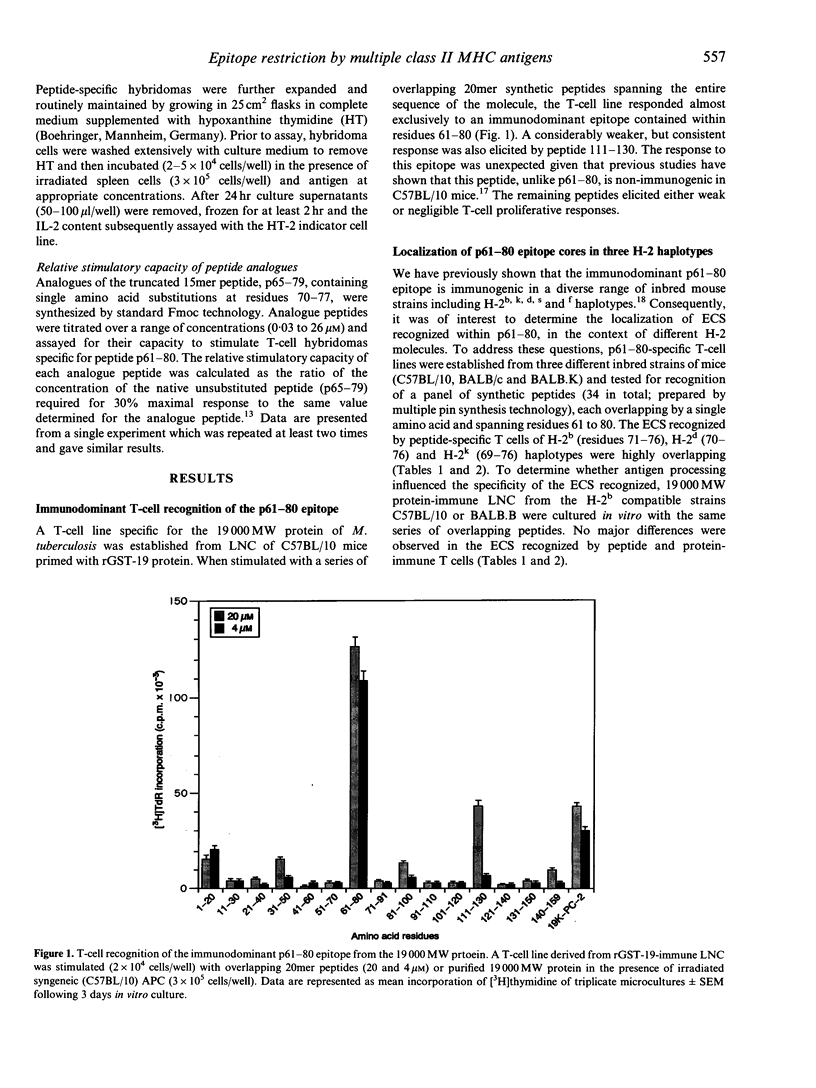
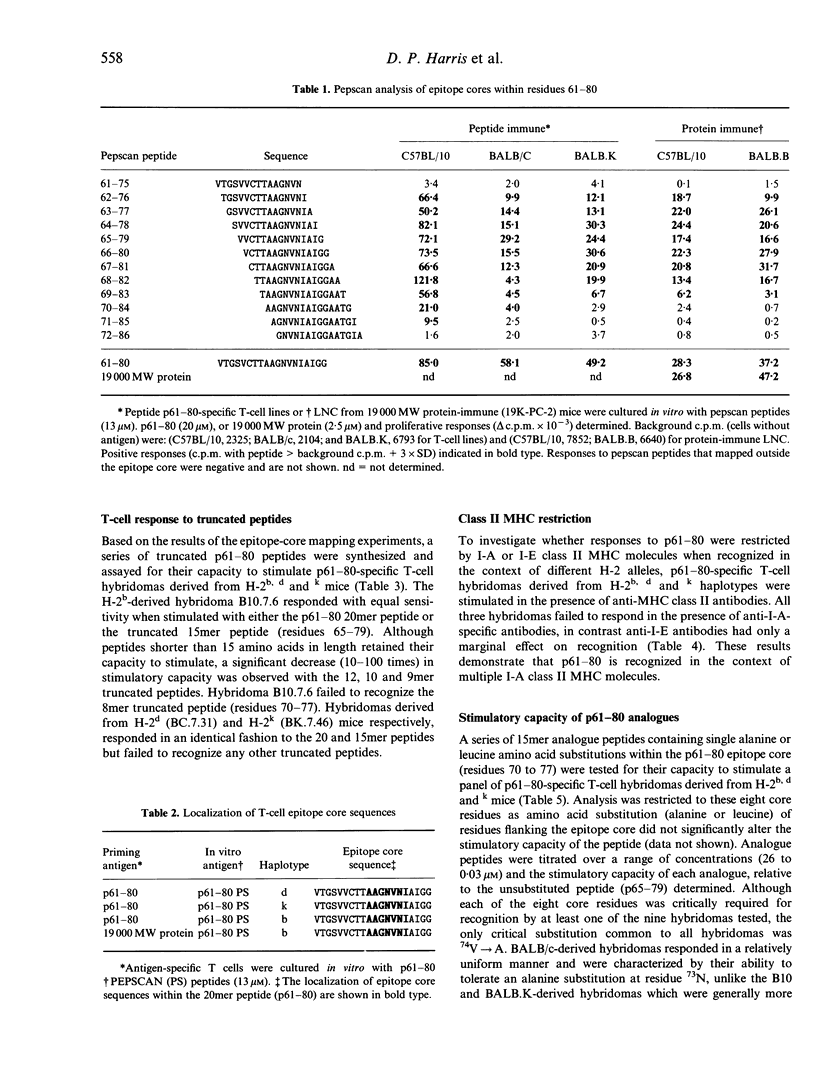
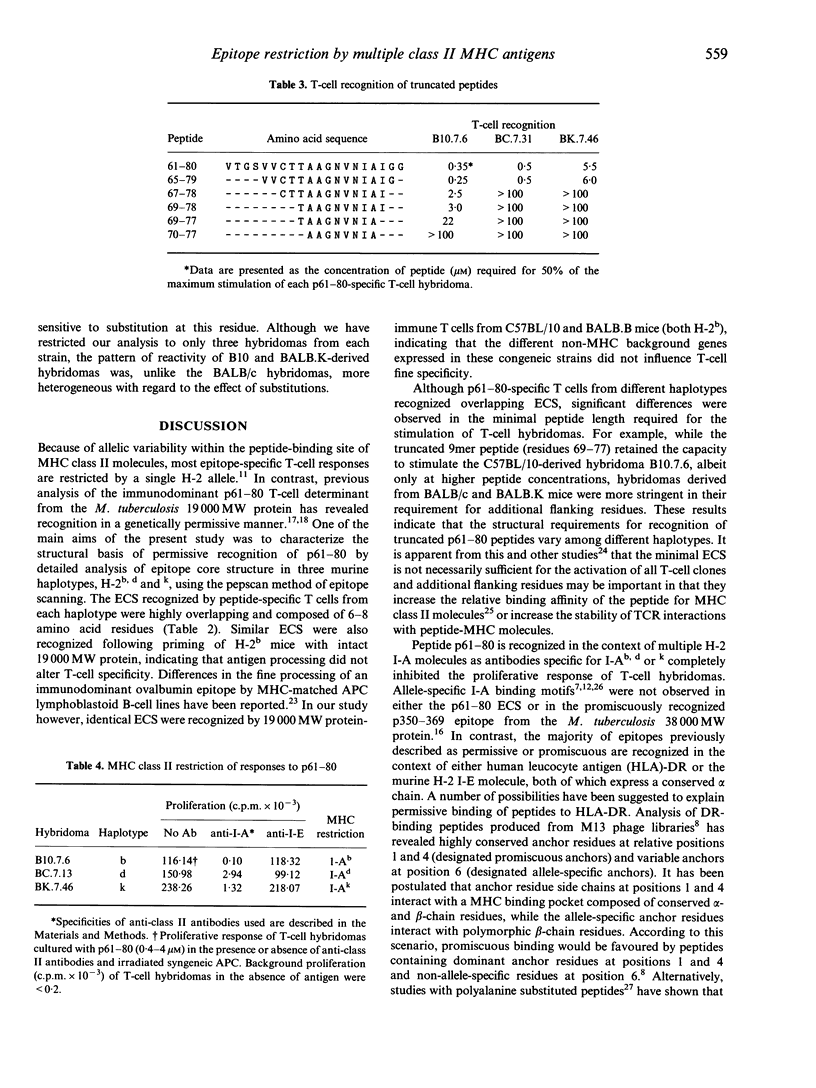
Abstract
Most T-cell epitopes are recognized in the context of a single or limited number of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules. We have shown previously, however, that the immunodominant p61-80 epitope from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19,000 MW protein is recognized in a genetically permissive manner. In this study, permissive recognition of p61-80 was analysed in three murine MHC haplotypes (H-2b,d and k) with respect to: (i) T-cell-epitope core structure; (ii) I-A/I-E class II MHC restriction; and (iii) the identification of critical amino acid residues within the core region. Overlapping epitope core sequences composed of 6 to 8 amino acids were identified for each of the three H-2 haplotypes by T-cell epitope scanning (PEPSCAN) using peptide-specific T-cell lines. The epitope core sequences recognized by peptide and 19,000 MW protein-specific T cells were similar. In all three haplotypes, responses to p61-80 were restricted by class II MHC I-A molecules. To identify residues within the epitope core critically required for recognition, single substitution (alanine or leucine) analogue peptides were tested for their capacity to stimulate p61-80-specific T-cell hybridomas. A heterogeneous pattern of reactivity was observed, even among individual hybridomas derived from the same H-2 haplotype. Although every core residue could be defined as critical for at least one hybridoma, only one critical substitution (74Val-->Ala) was common to all hybridomas. The identification and structural analysis of genetically permissive epitopes of mycobacteria may be a useful strategy for the rational design of peptide-based vaccines for tuberculosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altuvia Y., Berzofsky J. A., Rosenfeld R., Margalit H. Sequence features that correlate with MHC restriction. Mol Immunol. 1994 Jan;31(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(94)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhayani H., Paterson Y. Analysis of peptide binding patterns in different major histocompatibility complex/T cell receptor complexes using pigeon cytochrome c-specific T cell hybridomas. Evidence that a single peptide binds major histocompatibility complex in different conformations. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1609–1625. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T. S., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Urban R. G., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):33–39. doi: 10.1038/364033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Miles C., Grey H. M. The relation between major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restriction and the capacity of Ia to bind immunogenic peptides. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1353–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.2435001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Lorenz R. G., Goldberg J., Allen P. M. Identification and characterization of a T cell-inducing epitope of bovine ribonuclease that can be restricted by multiple class II molecules. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3672–3678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Stevanović S., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):290–296. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon G., Geysen H. M., Apple R. J., Pickett E., Palmer M., Ametani A., Sercarz E. E. T cell determinant structure: cores and determinant envelopes in three mouse major histocompatibility complex haplotypes. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):609–617. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbe T., Harris D., Vordermeier M., Lathigra R., Ivanyi J., Young D. Expression of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19-kilodalton antigen in Mycobacterium smegmatis: immunological analysis and evidence of glycosylation. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):260–267. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.260-267.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer J., Belunis C., Bolin D., Papadopoulos J., Walsky R., Higelin J., Danho W., Sinigaglia F., Nagy Z. A. High-affinity binding of short peptides to major histocompatibility complex class II molecules by anchor combinations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4456–4460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer J., Valsasnini P., Tolba K., Bolin D., Higelin J., Takacs B., Sinigaglia F. Promiscuous and allele-specific anchors in HLA-DR-binding peptides. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90306-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. P., Vordermeier H. M., Friscia G., Román E., Surcel H. M., Pasvol G., Moreno C., Ivanyi J. Genetically permissive recognition of adjacent epitopes from the 19-kDa antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by human and murine T cells. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):5041–5050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. P., Vordermeier H. M., Roman E., Lathigra R., Brett S. J., Moreno C., Ivanyi J. Murine T cell-stimulatory peptides from the 19-kDa antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Epitope-restricted homology with the 28-kDa protein of Mycobacterium leprae. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2706–2712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber-Katz E., Schwartz R. H., Matis L. A., Hannum C., Fairwell T., Appella E., Hansburg D. Contribution of antigen-presenting cell major histocompatibility complex gene products to the specificity of antigen-induced T cell activation. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1086–1099. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Michel H., Dickinson T. A., Shabanowitz J., Cox A. L., Sakaguchi K., Appella E., Grey H. M., Sette A. Peptides presented to the immune system by the murine class II major histocompatibility complex molecule I-Ad. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1817–1820. doi: 10.1126/science.1319610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Gorga J. C., Busch R., Rothbard J., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Peptide binding to HLA-DR1: a peptide with most residues substituted to alanine retains MHC binding. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1797–1803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08304.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilgus J., Jardetzky T., Gorga J. C., Trzeciak A., Gillessen D., Sinigaglia F. Analysis of the permissive association of a malaria T cell epitope with DR molecules. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropshofer H., Max H., Halder T., Kalbus M., Muller C. A., Kalbacher H. Self-peptides from four HLA-DR alleles share hydrophobic anchor residues near the NH2-terminal including proline as a stop signal for trimming. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4732–4742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata A., Berzofsky J. A. Analysis of peptide residues interacting with MHC molecule or T cell receptor. Can a peptide bind in more than one way to the same MHC molecule? J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4526–4535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeji N. J., Bray A. M., Geysen H. M. Multi-pin peptide synthesis strategy for T cell determinant analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Nov 6;134(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek M. T., Benacerraf B., Rock K. L. Two genetically identical antigen-presenting cell clones display heterogeneity in antigen processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3316–3320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda N. K., Arzoo K. K., Sercarz E. E. In a small multideterminant peptide, each determinant is recognized by a different V beta gene segment. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):297–302. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan D., Arrhenius T., Sidney J., Del Guercio M. F., Albertson M., Wall M., Oseroff C., Southwood S., Colón S. M., Gaeta F. C. On the interaction of promiscuous antigenic peptides with different DR alleles. Identification of common structural motifs. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2663–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudensky AYu, Preston-Hurlburt P., Hong S. C., Barlow A., Janeway C. A., Jr Sequence analysis of peptides bound to MHC class II molecules. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):622–627. doi: 10.1038/353622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudensky AYu, Preston-Hurlburt P., al-Ramadi B. K., Rothbard J., Janeway C. A., Jr Truncation variants of peptides isolated from MHC class II molecules suggest sequence motifs. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):429–431. doi: 10.1038/359429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Buus S., Appella E., Smith J. A., Chesnut R., Miles C., Colon S. M., Grey H. M. Prediction of major histocompatibility complex binding regions of protein antigens by sequence pattern analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3296–3300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vordermeier H. M., Harris D. P., Moreno C., Ivanyi J. Promiscuous T cell recognition of an H-2 IA-presented mycobacterial epitope. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Sep;24(9):2061–2067. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Young A. C., Imarai M., Nathenson S. G., Sacchettini J. C. Crystal structure of the major histocompatibility complex class I H-2Kb molecule containing a single viral peptide: implications for peptide binding and T-cell receptor recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8403–8407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]