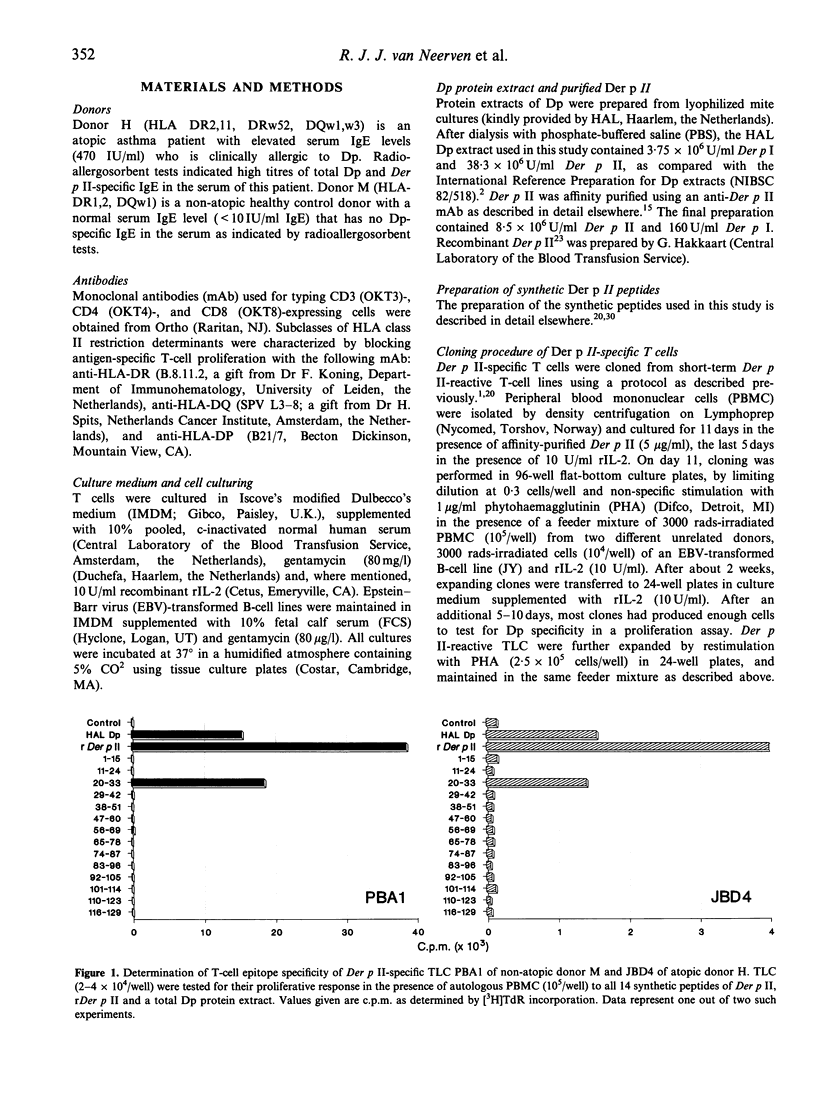
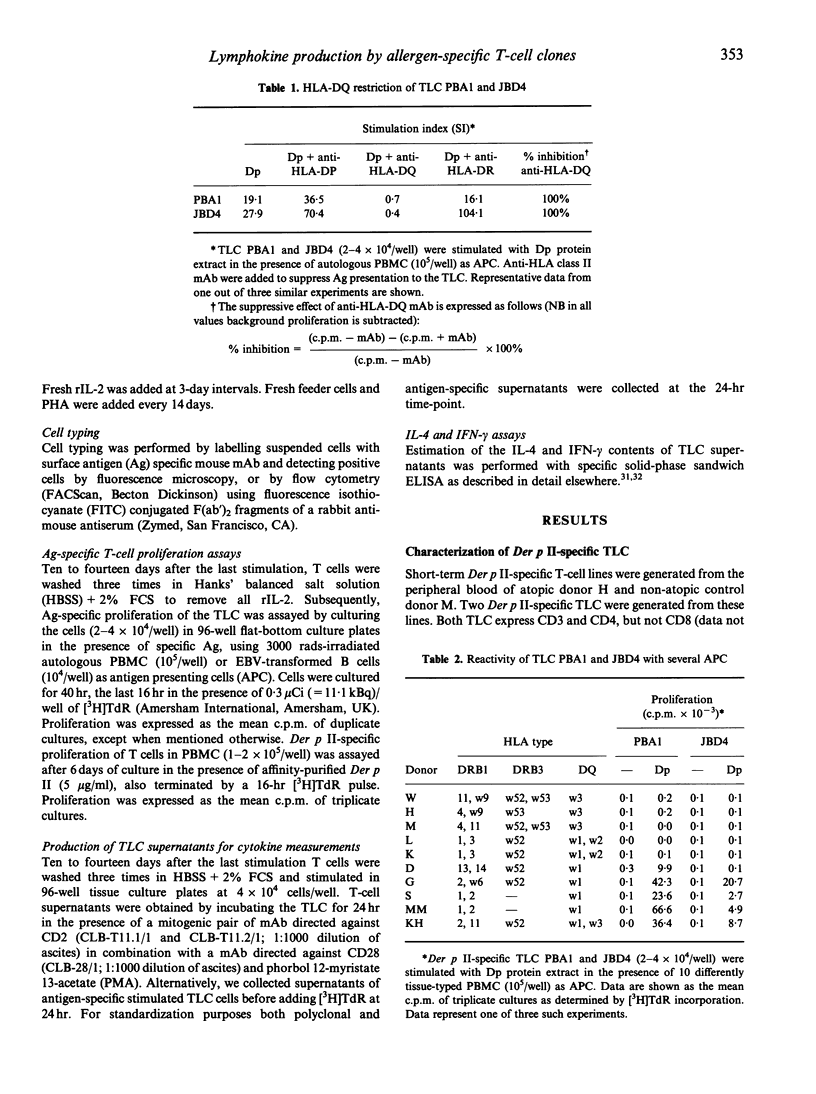
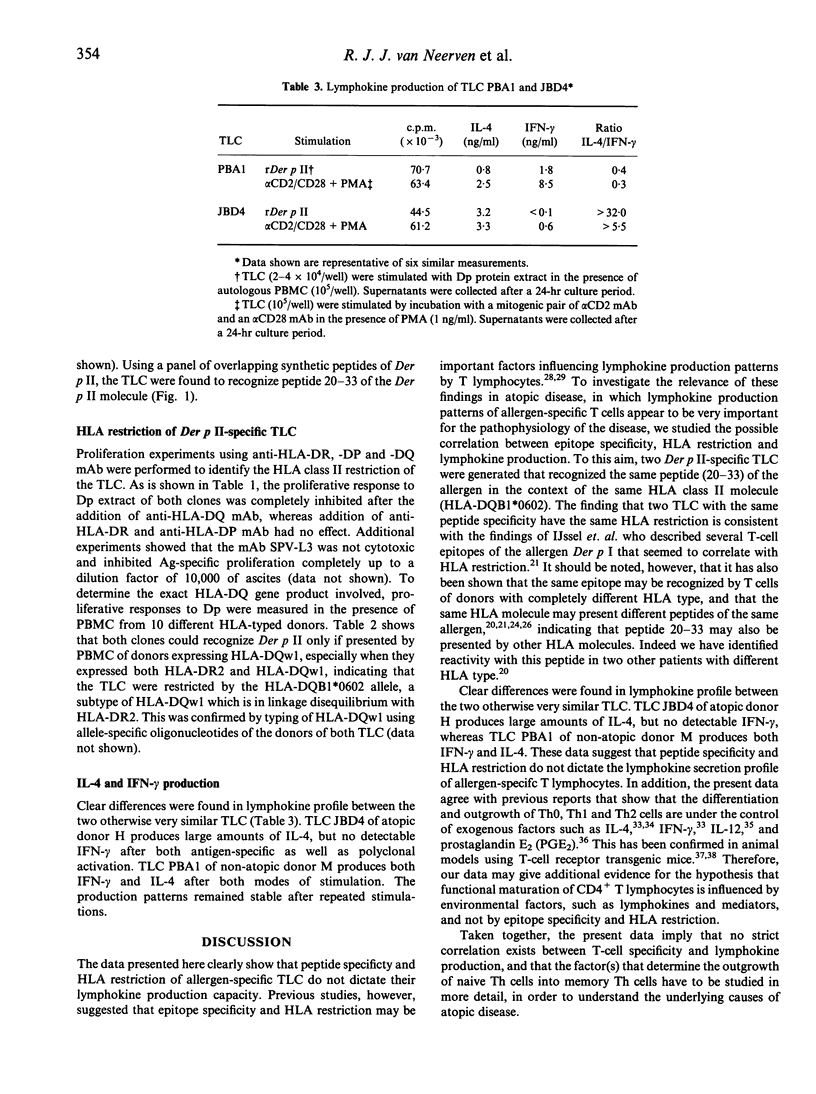
Abstract
Human and murine CD4+ T lymphocytes can be subdivided into distinct subsets [T-helper type 0 (Th0), Th1 or Th2], based on their lymphokine production profiles. Not much is known about the factors that determine these restricted lymphokine secretion profiles. Peptide specificity and human leucocyte antigen (HLA) restriction may be such factors. As it is well established that allergen-specific T lymphocytes from atopic individuals and non-atopic controls differ in their lymphokine secretion profile, we studied two allergen-specific T-lymphocyte clones (TLC) with identical peptide specificity and HLA restriction that were generated from the peripheral blood of an atopic donor and a non-atopic control donor. The two CD4+ TLC recognize the same epitope (20-33) of the house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus major allergen Der p II. Both TLC recognize the epitope in an HLA-DQB1*0602-restricted manner. However, the lymphokine production profiles of these TLC show clear differences after allergen-specific or polyclonal activation. As expected, TLC JBD4 from the atopic donor produced high levels of interleukin-4 (IL-4) without detectable interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), whereas TLC PBA1 from the non-atopic donor produced both IFN-gamma and IL-4 upon allergen-specific or polyclonal activation. Inasmuch as both TLC recognized the same epitope of Der p II in association with the same HLA-DQ molecule, these data suggest that peptide specificity and HLA restriction of human allergen-specific TLC do not dictate their lymphokine secretion profile.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abehsira-Amar O., Gibert M., Joliy M., Thèze J., Jankovic D. L. IL-4 plays a dominant role in the differential development of Tho into Th1 and Th2 cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3820–3829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carballido J. M., Carballido-Perrig N., Kägi M. K., Meloen R. H., Wüthrich B., Heusser C. H., Blaser K. T cell epitope specificity in human allergic and nonallergic subjects to bee venom phospholipase A2. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3582–3591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrétien I., Van Kimmenade A., Pearce M. K., Banchereau J., Abrams J. S. Development of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies for immunoassay and neutralization of human interleukin-4. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Feb 8;117(1):67–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua K. Y., Doyle C. R., Simpson R. J., Turner K. J., Stewart G. A., Thomas W. R. Isolation of cDNA coding for the major mite allergen Der p II by IgE plaque immunoassay. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;91(2):118–123. doi: 10.1159/000235101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua K. Y., Stewart G. A., Thomas W. R., Simpson R. J., Dilworth R. J., Plozza T. M., Turner K. J. Sequence analysis of cDNA coding for a major house dust mite allergen, Der p 1. Homology with cysteine proteases. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):175–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Ohara J., Bond M. W., Carty J., Zlotnik A., Paul W. E. B cell stimulatory factor-1 enhances the IgE response of lipopolysaccharide-activated B cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4538–4541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G. F., De Carli M., D'Elios M. M., Maestrelli P., Ricci M., Fabbri L., Romagnani S. Allergen exposure induces the activation of allergen-specific Th2 cells in the airway mucosa of patients with allergic respiratory disorders. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1445–1449. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham S. R., Ying S., Varney V. A., Jacobson M. R., Sudderick R. M., Mackay I. S., Kay A. B., Hamid Q. A. Cytokine messenger RNA expression for IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, and granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor in the nasal mucosa after local allergen provocation: relationship to tissue eosinophilia. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2390–2394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner C., Szépfalusi Z., Ferreira F., Jilek A., Valenta R., Parronchi P., Maggi E., Romagnani S., Scheiner O., Kraft D. Identification of multiple T cell epitopes on Bet v I, the major birch pollen allergen, using specific T cell clones and overlapping peptides. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):1047–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann P. W., Chapman M. D., Aalberse R. C., Fox J. W., Platts-Mills T. A. Antigenic and structural analysis of group II allergens (Der f II and Der p II) from house dust mites (Dermatophagoides spp). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 Jun;83(6):1055–1067. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90447-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. S., Heimberger A. B., Gold J. S., O'Garra A., Murphy K. M. Differential regulation of T helper phenotype development by interleukins 4 and 10 in an alpha beta T-cell-receptor transgenic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6065–6069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost van Neerven R., van t'Hof W., Ringrose J. H., Jansen H. M., Aalberse R. C., Wierenga E. A., Kapsenberg M. L. T cell epitopes of house dust mite major allergen Der p II. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):2326–2335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Ying S., Varney V., Gaga M., Durham S. R., Moqbel R., Wardlaw A. J., Hamid Q. Messenger RNA expression of the cytokine gene cluster, interleukin 3 (IL-3), IL-4, IL-5, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, in allergen-induced late-phase cutaneous reactions in atopic subjects. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):775–778. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krilis S., Baldo B. A., Basten A. Antigens and allergens from the common house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Part II. Identification of the major IgE-binding antigens by crossed radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Aug;74(2):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi E., Parronchi P., Manetti R., Simonelli C., Piccinni M. P., Rugiu F. S., De Carli M., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Reciprocal regulatory effects of IFN-gamma and IL-4 on the in vitro development of human Th1 and Th2 clones. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2142–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manetti R., Parronchi P., Giudizi M. G., Piccinni M. P., Maggi E., Trinchieri G., Romagnani S. Natural killer cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12 [IL-12]) induces T helper type 1 (Th1)-specific immune responses and inhibits the development of IL-4-producing Th cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1199–1204. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. S., Madri J., Tite J., Carding S. R., Bottomly K. MHC control of CD4+ T cell subset activation. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2135–2140. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hehir R. E., Eckels D. D., Frew A. J., Kay A. B., Lamb J. R. MHC class II restriction specificity of cloned human T lymphocytes reactive with Dermatophagoides farinae (house dust mite). Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):627–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hehir R. E., Verhoef A., Panagiotopoulou E., Keswani S., Hayball J. D., Thomas W. R., Lamb J. R. Analysis of human T cell responses to the group II allergen of Dermatophagoides species: localization of major antigenic sites. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Jul;92(1 Pt 1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90044-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hehir R. E., Young D. B., Kay A. B., Lamb J. R. Cloned human T lymphocytes reactive with Dermatophagoides farinae (house dust mite): a comparison of T- and B-cell antigen recognition. Immunology. 1987 Dec;62(4):635–640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parronchi P., Macchia D., Piccinni M. P., Biswas P., Simonelli C., Maggi E., Ricci M., Ansari A. A., Romagnani S. Allergen- and bacterial antigen-specific T-cell clones established from atopic donors show a different profile of cytokine production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punnonen J., Aversa G., Cocks B. G., McKenzie A. N., Menon S., Zurawski G., de Waal Malefyt R., de Vries J. E. Interleukin 13 induces interleukin 4-independent IgG4 and IgE synthesis and CD23 expression by human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3730–3734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Bonnefoy J. Y., Spits H., Yokota T., Arai N., Arai K., Banchereau J. IgE production by normal human lymphocytes is induced by interleukin 4 and suppressed by interferons gamma and alpha and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6880–6884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawle F. C., Mitchell E. B., Platts-Mills T. A. T cell responses to the major allergen from the house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Antigen P1: comparison of patients with asthma, atopic dermatitis, and perennial rhinitis. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):195–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. S., Hamid Q., Ying S., Tsicopoulos A., Barkans J., Bentley A. M., Corrigan C., Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Predominant TH2-like bronchoalveolar T-lymphocyte population in atopic asthma. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 30;326(5):298–304. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201303260504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Paul W. E., Davis M. M., Fazekas de St Groth B. The presence of interleukin 4 during in vitro priming determines the lymphokine-producing potential of CD4+ T cells from T cell receptor transgenic mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1091–1098. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):944–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3107127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijdewint F. G., Kaliński P., Wierenga E. A., Bos J. D., Kapsenberg M. L. Prostaglandin E2 differentially modulates cytokine secretion profiles of human T helper lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 15;150(12):5321–5329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway P., Fish S., Passmore H., Gefter M., Coffee R., Manser T. Regulation of the immune response to peptide antigens: differential induction of immediate-type hypersensitivity and T cell proliferation due to changes in either peptide structure or major histocompatibility complex haplotype. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):847–858. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. A., Thompson P. J., Simpson R. J. Protease antigens from house dust mite. Lancet. 1989 Jul 15;2(8655):154–155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meide P. H., Dubbeld M., Schellekens H. Monoclonal antibodies to human immune interferon and their use in a sensitive solid-phase ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1985 May 23;79(2):293–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga E. A., Backx B., Snoek M., Koenderman L., Kapsenberg M. L. Relative contributions of human types 1 and 2 T-helper cell-derived eosinophilotrophic cytokines to development of eosinophilia. Blood. 1993 Sep 1;82(5):1471–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga E. A., Snoek M., Bos J. D., Jansen H. M., Kapsenberg M. L. Comparison of diversity and function of house dust mite-specific T lymphocyte clones from atopic and non-atopic donors. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jul;20(7):1519–1526. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga E. A., Snoek M., de Groot C., Chrétien I., Bos J. D., Jansen H. M., Kapsenberg M. L. Evidence for compartmentalization of functional subsets of CD2+ T lymphocytes in atopic patients. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4651–4656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., Johnson K. E., Schneider P. V., Wideman J., Terr A., Kastelein R., De Vries J. E. T cell activation-inducing epitopes of the house dust mite allergen Der p I. Proliferation and lymphokine production patterns by Der p I-specific CD4+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):738–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van 't Hof W., Driedijk P. C., van den Berg M., Beck-Sickinger A. G., Jung G., Aalberse R. C. Epitope mapping of the Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus house dust mite major allergen Der p II using overlapping synthetic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1991 Nov;28(11):1225–1232. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijden F. L., Wierenga E. A., Bos J. D., Kapsenberg M. L. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Sep;97(3):389–394. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12480966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


