarizations can cause more exocytosis than a maintained depolarization.
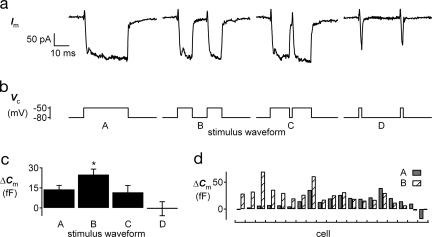
To test this hypothesis, we used four different patterns of depolarization (Fig. 2) that were weak compared with the stimuli commonly used in voltage-clamp experiments but probably larger than the receptor potentials that modulate synaptic transmission in vivo (15). Continuous depolarization for 30 ms (stimulus A) evoked a ΔCm of 14 ± 3 fF, whereas two 10-ms depolarizations separated by 10 ms of hyperpolarization (stimulus B) delivered to the same 19 cells evoked a significantly larger ΔCm of 25 ± 4 fF (P = 0.018), although stimulus A caused more total Ca2+ influx than stimulus B (Fig. 2a). Stimulus B can be thought of as a 30-ms depolarization that has been interrupted in the middle by a 10-ms hyperpolarization to −80 mV. A briefer (2 ms) interruption (stimulus C) evoked a significantly smaller ΔCm than stimulus B (12 ± 5 fF, n = 7, P = 0.03), which was not significantly different from the response to stimulus A. This result is particularly intriguing because stimuli B and C produce identical Ca2+ tail currents. The large difference in ΔCm evoked by stimuli B and C argues against the possibility that the additional tail current alone was responsible for the increased ΔCm response to stimulus B. The response to stimulus C also shows that 2 ms of hyperpolarization to −80 mV is insufficient to have the facilitating effect caused by 10 ms of interposed hyperpolarization (stimulus B). A pair of brief (2 ms) depolarizations separated by 26 ms (stimulus D) evoked no measurable ΔCm (−1 ± 5 fF). The lack of ΔCm response to stimulus D provides further evidence that Ca2+ tail currents generated by these weak depolarizations did not cause exocytosis, although the tails in stimulus D are expected to be slightly smaller than in stimuli A–C because ICa had not reached steady-state activation (Fig. 2a). When we applied stimulus patterns with the same timing as stimuli A and B but used depolarization to −20 mV, we found no significant effect of the interposed hyperpolarization on ΔCm (data not shown).
Fig. 2.
Interposed hyperpolarization can increase ΔCm. (a) Representative ICa during the four stimulus patterns shown in b. Each cell received patterns A and B, plus one or more of the other patterns. (b) Stimuli A–D are steps to −55 mV, except in a few cells in which the ΔCm responses to stimuli A and B were too small to measure, in which case the depolarization was increased to −50 mV. Step timing: stimulus A, 30 ms; stimulus B, 2 × 10 ms separated by 10 ms; stimulus C, 2 × 14 ms separated by 2 ms; stimulus D, 2 × 2 ms separated by 26 ms. (c) Mean ΔCm responses (±SEM) to the four stimulus patterns. The response to stimulus B was significantly larger than all others (see text). An alternative analysis in which the ΔCm responses in each cell were first normalized by the ΔCm response to stimulus waveform B gave similar results. (d) Individual ΔCm from the 19 cells receiving stimulus patterns A and B. Responses to the first stimulus presentation are shown for waveforms A (solid gray bars) and B (striped bars).
Frequency Dependence of Synaptic Exocytosis.
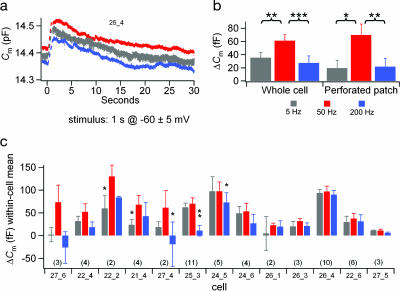
We measured the ΔCm caused by small, sinusoidal voltage changes (±5 mV centered at −60 mV) delivered for 1 s at 5, 50, and 200 Hz. We hypothesized that ΔCm would be largest at 50 Hz, the frequency where the sacculus is most sensitive to sound and seismic stimuli (13, 14). The sinusoidal stimuli evoked periodic Ca2+ currents that varied among cells (50–200 pA peak-to-peak and 0 to −100 pA offset), but the peak ICa amplitude (Fig. 3a) and the integrated Ca2+ influx (Fig. 3b) in each cell were nearly the same across the three frequencies. Nevertheless, ΔCm was significantly greater at 50 Hz than at 5 or 200 Hz (Fig. 3d). ΔCm was not accompanied by any apparent change in series resistance (Fig. 3c). The preference for 50 Hz was absent when stronger stimuli (±10 mV centered at −55 mV) were applied to other cells (Fig. 3d). A similar preference for 50 Hz was seen in perforated-patch experiments (Figs. 3 e and f), which maintain the cell’s endogenous Ca2+ buffering conditions.
Fig. 3.
ΔCm responses to sinusoidal stimulation at 5 (gray), 50 (red), and 200 (blue) Hz. Each cell received either weak (±5 mV centered at −60 mV, solid bars) or strong (±10 mV centered at −55 mV, striped bars) stimulation for 1 s at each frequency with 30 s between stimuli. Presentation order was randomized among cells from the six possibilities. The strong stimuli were delivered around a more depolarized baseline than the weak stimuli to mimic the asymmetric transduction current in these cells (45). To avoid possible rundown effects, only responses to the first presentation of the three frequencies are included in this figure. (a) Vm and leak-subtracted Im from one representative whole-cell recording. (b) Total Ca2+ influx did not differ across frequencies (same cells as d). (c) Ensemble-averaged Rs (Upper) and Cm (Lower) for all weak stimuli (same cells as d). (d) For weak stimuli (whole-cell, n = 11 cells), ΔCm at 50 Hz was significantly greater (55 ± 12 fF) than at 5 Hz (20 ± 10 fF, P = 0.0001) or 200 Hz (18 ± 12 fF, P = 0.008). No significant differences between frequencies were observed for strong stimuli (whole-cell, n = 5 cells). (e and f) Similar results were obtained from perforated-patch recordings (n = 11 cells; only the weak stimuli were used). ΔCm at 50-Hz stimuli (76 ± 17 fF) was significantly greater than ΔCm at 5 Hz (26 ± 14 fF, P = 0.014) or 200 Hz (20 ± 13 fF, P = 0.006).
We observed a large coefficient of variation (cv) between cells in the amplitude of the Ca2+ currents evoked by the small sinusoidal stimuli in both whole-cell (cv = 0.9; mean peak ICa = 99 pA) and perforated-patch (cv = 1.0; mean peak ICa = 65 pA) experiments (Fig. 4). Much of this variability can be explained by small errors in Vm, which have large effects on ICa near −60 mV, where ICa is steeply voltage-dependent. We used this variability to test the hypothesis that frequency selectivity was most pronounced when ICa was small. Fig. 4b shows the predicted negative correlation (r = −0.4), although not all cells with small Ca2+ currents had a strong preference for 50 Hz.
Fig. 4.
Correlation of ICa amplitude during weak sinusoidal stimulation with the frequency selectivity of ΔCm. Combined whole-cell and perforated-patch data. (a) Representative current traces from one cell that had a large ICa and one cell that had a small ICa. (b) To quantify the preference for 50 Hz in each cell, we divided the ΔCm at 50 Hz by the mean ΔCm at all three frequencies and correlated this measure with the mean integrated Ca2+ influx across frequencies for perforated-patch (gray inverted triangle) and whole-cell (black inverted triangle) recordings. The regression line and correlation coefficient are shown.
Data from the 13 cells in which we were able to present two or more repetitions of the weak stimulus at each frequency revealed a range of responses. The cell shown in Fig. 5a had no significant preference for 50 Hz. The means of within-cell means (Fig. 5b) showed a clear preference for 50 Hz, and 12 of the 13 cells had the greatest mean ΔCm at 50 Hz (Fig. 5c), but the ΔCm at 50 Hz was significantly greater than the ΔCm at 5 Hz or 200 Hz in only 5 of the 13 cells. Although this diversity of responses might reflect subpopulations of hair cells in the frog sacculus tuned to other physiologically relevant stimuli, the noise in the ΔCm measurement and limited repetitions make it difficult to differentiate the behavior of individual cells.
Fig. 5.
Frequency selectivity in individual cells. ΔCm responses from the subset of cells in Fig. 3, from which two or more stimulus presentations were delivered at each frequency. Sinusoidal stimuli were delivered for 1 s in a fixed order within each cell (e.g., 5, 50, 200, 5, 50, 200, and so on) and randomized between cells, with a 30-s interstimulus interval. (a) Averaged Cm traces for 10 stimulus presentations at each frequency to one cell (perforated-patch recording) collected over 15 min. (b) Means (±SEM) of within-cell means. Whole cell (n = 11): ΔCm at 50 Hz (61 ± 9 fF) was significantly greater than at 5 Hz (35 ± 8 fF, P = 0.001) and 200 Hz (27 ± 11 fF, P = 0.0006); perforated patch (n = 11): ΔCm at 50 Hz (70 ± 17 fF) was significantly greater than at 5 Hz (19 ± 12 fF, P = 0.012) and 200 Hz (20 ± 12 fF, P = 0.006). (c) Within-cell ΔCm means (±SEM, number of repetitions in parentheses) are plotted across frequencies for 13 cells. Ensemble-averaged Cm(t) traces for two cells are shown in Fig. 10, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site.
Steep Voltage Sensitivity of Im and ΔCm Suggests a Narrow Operational Range.
Large or prolonged depolarizations (Fig. 6) evoked much larger ΔCm responses that were qualitatively different from responses to weaker stimuli. Sinusoidal stimuli (10 s duration) centered at −70 and −65 mV evoked small Ca2+ currents and capacitance increases that either remained constant or returned toward baseline after the stimulus, whereas stimuli centered at −60 mV and −55 mV evoked large Ca2+ currents and capacitance increases that continued to rise for several seconds after Vm was returned to −80 mV.
Fig. 6.
Steep voltage sensitivity of Im and ΔCm. Continuous recording of Vm, Im, and Cm in a cell that was presented with a series of sinusoidal voltage oscillations (50 Hz, ±5 mV, 10-s duration, 10 s between stimuli) centered at −70, −65, −60, and −55 mV (see also Fig. 7). (Inset) Enlargement of stimulus response (Vm) and current response (Im) around the onset of the −60 ± 5 mV stimulus. The Vm oscillation during the rest period that ends at t = 65 ms appears as a broad black band in Vm and is the result of the 1.5-kHz probe from the lock-in amplifier, which is turned off during the 50-Hz stimulation.
Discussion
Ribbon synapses, which have been described only in the retina, pineal body, and acousticolateralis sensory organs of vertebrate animals are defined by the presence of a prominent presynaptic structure (the SB or ribbon) at each active zone. Numerous physiological investigations have sought to understand the function of the SB (7–9, 11, 12, 16–22). The predominant hypothesis is that the SB facilitates high rates of sustained transmission by capturing and/or transporting SVs to release sites, although other functions have been proposed (23), including frequency selectivity (24).
Functional and Anatomical Vesicle Pools.
Only a small fraction (1–2%) of SVs at most chemical synapses are immediately available to undergo exocytosis (i.e., within a few milliseconds after the onset of a depolarization that maximally activates the presynaptic Ca2+ current). This SV population is often called the “readily releasable pool” (RRP) and has been proposed to correspond anatomically to the “docked” SVs, defined as those in contact with the plasmalemma at the synapse (25). To estimate the size of the RRP in frog saccular hair cells, we held Vm at −80 mV to inhibit synaptic transmission and then stepped to −20 mV to maximally stimulate exocytosis. We found a clear temporal separation between the fastest exocytic component, which is complete in 10 ms (Fig. 1d), and the slower component(s) that begin ≈20 ms later, similar to the 25-ms recovery time for postsynaptic potentials in the goldfish saccular afferents (26). These results agree with more extensive studies of SV pools at ribbon synapses in mouse inner hair cells (8), chick cochlear hair cells (27), and retinal bipolar cells (16, 28), in which paired-pulse paradigms have shown that the most rapidly available SV pool can be depleted faster than it can be refilled. The fastest component, which we define as the RRP at these synapses, corresponds to 59 SVs per active zone, similar to the 43 docked SB-associated SVs (66 docked SVs within 300 nm of the active zone center) that were counted in cells in which transmission had been inhibited before and during fixation (12).
In contrast, the RRP estimate from ΔCm measurements in mouse inner hair cells is ≈53–64 SVs per synapse, whereas the morphologically docked SV pool contains only 16–30 SVs (29). Some of this difference may be due to the fact that synaptic exocytosis had not been inhibited before fixation, which in frog saccular hair cells reduced the number of docked SVs per synapse from 43 to 32 (11). Another difference arises from the 25% smaller capacitance per SV (28 aF) used in their calculations compared with ours (37 aF). Both calculations assumed the same rough estimate of specific membrane capacitance (1 μF/cm2), but different estimates of SV diameter (30.0 nm in mouse inner hair cells vs. 34.3 nm in frog sacculus, both of which were measured in electron micrographs of glutaraldehyde-fixed tissue at the middle of the apparent membrane thickness) (11, 29). Such measurements are subject to significant errors due to shrinkage and ovoid SV shapes. For example, electron tomographic reconstruction of SVs in three dimensions (11) gave a mean volume of 12,500 nm3, which corresponds to a spherical diameter of 28.8 nm (estimated capacitance, 26 aF), significantly smaller than the value calculated from the same data as the diameter of the circle having the same area as the largest cross section through the SV. We favor the larger estimate to compensate for overall shrinkage, but clearly these are all rough estimates of SV capacitance. Multivesicular fusion of nondocked ribbon-associated SVs (22, 30) could also contribute to discrepancies between the sizes of RRPs and docked SV pools in ΔCm measurements at ribbon synapses. Given the many sources of error, comparisons of pool sizes should be interpreted cautiously (29).
Experiments in chick cochlear hair cells (31) did not investigate responses to depolarizations <50 ms, but we expect that the ΔCm corresponding to the docked SV pool would be difficult to see in these cells because this pool is very small (18).
Other recent perforated-patch experiments (32) using enzymatically dissociated saccular hair cells from Rana pipiens reported nearly 5-fold larger ΔCm responses to 10-ms depolarizing steps than we report in whole-cell recordings from the semiintact sacculus (Fig. 1d) and a mean ICa that was twice as large as what we found in either perforated-patch or whole-cell recordings. We do not have a compelling explanation for these differences, but they could be due to the different preparations used (isolated cells vs. semiintact sacculus), selection of different subpopulations of hair cells, or other methodological differences.
As in previous studies, we interpret ΔCm measurements as purely exocytic because the time constant for endocytosis stimulated by depolarization (7.5–14 s) (7, 8) appears to be too slow for endocytosis to significantly contribute to ΔCm measurements over times ≤ 1 s, although faster membrane retrieval (τ = 300 ms) was reported in response to global elevation of intracellular Ca2+ (33). Nevertheless, we cannot rule out the alternative explanation that some stimulus frequencies favor a mode of SV cycling, such as kiss-and-run (34), in which fast endocytosis predominates. Experiments using fluorescent membrane tracers are needed to test this possibility.
Frequency Selectivity.
The frequency selectivity of exocytosis that we observed is expected to contribute to the overall tuning of the sacculus (35), which matches the power spectrum of seismic signals associated with frog mating calls (peak power between 20 and 70 Hz) (36) and other sources. Recordings from saccular afferent fibers in bullfrogs, white-lipped frogs, and the northern leopard frog (R. pipiens) have shown that weak seismic and auditory stimuli evoke maximum spike rates for frequencies near 50 Hz (13, 14, 37, 38), and that the low-frequency roll-off can be due to the phase-locked firing of a single spike in the postsynaptic cell per stimulus cycle (13, 14). The sinusoidal stimuli used here (±5 mV centered at −60 mV), were small compared with the stimuli used in most voltage-clamp studies but were larger than the Vm oscillations expected to occur at sensory threshold (15). In both whole-cell and perforated-patch experiments, the exocytic rate during 1 s of 50-Hz stimulation was two to three times the rate for 5- or 200-Hz stimulation, but, when expressed as vesicles per stimulus cycle, the rate was greatest at 5 Hz (5.1 SV per cycle, compared with 1.9 SV per cycle at 50 Hz and 0.14 SV per cycle at 200 Hz) (Fig. 5b, perforated patch). Therefore, the presynaptic frequency selectivity that we observed may not by itself be sufficient to account for the low-frequency roll-off in firing rate (Hz) of the postsynaptic cell.
It is difficult to invoke mechanisms involving depletion of the RRP to explain our results using interrupted steps (Fig. 2) and sinusoids (Figs. 3–5), in which the ΔCm responses are smaller than the RRP and the effects are largest for weak stimuli. For example, the response to 30 ms of weak depolarization (Fig. 2, pattern A) caused only a 32% depletion of the RRP; interrupting this depolarization by 10 ms of hyperpolarization (pattern B) nearly doubled the response but still caused only 57% depletion of the RRP. Similarly, the ΔCm responses to 1 s of sinusoidal stimulation at 5 and 200 Hz caused only ≈45% depletion of the RRP (Fig. 5b, perforated patch). Therefore, if SV depletion is involved, the depleted pool must be smaller than the RRP measured using strong depolarizations (Fig. 1). Such a model was proposed by Furukawa et al. (26, 39) to explain the “adaptive rundown” in excitatory postsynaptic potential amplitude that they observed in recordings from goldfish saccular afferents. The authors proposed that weak stimuli cause exocytosis only at the center of the active zone, causing depletion of this subset of docked SVs, which must be replenished by migration of SVs from the surrounding region. If this migration were inhibited while Ca2+ channels are open, depletion of this small pool might explain the small ΔCm responses that we observed during 5-Hz stimulation and during 30 ms of maintained weak depolarization. A separate mechanism would be needed to explain the small ΔCm response to 200-Hz stimulation. It is also important to note that many other possible mechanisms involving a delayed inhibitory effect of Ca2+ (or even Vm by itself), could account for our results. It has been proposed that at some central synapses, an unexplained mechanism prohibits exocytosis of more than one SV per action potential (40). There is no straightforward way to apply this type of rule to explain the ΔCm responses to small sinusoids that we observed, which correspond to much more than 1 SV per cycle at 5 Hz and much less than 1 SV per cycle at 200 Hz.
Materials and Methods
Frogs (R. pipiens) were maintained at 17°C on a 12 h:12 h light/dark cycle. All procedures were in compliance with the University of Oregon Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. The semiintact saccular preparation (4) was visualized at ×40 magnification with differential interference contrast microscopy optics under an upright microscope (Zeiss). Dissection and recording were performed in an extracellular solution (112 mM Na+/119 mM Cl−/5 mM Hepes/3 mM d-glucose/2 mM K+/1.8 mM Ca2+) with 0.01 mM d-tubocurarine to block Ca2+ entry through mechanoelectrical transduction channels (41).
Electrophysiology.
All experiments were performed at 20°C within 3 h of dissection. We only used cells that showed no evidence of swelling or internal Brownian motion. Recording pipettes (2–6 MΩ; tip diameter, 1–2 μm) were pulled from borosilicate glass and shaped by heating under pressure (42). The pipette solution contained 94 mM glutamate, 93 mM Cs+, 10 mM Hepes, 10 mM tetraethylammonium, 2 mM Mg2+, 1 mM EGTA, 0.274 mM Ca2+ ([Ca2+]free = 50 nM), 14 mM Cl−, 8 mM Na+, 5 mM glutathione, 3 mM ATP, 1 mM GTP. Dry glutathione, ATP, and GTP were added immediately before the recording session. For perforated-patch experiments, gluconate was substituted for glutamate and the back ends of filament-glass electrodes were dipped into pipette solution for 5–10 s to fill the tip; the electrodes were then filled with pipette solution supplemented with 500 μg/ml solubilized amphotericin. All reagents were purchased from Sigma.
Pipette current was zeroed in the bath at −13 mV to account for the liquid junction potential (4). Perfusion of the extracellular solution was paused during data acquisition to minimize changes in stray pipette capacitance. Recordings were predominantly from “short” hair cells (43).
Cells were held at −80 mV except during stimulation. Of the 122 cells used in this study, 102 had holding currents between +25 and −100 pA (total range, +50 to −299 pA). Cm values before stimulation ranged from 8 to 20 pF. See Table 1, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site, for recording parameters. We excluded the ≈8% of cells (six whole-cell and four perforated-patch cells) in which ΔCm ≤ 0 in response to all weak depolarizing stimuli.
In most cells IK was negligible (blocked by Cs+ and tetraethylammonium), leaving ICa as the predominant voltage-gated current. We calculated Ca2+ influx by integrating ICa: ICa = Im − Ileak, where Ileak = (Vm − Eleak)/Rm. Rm was determined with 10-mV pulses from −80 mV and Eleak = −(Ihold Rm + 80 mV). We did not correct for voltage errors due to series resistance (Rs) (except for Figs. 7a and 8b, which are published as supporting information on the PNAS web site; see also Table 1), which were small because Ik was blocked.
Membrane Impedance Measurements.
We used an Optopatch amplifier (Cairn, Kent, U.K.), in whole-cell voltage-clamp mode with passive RC compensation and feedback RC tracking, using the amplifier’s internally generated sinusoidal probe stimulus (44). The sinusoidal probe input (±23 mV at 1.5 kHz, centered at −80 mV) was on continuously except during depolarizations. The probe did not activate Ca2+ channels. For example, the current in Fig. 3a (gray trace, 5 Hz) was the same for t < 0 (probe on) and at t = 0.15 s (probe off; Vm = −65 mV). For additional details, see Supporting Materials and Methods, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site.
Statistics.
Population measures of central tendency and variance are expressed as mean ± SEM. We used independent and paired Student’s t tests for comparisons of means between groups when applicable. P < 0.05 was considered significant. Data groups were confirmed normal with Shapiro–Wilk and Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests. One-tailed t tests were used for tests of a priori hypotheses in Figs. 2, 3, and 5 (see Supporting Materials and Methods). Alpha was adjusted to the familywise error rate for multiple comparisons.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. David Lenzi and Mr. J. W. Runyeon for electron microscopy (Fig. 1a) and analysis. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Research Grant R01 27142.
Abbreviations
- RRP
readily releasable pool
- SB
synaptic dense body
- SV
synaptic vesicle.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
References
- 1.Fettiplace R., Fuchs P. A. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1999;61:809–834. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.61.1.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bruns V., Goldbach M. Anat. Embryol. Hist. Arch. 1980;161:51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00304668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Purgue A. P., Narins P. M. J. Comp. Physiol. A. 2000;186:481–488. doi: 10.1007/s003590050446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Armstrong C. E., Roberts W. M. J. Neurosci. 1998;18:2962–2973. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-08-02962.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Martin P., Bozovic D., Choe Y., Hudspeth A. J. J. Neurosci. 2003;23:4533–4548. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-11-04533.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.de Boer E., Nuttall A. L. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000;107:1497–1507. doi: 10.1121/1.428436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Parsons T. D., Lenzi D., Almers W., Roberts W. M. Neuron. 1994;13:875–883. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Moser T., Beutner D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:883–888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.2.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mennerick S., Matthews G. Neuron. 1996;17:1241–1249. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Roberts W., Jacobs R., Hudspeth A. J. J. Neurosci. 1990;10:3664–3684. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03664.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lenzi D., Crum J., Ellisman M. H., Roberts W. M. Neuron. 2002;36:649–659. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)01025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lenzi D., Runyeon J. W., Crum J., Ellisman M. H., Roberts W. M. J. Neurosci. 1999;19:119–132. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-01-00119.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Koyama H., Lewis E. R., Leverenz E. L., Baird R. A. Brain Res. 1982;250:168–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Christensen-Dalsgaard J., Narins P. M. J. Comp. Physiol. A. 1993;172:653–662. doi: 10.1007/BF00195391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dallos P. J. Neurosci. 1985;5:1591–1608. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-06-01591.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.von Gersdorff H., Sakaba T., Berglund K., Tachibana M. Neuron. 1998;21:1177–1188. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.McNulty J., Fox L. M. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1992;21:175–187. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Martinez-Dunst C., Michaels R. L., Fuchs P. A. J. Neurosci. 1997;17:9133–9144. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-23-09133.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Adly M. A., Spiwoks-Becker I., Vollrath L. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999;40:2165–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schmitz F., Konigstorfer A., Südhof T. C. Neuron. 2000;28:857–872. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Llobet A., Cooke A., Lagnado L. J. Neurosci. 2003;23:2706–2714. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02706.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Glowatzki E., Fuchs P. A. Nat. Neurosci. 2002;5:147–154. doi: 10.1038/nn796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parsons T. D., Sterling P. Neuron. 2003;37:379–382. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schnee M. E., Lawton D. M., Furness D. N., Benke T. A., Ricci A. J. Neuron. 2005;47:243–254. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rizzoli S. O., Betz W. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005;6:57–69. doi: 10.1038/nrn1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Furukawa T., Kuno M., Matsuura S. J. Physiol. (London) 1982;322:181–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Spassova M. A., Avissar M., Furman A. C., Crumling M. A., Saunders J. C., Parsons T. D. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2004;5:376–390. doi: 10.1007/s10162-004-5003-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gomis A., Burrone J., Lagnado L. J. Neurosci. 1999;15:6309–6317. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06309.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Khimich D., Nouvian R., Pujol R., Tom Dieck S., Egner A., Gundelfinger E. D., Moser T. Nature. 2005;434:889–894. doi: 10.1038/nature03418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Singer J. H., Lassova L., Vardi N., Diamond J. S. Nat. Neurosci. 2004;7:826–833. doi: 10.1038/nn1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Eisen M. D., Spassova M., Parsons T. D. J. Neurophysiol. 2004;91:2422–2428. doi: 10.1152/jn.01130.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Edmonds B. W., Gregory F. D., Schweizer F. E. J. Physiol. (London) 2004;560:439–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.066035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Beutner D., Voets T., Neher E., Moser T. Neuron. 2001;29:681–690. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Alés E., Tabares L., Poyato J. M., Valero V., Lindau M., Alvarez de Toledo G. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999;1:40–44. doi: 10.1038/9012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lewis E. Biophys. J. 1988;53:441–447. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83120-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lewis E. R., Narins P. M. Science. 1985;227:187–189. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4683.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Narins P. M., Lewis E. R. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1984;76:1384–1387. doi: 10.1121/1.391455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yu X. L., Lewis E. R., Feld D. J. Comp. Physiol. A. 1991;169:241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00215871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Furukawa T., Matsuura S. J. Physiol. (London) 1978;276:193–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Stevens C. F., Wang Y. Neuron. 1995;14:795–802. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Glowatzki E., Ruppersberg J. P., Zenner H.-P., Rusch A. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1269–1275. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(97)00108-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Goodman M. B., Lockery S. R. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2000;100:13–15. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0270(00)00224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Edmonds B., Reyes R., Schwaller B., Roberts W. M. Nat. Neurosci. 2000;3:786–790. doi: 10.1038/77687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Johnson S. L., Thomas M. V., Kros C. J. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2002;443:653–663. doi: 10.1007/s00424-001-0763-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Corey D., Hudspeth A. J. J. Neurosci. 1983;3:962–976. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-05-00962.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.