Abstract
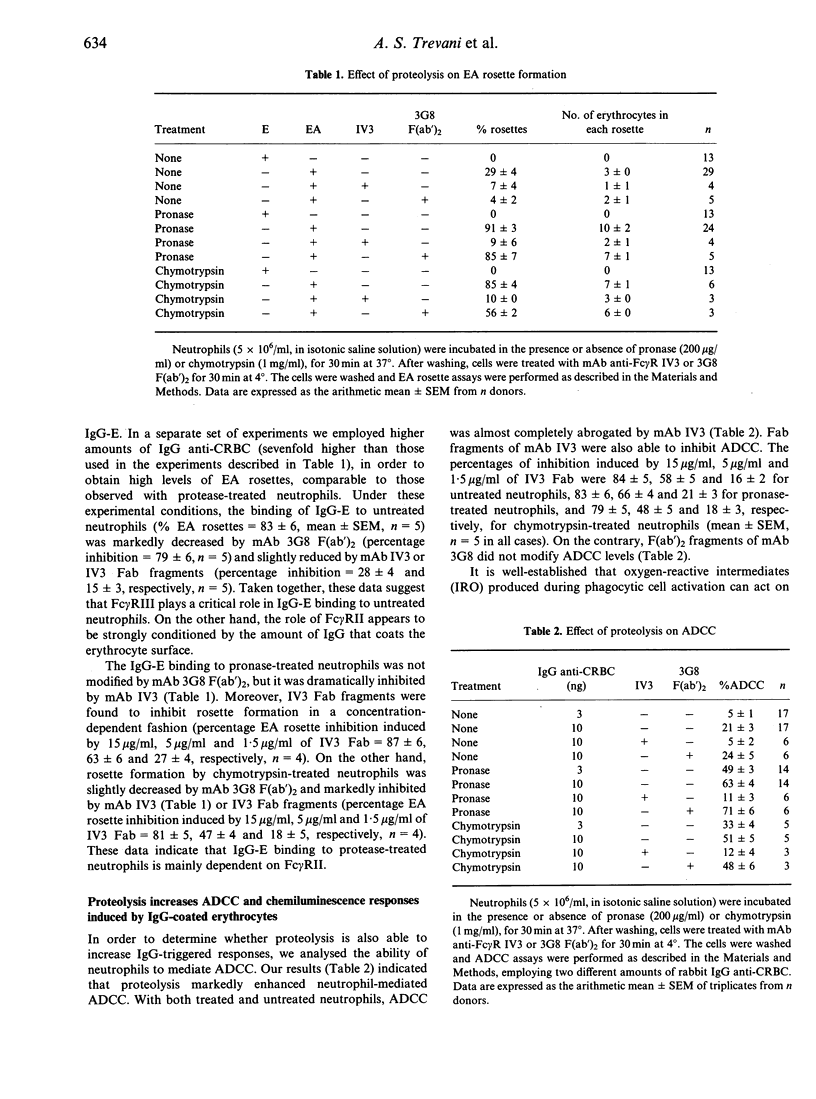
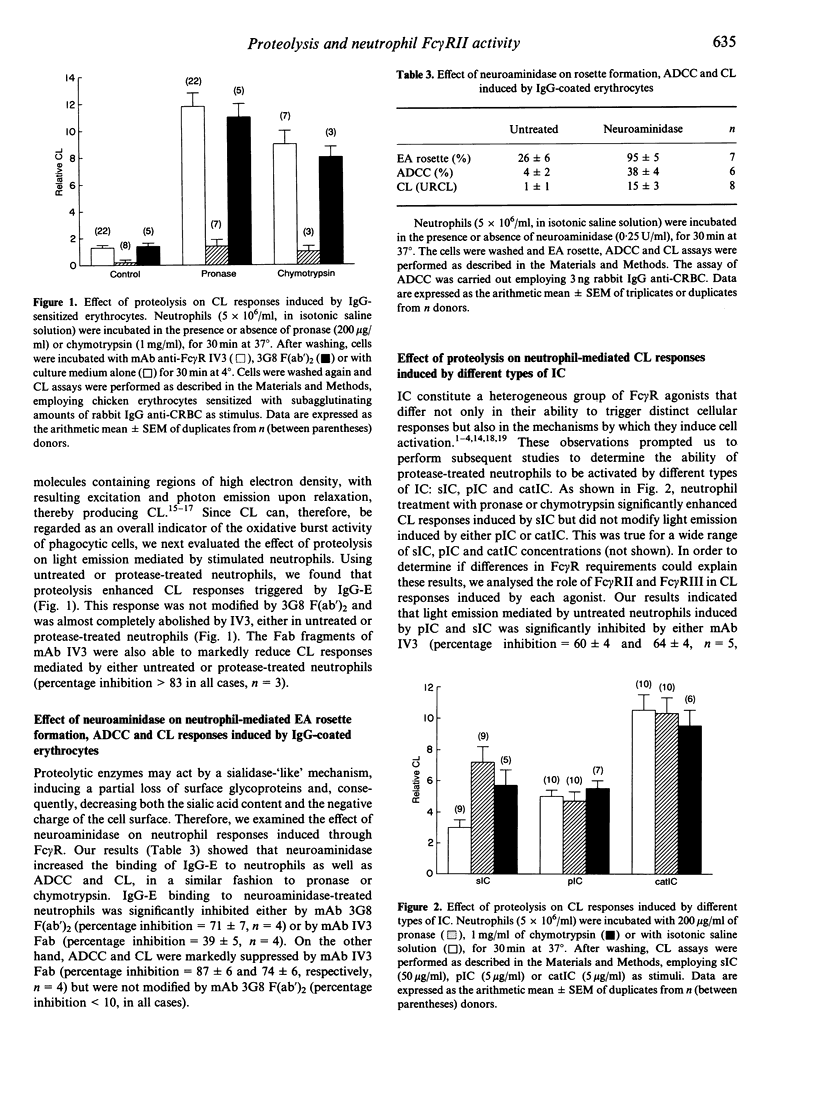
Previous studies have demonstrated that the treatment of neutrophils with proteolytic enzymes markedly reduces the expression of receptor III for the Fc portion of IgG (Fc gamma RIII), but it does not affect the number of Fc gamma RII on the cell surface. In the present study, we analysed the effect of proteolytic enzymes on functional responses of neutrophils induced by immune complexes (IC). Our results showed that treatment with pronase or chymotrypsin markedly increased the binding of IgG-coated erythrocytes (IgG-E) to neutrophils, as well as their capability to display IgG-mediated functions such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and chemiluminescence (CL) induced by IgG-E, responses that have been shown to be completely dependent on Fc gamma RII. A similar enhancing effect was observed, in all cases, after neutrophil treatment with neuroaminidase. We also studied the effect of proteolysis on neutrophil activation induced by other types of IC. It was found that pronase and chymotrypsin significantly enhanced CL responses induced by soluble IC (sIC) but did not modify the responses induced by either precipitating IC (pIC) or soluble IC prepared with cationized antibodies (catIC). On the other hand, neuroaminidase significantly enhanced CL induced by either sIC, pIC or catIC. Taken together, our data suggest that the activity of Fc gamma RII can be up-regulated by proteolysis. However, this effect appears to be strongly dependent on the characteristics of the IC employed as stimulus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheson B. D., Christensen R. L., Sperling R., Kohler B. E., Babior B. M. The origin of the chemiluminescence of phagocytosing granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI108530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K., Archibald A. C., Robinson M. F. The origin of chemiluminescence produced by neutrophils stimulated by opsonized zymosan. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2324–2329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debets J. M., Van de Winkel J. G., Ceuppens J. L., Dieteren I. E., Buurman W. A. Cross-linking of both Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RII induces secretion of tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes, requiring high affinity Fc-Fc gamma R interactions. Functional activation of Fc gamma RII by treatment with proteases or neuraminidase. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1304–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Kuhnle M. Biochemical characterization of an Fc gamma receptor purified from human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3120–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier V. J., Mannik M., Striker G. E. Effect of cationized antibodies in performed immune complexes on deposition and persistence in renal glomeruli. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):766–777. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffner J. R., Giordano M., Serebrinsky G., Isturiz M. A. Different activation pathways involved in antibody-dependent and immune-complexes-triggered cytotoxicity mediated by neutrophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Dec;74(3):471–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffner J. R., Trevani A. S., Malchiodi E., Serebrinsky G. P., Isturiz M. A. Neutrophil cytotoxicity induced by immune complexes prepared with cationized antibodies. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Feb;37(2):187–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffner J. R., Trevani A. S., Minnucci F., Palermo M. S., Maugeri N., Isturiz M. A. Extracellular acidic pH modulates oxygen-dependent cytotoxic responses mediated by polymorphonuclear leucocytes and monocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):164–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricks P. A., van Erne-van der Tol M. E., Verhoef J. Partial removal of sialic acid enhances phagocytosis and the generation of superoxide and chemiluminescence by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):745–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga T. W., van Kemenade F., Koenderman L., Dolman K. M., von dem Borne A. E., Tetteroo P. A., Roos D. The 40-kDa Fc gamma receptor (FcRII) on human neutrophils is essential for the IgG-induced respiratory burst and IgG-induced phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2365–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundt M., Schmidt R. E. The glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked Fc gamma receptor III represents the dominant receptor structure for immune complex activation of neutrophils. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Mar;22(3):811–816. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman M. A., Weed R. I. Electrophoretic mobility and N-acetyl neuraminic acid content of human normal and leukemic lymphocytes and granulocytes. Blood. 1970 Jan;35(1):12–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax W. J., van de Winkel J. G. Human Fc gamma receptor II: a standby receptor activated by proteolysis? Immunol Today. 1990 Sep;11(9):308–310. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90125-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M. F., Berger M. Functional differences between the 40 kDa and 50 to 70 kDa IgG Fc receptors on human neutrophils revealed by elastase treatment and antireceptor antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2097–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Function and heterogeneity of human Fc receptors for immunoglobulin G. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):355–361. doi: 10.1172/JCI113891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Action of sphingomyelinase C and other lipid-specific agents as inhibitors of Fc binding and locomotion in human leucocytes. Immunology. 1977 Sep;33(3):407–412. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Capel P. J. Human IgG Fc receptor heterogeneity: molecular aspects and clinical implications. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90166-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., van Ommen R., Huizinga T. W., de Raad M. A., Tuijnman W. B., Groenen P. J., Capel P. J., Koene R. A., Tax W. J. Proteolysis induces increased binding affinity of the monocyte type II FcR for human IgG. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


