Abstract
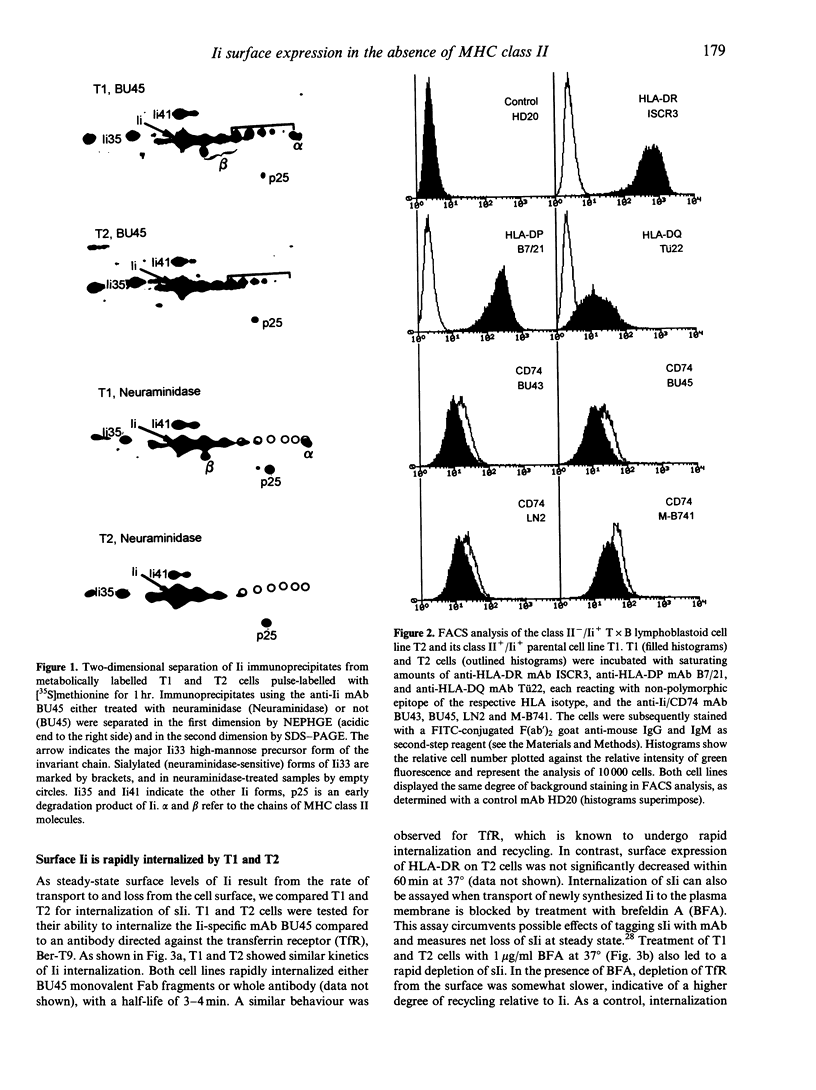
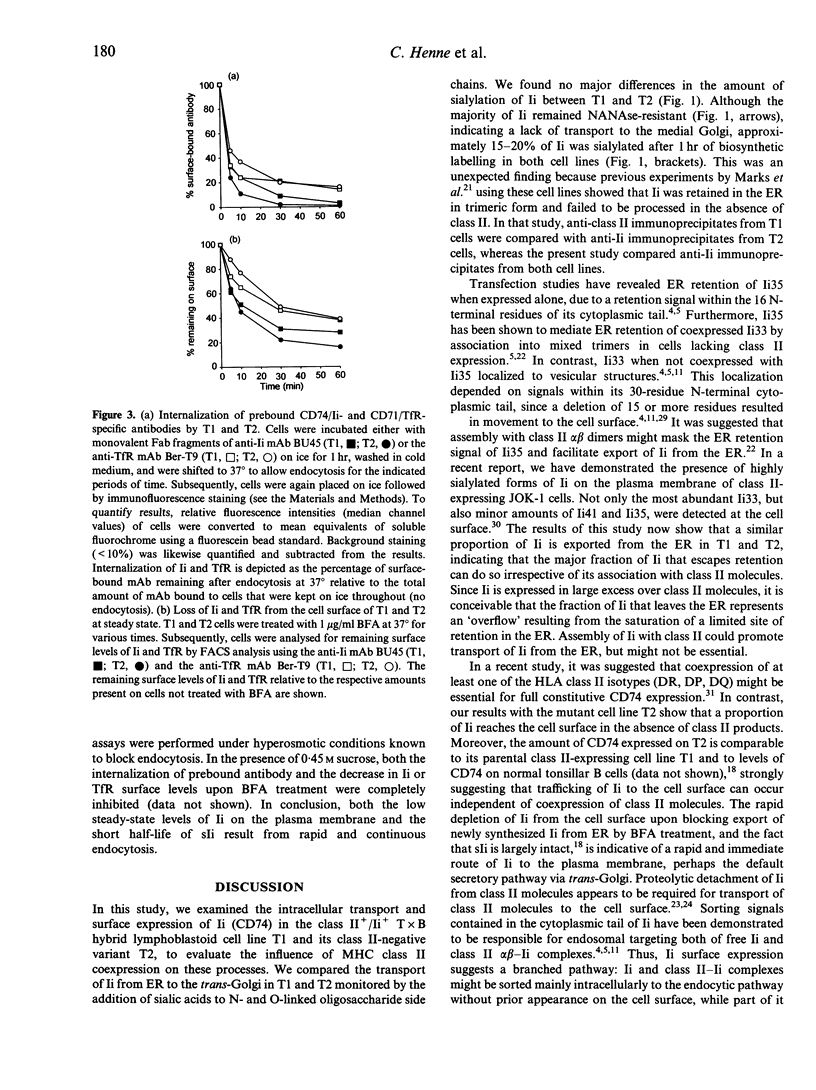
Whether or not intracellular transport and surface expression of the invariant chain (Ii; CD74) occurs independent of the presence of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules was examined by comparing the class II-negative mutant lymphoblastoid cell line 174 x CEM.T2 (T2) and its class II-positive parental cell line 174 x CEM.T1 (T1). We found a similar proportion of Ii being transported to the Golgi complex in T1 and T2, as monitored by the degree of sialic acid addition to glycan side chains of Ii. In agreement with this result, T1 and T2 expressed comparable amounts of Ii at the cell surface, as measured by flow cytometry. This indicates that, although not associated with class II molecules, a proportion of Ii is transported to the plasma membrane. Both in T1 and T2, surface Ii (sIi) was rapidly internalized with a half-life of 3-4 min, suggesting that some Ii enters the endocytic route via the cell surface after being internalized. Our data demonstrate transport of Ii on a route alternative to the endocytic pathway. This alternative route could also account for delivery of newly synthesized class II-Ii complexes to processing compartments in antigen-presenting cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakke O., Dobberstein B. MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains a sorting signal for endosomal compartments. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J. S., Cresswell P. Role for intracellular proteases in the processing and transport of class II HLA antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3975–3979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cresswell P. Intracellular class II HLA antigens are accessible to transferrin-neuraminidase conjugates internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8188–8192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Hendrix L. R. MHC class II structure, occupancy and surface expression determined by post-endoplasmic reticulum antigen binding. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):134–139. doi: 10.1038/353134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Margulies D. H. The biochemistry and cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:403–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter C., Mellman I. Transport of the lysosomal membrane glycoprotein lgp120 (lgp-A) to lysosomes does not require appearance on the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):311–325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch N., Moldenhauer G., Hofmann W. J., Möller P. Rapid intracellular pathway gives rise to cell surface expression of the MHC class II-associated invariant chain (CD74). J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2643–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb C. A., Cresswell P. Assembly and transport properties of invariant chain trimers and HLA-DR-invariant chain complexes. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3478–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb C. A., Yewdell J. W., Bennink J. R., Cresswell P. Invariant chain targets HLA class II molecules to acidic endosomes containing internalized influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5998–6002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. A novel di-leucine motif and a tyrosine-based motif independently mediate lysosomal targeting and endocytosis of CD3 chains. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1143–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90636-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loss G. E., Jr, Sant A. J. Invariant chain retains MHC class II molecules in the endocytic pathway. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3187–3197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotteau V., Teyton L., Peleraux A., Nilsson T., Karlsson L., Schmid S. L., Quaranta V., Peterson P. A. Intracellular transport of class II MHC molecules directed by invariant chain. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):600–605. doi: 10.1038/348600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Cresswell P. Biosynthesis and glycosylation of the invariant chain associated with HLA-DR antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2564–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Cresswell P. Monensin prevents terminal glycosylation of the N- and O-linked oligosaccharides of the HLA-DR-associated invariant chain and inhibits its dissociation from the alpha-beta chain complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1287–1291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Blum J. S., Cresswell P. Invariant chain trimers are sequestered in the rough endoplasmic reticulum in the absence of association with HLA class II antigens. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):839–855. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Ploegh H. L. Inhibition of endosomal proteolytic activity by leupeptin blocks surface expression of MHC class II molecules and their conversion to SDS resistance alpha beta heterodimers in endosomes. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):411–416. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05069.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Stollorz V., Peters P. J., Geuze H. J., Ploegh H. L. The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb J. R., Cresswell P. Characterization of endogenous peptides bound to purified HLA-DR molecules and their absence from invariant chain-associated alpha beta dimers. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):499–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan D. M., Noonan D., Quaranta V. Four Ia invariant chain forms derive from a single gene by alternate splicing and alternate initiation of transcription/translation. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):444–460. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieters J., Bakke O., Dobberstein B. The MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains two endosomal targeting signals within its cytoplasmic tail. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):831–846. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P. A., Watts C. Constitutive endocytosis and recycling of major histocompatibility complex class II glycoproteins in human B-lymphoblastoid cells. Immunology. 1992 Dec;77(4):539–542. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Cresswell P. Invariant chain association with HLA-DR molecules inhibits immunogenic peptide binding. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):615–618. doi: 10.1038/345615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Cresswell P. Proteolysis of the class II-associated invariant chain generates a peptide binding site in intracellular HLA-DR molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3150–3154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Teletski C. L., Karp D. R., Pinet V., Bakke O., Long E. O. Stable surface expression of invariant chain prevents peptide presentation by HLA-DR. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2841–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Teletski C. L., Stang E., Bakke O., Long E. O. Cell surface HLA-DR-invariant chain complexes are targeted to endosomes by rapid internalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8581–8585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Cresswell P. Impaired assembly and transport of HLA-A and -B antigens in a mutant TxB cell hybrid. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):943–949. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Berte C., Mach B. Alternative splicing and alternative initiation of translation explain the four forms of the Ia antigen-associated invariant chain. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3483–3488. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teyton L., O'Sullivan D., Dickson P. W., Lotteau V., Sette A., Fink P., Peterson P. A. Invariant chain distinguishes between the exogenous and endogenous antigen presentation pathways. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):39–44. doi: 10.1038/348039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Suzuki T., Taniguchi M., Shinohara N. Monoclonal anti-Ia murine alloantibodies crossreactive with the Ia-homologues of other mammalian species including humans. Transplantation. 1983 Dec;36(6):712–718. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198336060-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. M., Labeta M. O., Pawelec G., Fernandez N. Cell-surface expression of human histocompatibility leucocyte antigen (HLA) class II-associated invariant chain (CD74) does not always correlate with cell-surface expression of HLA class II molecules. Immunology. 1993 Jun;79(2):331–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraight C. J., van Endert P., Möller P., Lipp J., Ling N. R., MacLennan I. C., Koch N., Moldenhauer G. Human major histocompatibility complex class II invariant chain is expressed on the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5787–5792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


