Abstract
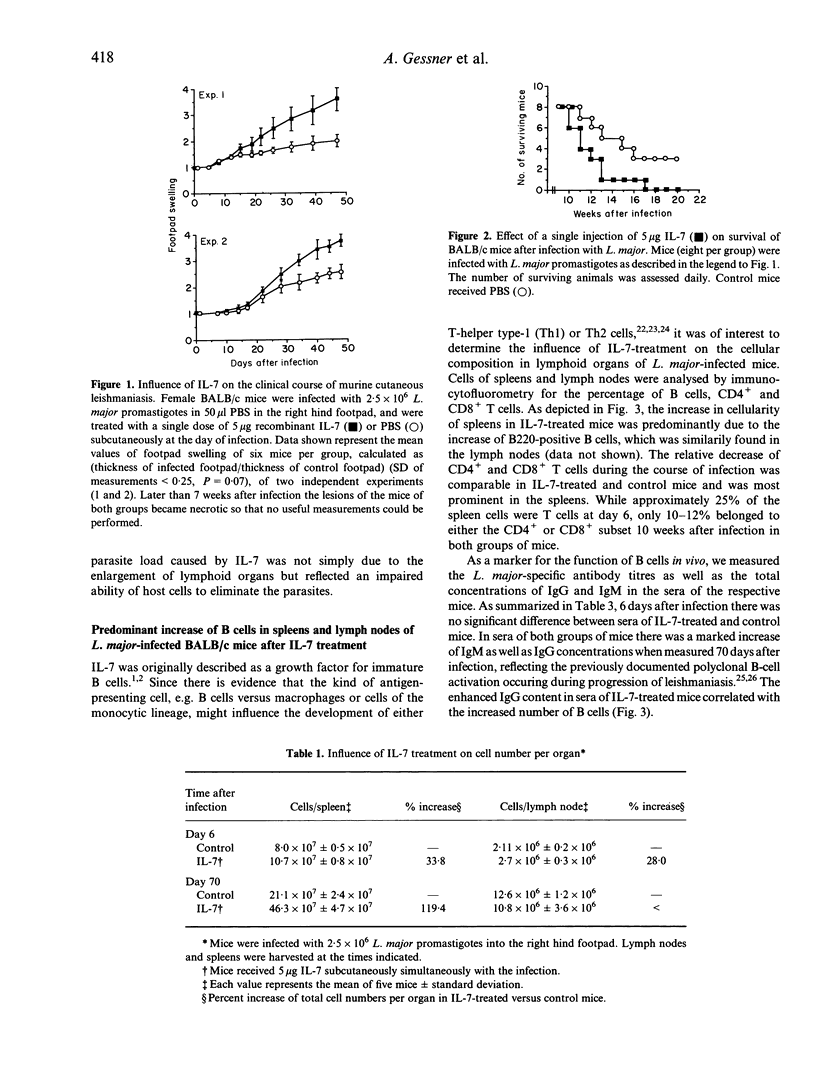
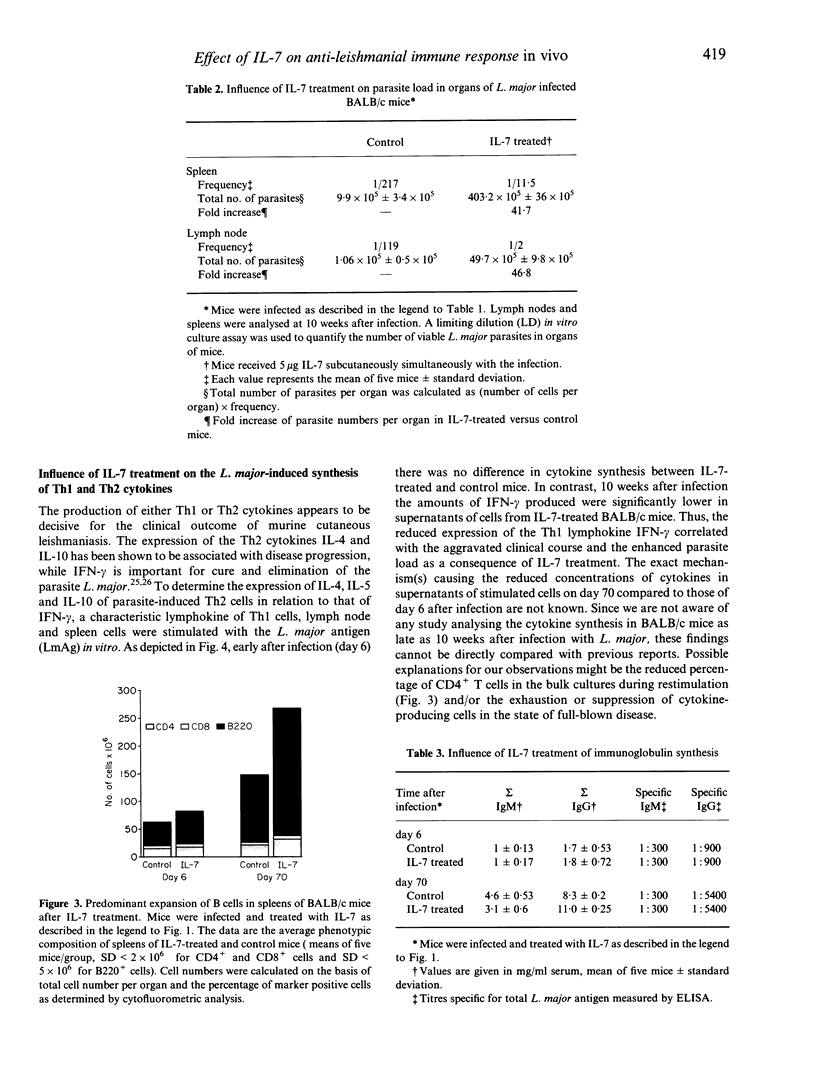
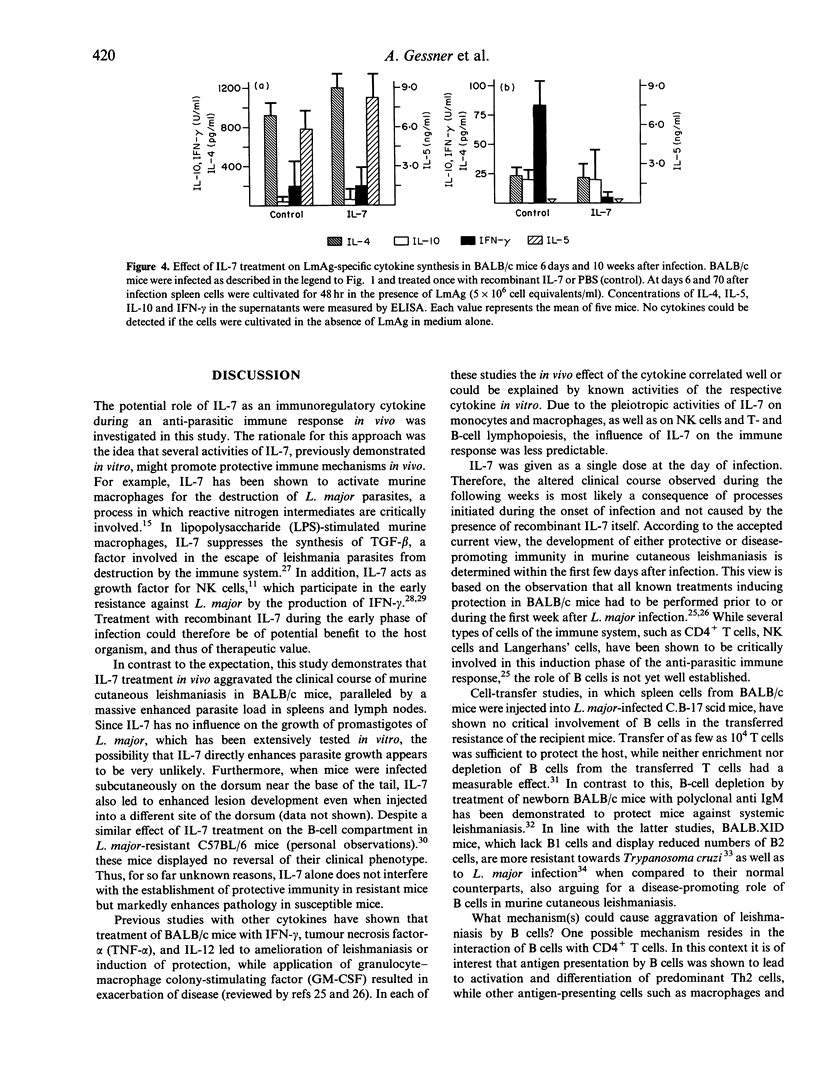
The effect of recombinant interleukin-7 (IL-7) on the clinical course of murine leishmaniasis and the development of the accompanying immune response was investigated. Previously, IL-7 has been shown to possess stimulatory capacity for different cell types of the immune and haematopoietic system critically involved in the defence against Leishmania major (L. major), such as macrophages which are activated for the elimination of the parasite by IL-7. In contrast to these in vitro data, the present study indicates that treatment of genetically susceptible BALB/c mice with IL-7 at the onset of the infection leads to enhanced lesion development and a significantly accelerated death of the animals. This was correlated with a 40-fold increased parasite burden in spleens and lymph nodes. While the specific antibody response against L. major was not altered and lymphocytes of IL-7-treated mice produced comparable amounts of the T-helper type-2 (Th2) cytokines IL-4 and IL-10, less interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) was measurable after antigenic stimulation of lymph node and spleen cells in vitro. One of the major changes appearing by the first week after infection in IL-7-treated mice was the increase of the total cell number in spleen and lymph nodes draining the local infection. Analysis of the cellular composition revealed that the enhanced cellularity was predominantly due to a rise in the B-cell compartment. Since antigen presentation by B cells has been implicated in the development of Th2 cells, the disease-aggravating activity of IL-7 is thought to be primarily due to augmentation of B lymphopoiesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderson M. R., Sassenfeld H. M., Widmer M. B. Interleukin 7 enhances cytolytic T lymphocyte generation and induces lymphokine-activated killer cells from human peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):577–587. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderson M. R., Tough T. W., Ziegler S. F., Grabstein K. H. Interleukin 7 induces cytokine secretion and tumoricidal activity by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):923–930. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barral-Netto M., Barral A., Brownell C. E., Skeiky Y. A., Ellingsworth L. R., Twardzik D. R., Reed S. G. Transforming growth factor-beta in leishmanial infection: a parasite escape mechanism. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.1636092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Gessner A., Röllinghoff M. Cytokines in leishmaniasis: a complex network of stimulatory and inhibitory interactions. Immunobiology. 1993 Nov;189(3-4):356–396. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80366-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Schröppel K., Lohoff M., Röllinghoff M., Solbach W. Immunization of susceptible hosts with a soluble antigen fraction from Leishmania major leads to aggravation of murine leishmaniasis mediated by CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2533–2540. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chazen G. D., Pereira G. M., LeGros G., Gillis S., Shevach E. M. Interleukin 7 is a T-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5923–5927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon P. J., Morrissey P. J., Nordan R. P., Grabstein K. H., Prickett K. S., Reed S. G., Goodwin R., Cosman D., Namen A. E. Murine thymocytes proliferate in direct response to interleukin-7. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1368–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinett S. M., Huang M., Dhanani S., Wang J., Beroiza T. Down-regulation of macrophage transforming growth factor-beta messenger RNA expression by IL-7. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6670–6680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Pinnas M., Wong T., Fitch F. W. Murine Th1 and Th2 clones proliferate optimally in response to distinct antigen-presenting cell populations. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1750–1758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner A., Blum H., Röllinghoff M. Differential regulation of IL-9-expression after infection with Leishmania major in susceptible and resistant mice. Immunobiology. 1993 Dec;189(5):419–435. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80414-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner A., Moskophidis D., Lehmann-Grube F. Enumeration of single IFN-gamma-producing cells in mice during viral and bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1293–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner A., Vieth M., Will A., Schröppel K., Röllinghoff M. Interleukin-7 enhances antimicrobial activity against Leishmania major in murine macrophages. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):4008–4012. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.4008-4012.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Lupton S., Schmierer A., Hjerrild K. J., Jerzy R., Clevenger W., Gillis S., Cosman D., Namen A. E. Human interleukin 7: molecular cloning and growth factor activity on human and murine B-lineage cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabstein K. H., Namen A. E., Shanebeck K., Voice R. F., Reed S. G., Widmer M. B. Regulation of T cell proliferation by IL-7. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3015–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabstein K. H., Waldschmidt T. J., Finkelman F. D., Hess B. W., Alpert A. R., Boiani N. E., Namen A. E., Morrissey P. J. Inhibition of murine B and T lymphopoiesis in vivo by an anti-interleukin 7 monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1993 Jul 1;178(1):257–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman C. J., Crim J. A., Mostowski H. S., Siegel J. P. Regulation of human cytotoxic T lymphocyte development by IL-7. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2415–2420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoerauf A., Solbach W., Lohoff M., Röllinghoff M. The Xid defect determines an improved clinical course of murine leishmaniasis in susceptible mice. Int Immunol. 1994 Aug;6(8):1117–1124. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.8.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. S., Macatonia S. E., O'Garra A., Murphy K. M. Pathogen-induced Th1 phenotype development in CD4+ alpha beta-TCR transgenic T cells is macrophage dependent. Int Immunol. 1993 Apr;5(4):371–382. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.4.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jicha D. L., Mulé J. J., Rosenberg S. A. Interleukin 7 generates antitumor cytotoxic T lymphocytes against murine sarcomas with efficacy in cellular adoptive immunotherapy. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1511–1515. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskay T., Röllinghoff M., Solbach W. Natural killer cells participate in the early defense against Leishmania major infection in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2237–2241. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minoprio P., Coutinho A., Spinella S., Hontebeyrie-Joskowicz M. Xid immunodeficiency imparts increased parasite clearance and resistance to pathology in experimental Chagas' disease. Int Immunol. 1991 May;3(5):427–433. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.5.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey P. J., Conlon P., Charrier K., Braddy S., Alpert A., Williams D., Namen A. E., Mochizuki D. Administration of IL-7 to normal mice stimulates B-lymphopoiesis and peripheral lymphadenopathy. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey P. J., Goodwin R. G., Nordan R. P., Anderson D., Grabstein K. H., Cosman D., Sims J., Lupton S., Acres B., Reed S. G. Recombinant interleukin 7, pre-B cell growth factor, has costimulatory activity on purified mature T cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):707–716. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namen A. E., Lupton S., Hjerrild K., Wignall J., Mochizuki D. Y., Schmierer A., Mosley B., March C. J., Urdal D., Gillis S. Stimulation of B-cell progenitors by cloned murine interleukin-7. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):571–573. doi: 10.1038/333571a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naume B., Espevik T. Effects of IL-7 and IL-2 on highly enriched CD56+ natural killer cells. A comparative study. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2208–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Scott P. T-cell and cytokine responses in leishmaniasis. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Aug;5(4):524–531. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90033-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi-Bergmann B., Müller I., Godinho E. B. TH1 and TH2 T-cell subsets are differentially activated by macrophages and B cells in murine leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2266–2269. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2266-2269.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Scott P. A., Asofsky R., Sher F. A. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in anti-IgM-treated mice: enhanced resistance due to functional depletion of a B cell-dependent T cell involved in the suppressor pathway. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2072–2077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharton T. M., Scott P. Natural killer cells are a source of interferon gamma that drives differentiation of CD4+ T cell subsets and induces early resistance to Leishmania major in mice. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):567–577. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solbach W., Forberg K., Röllinghoff M. Effect of T-lymphocyte suppression on the parasite burden in Leishmania major-infected, genetically susceptible BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):909–912. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.909-912.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Marchand M., Boon T., Louis J. A. A limiting dilution assay for quantifying Leishmania major in tissues of infected mice. Parasite Immunol. 1985 Sep;7(5):545–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varkila K., Chatelain R., Leal L. M., Coffman R. L. Reconstitution of C.B-17 scid mice with BALB/c T cells initiates a T helper type-1 response and renders them capable of healing Leishmania major infection. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jan;23(1):262–268. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. D., Morrissey P. J., Namen A. E., Conlon P. J., Widmer M. B. Effect of IL-7 on the growth of fetal thymocytes in culture. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1215–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Tough T. W., Franklin T. L., Armitage R. J., Alderson M. R. Induction of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 beta gene expression in human monocytes by lipopolysaccharide and IL-7. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2234–2239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


