Abstract
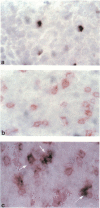
We have investigated the phenotype of interleukin-4 (IL-4) mRNA+ cells in the nasal mucosa of six subjects with allergic rhinitis before and 24 hr after local allergen provocation with grass pollen extract. Serial cryostat sections were cut from paraformaldehyde-fixed snap-frozen nasal biopsies, and immunocytochemistry (APAAP) followed by in situ hybridization performed on the same sections. For immunocytochemistry, antibodies against CD3, tryptase, major basic protein (MBP) and CD68 were used to identify T cells, mast cells, eosinophils and macrophages, respectively. Hybridization studies were performed using a digoxigenin-labelled IL-4 riboprobe. Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) and X-phosphate-5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoly phosphate (BCIP) served as chromogens to detect hybridization IL-4 mRNA signals. Significant increases in T lymphocytes and eosinophils and in the number of IL-4 mRNA+ cells were observed after allergen challenge. Double immunocytochemistry/in situ hybridization demonstrated that the majority of IL-4 mRNA+ cells after allergen challenge were CD3+ (73.7% +/- 1.6). Lower numbers of IL-4 mRNA hybridization signals were co-localized to tryptase+ cells (26.0% +/- 1.6). In contrast, no IL-4 mRNA hybridization signals were co-localized to either eosinophils or macrophages. These results indicate that after allergen challenge T cells are the principal cellular source of IL-4 mRNA transcripts during human late nasal responses, with a lesser contribution from mast cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abehsira-Amar O., Gibert M., Joliy M., Thèze J., Jankovic D. L. IL-4 plays a dominant role in the differential development of Tho into Th1 and Th2 cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3820–3829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bascom R., Pipkorn U., Lichtenstein L. M., Naclerio R. M. The influx of inflammatory cells into nasal washings during the late response to antigen challenge. Effect of systemic steroid pretreatment. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Aug;138(2):406–412. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.2.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. M., Jacobson M. R., Cumberworth V., Barkans J. R., Moqbel R., Schwartz L. B., Irani A. M., Kay A. B., Durham S. R. Immunohistology of the nasal mucosa in seasonal allergic rhinitis: increases in activated eosinophils and epithelial mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Apr;89(4):877–883. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. M., Meng Q., Robinson D. S., Hamid Q., Kay A. B., Durham S. R. Increases in activated T lymphocytes, eosinophils, and cytokine mRNA expression for interleukin-5 and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in bronchial biopsies after allergen inhalation challenge in atopic asthmatics. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;8(1):35–42. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradding P., Feather I. H., Howarth P. H., Mueller R., Roberts J. A., Britten K., Bews J. P., Hunt T. C., Okayama Y., Heusser C. H. Interleukin 4 is localized to and released by human mast cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1381–1386. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradding P., Feather I. H., Wilson S., Bardin P. G., Heusser C. H., Holgate S. T., Howarth P. H. Immunolocalization of cytokines in the nasal mucosa of normal and perennial rhinitic subjects. The mast cell as a source of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 in human allergic mucosal inflammation. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3853–3865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe D. M., Cotran R. S., Pober J. S. Effects of tumor necrosis factor, lipopolysaccharide, and IL-4 on the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in vivo. Correlation with CD3+ T cell infiltration. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2954–2960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. A., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Falco J., Ihle J. N., Paul W. E. B cell stimulatory factor-1/interleukin-4 mRNA is expressed by normal and transformed mast cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):809–818. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90339-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byron K. A., Varigos G., Wootton A. Hydrocortisone inhibition of human interleukin-4. Immunology. 1992 Dec;77(4):624–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G., Maggi E., Parronchi P., Chrétien I., Tiri A., Macchia D., Ricci M., Banchereau J., De Vries J., Romagnani S. IL-4 is an essential factor for the IgE synthesis induced in vitro by human T cell clones and their supernatants. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4193–4198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham S. R., Ying S., Varney V. A., Jacobson M. R., Sudderick R. M., Mackay I. S., Kay A. B., Hamid Q. A. Cytokine messenger RNA expression for IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, and granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor in the nasal mucosa after local allergen provocation: relationship to tissue eosinophilia. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2390–2394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery B. E., White M. V., Igarashi Y., Mullol J., Berkebile C., Peden D., Lotze M. T., Kaliner M. A. The effect of IL-4 on human nasal mucosal responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Nov;90(5):772–781. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L., Pipkorn U., Granerus G. Intraepithelial migration of nasal mucosal mast cells in hay fever. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;80(1):44–51. doi: 10.1159/000234024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fokkens W. J., Vroom T. M., Gerritsma V., Rijntjes E. A biopsy method to obtain high quality specimens of nasal mucosa. Rhinology. 1988 Dec;26(4):293–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Ying S., Varney V., Gaga M., Durham S. R., Moqbel R., Wardlaw A. J., Hamid Q. Messenger RNA expression of the cytokine gene cluster, interleukin 3 (IL-3), IL-4, IL-5, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, in allergen-induced late-phase cutaneous reactions in atopic subjects. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):775–778. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Prickett K. S., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Weaver M., Wilson C. B. Restricted production of interleukin 4 by activated human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9743–9747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li-Weber M., Eder A., Krafft-Czepa H., Krammer P. H. T cell-specific negative regulation of transcription of the human cytokine IL-4. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1913–1918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozewicz S., Gomez E., Clague J., Gatland D., Davies R. J. Allergen-induced changes in the nasal mucous membrane in seasonal allergic rhinitis: effect of nedocromil sodium. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Jan;85(1 Pt 1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90233-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moqbel R., Barkans J., Bradley B. L., Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Application of monoclonal antibodies against major basic protein (BMK-13) and eosinophil cationic protein (EG1 and EG2) for quantifying eosinophils in bronchial biopsies from atopic asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Feb;22(2):265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb03082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser R., Fehr J., Bruijnzeel P. L. IL-4 controls the selective endothelium-driven transmigration of eosinophils from allergic individuals. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1432–1438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K. M., Jaunin F., Masouyé I., Saurat J. H., Hauser C. Th2 cells mediate IL-4-dependent local tissue inflammation. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 15;150(12):5576–5584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naclerio R. M., Proud D., Togias A. G., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Meyers D. A., Kagey-Sobotka A., Plaut M., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Inflammatory mediators in late antigen-induced rhinitis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 11;313(2):65–70. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507113130201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipkorn U., Proud D., Lichtenstein L. M., Schleimer R. P., Peters S. P., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Kagey-Sobotka A., Norman P. S., Naclerio R. M. Effect of short-term systemic glucocorticoid treatment on human nasal mediator release after antigen challenge. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):957–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI113188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Hamid Q., Bentley A., Ying S., Kay A. B., Durham S. R. Activation of CD4+ T cells, increased TH2-type cytokine mRNA expression, and eosinophil recruitment in bronchoalveolar lavage after allergen inhalation challenge in patients with atopic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Aug;92(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90175-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset F., Robert J., Andary M., Bonnin J. P., Souillet G., Chrétien I., Brière F., Pène J., de Vries J. E. Shifts in interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma production by T cells of patients with elevated serum IgE levels and the modulatory effects of these lymphokines on spontaneous IgE synthesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Jan;87(1 Pt 1):58–69. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleimer R. P., Sterbinsky S. A., Kaiser J., Bickel C. A., Klunk D. A., Tomioka K., Newman W., Luscinskas F. W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, McIntyre B. W. IL-4 induces adherence of human eosinophils and basophils but not neutrophils to endothelium. Association with expression of VCAM-1. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 15;148(4):1086–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Boulay J. L., Finkelman F., Barbier S., Ben-Sasson S. Z., Le Gros G., Paul W. E. CD8+ T cells can be primed in vitro to produce IL-4. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1652–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Paul W. E., Davis M. M., Fazekas de St Groth B. The presence of interleukin 4 during in vitro priming determines the lymphokine-producing potential of CD4+ T cells from T cell receptor transgenic mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1091–1098. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsicopoulos A., Hamid Q., Varney V., Ying S., Moqbel R., Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Preferential messenger RNA expression of Th1-type cells (IFN-gamma+, IL-2+) in classical delayed-type (tuberculin) hypersensitivity reactions in human skin. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2058–2061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varney V. A., Jacobson M. R., Sudderick R. M., Robinson D. S., Irani A. M., Schwartz L. B., Mackay I. S., Kay A. B., Durham S. R. Immunohistology of the nasal mucosa following allergen-induced rhinitis. Identification of activated T lymphocytes, eosinophils, and neutrophils. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):170–176. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga E. A., Snoek M., de Groot C., Chrétien I., Bos J. D., Jansen H. M., Kapsenberg M. L. Evidence for compartmentalization of functional subsets of CD2+ T lymphocytes in atopic patients. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4651–4656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying S., Durham S. R., Barkans J., Masuyama K., Jacobson M., Rak S., Löwhagen O., Moqbel R., Kay A. B., Hamid Q. A. T cells are the principal source of interleukin-5 mRNA in allergen-induced rhinitis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;9(4):356–360. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/9.4.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]