Abstract
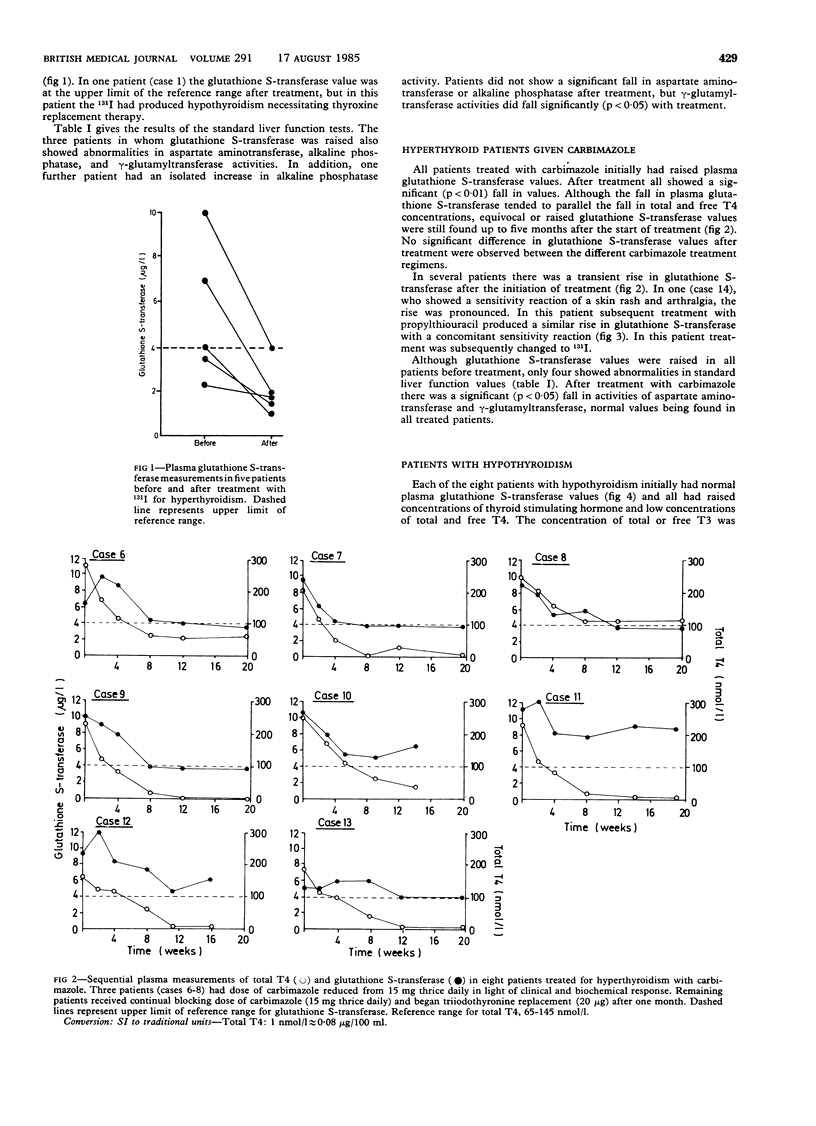
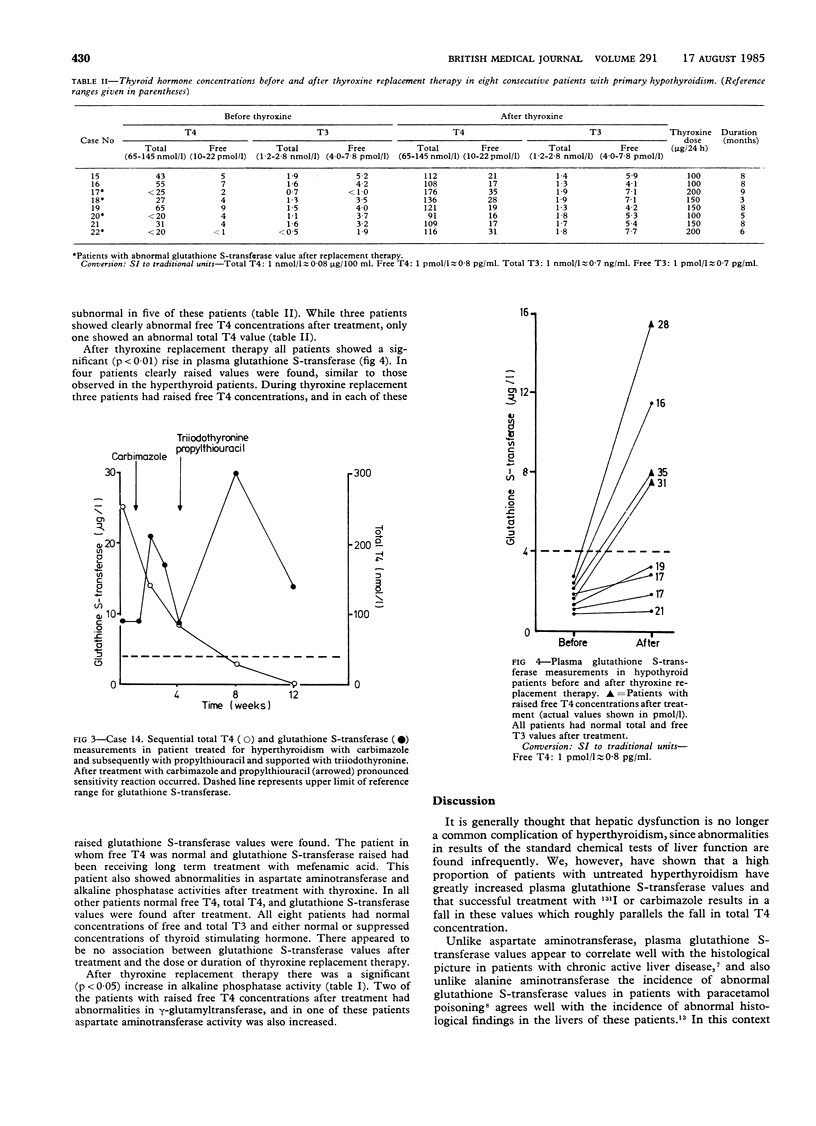
Using plasma glutathione S-transferase measurements hepatocellular integrity was assessed in groups of hyperthyroid and hypothyroid patients before and after treatment. Ten of 14 hyperthyroid patients had clearly raised plasma glutathione S-transferase values at presentation and in each patient treatment with either iodine-131 or carbimazole resulted in a significant fall in glutathione S-transferase. The eight hypothyroid patients had normal glutathione S-transferase values at presentation and all showed a significant increase in these after thyroxine replacement therapy. In three of these patients in whom standard doses of replacement therapy were associated with a raised free thyroxine (T4) concentration but normal total and free triiodothyronine (T3) values glutathione S-transferase was increased. Similar though less consistent changes were seen in the results of standard chemical tests of liver function. It is concluded that hyperthyroidism may produce subclinical liver damage in a high proportion of patients and that this resolves with effective treatment. More important, the data suggest that hypothyroid patients receiving thyroxine replacement therapy may have similar subclinical liver damage. Patients receiving thyroxine should be monitored by the measurement of free, not total hormone concentrations, and in those in whom free T4 is raised the dose of thyroxine should be reduced. It would also be expedient to include periodic biochemical assessment of liver function in patients receiving thyroxine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkar F. S., Miller R., Smoak W. M., 3rd, Gilson A. J. Liver disease in hyperthyroidism. South Med J. 1971 Apr;64(4):462–465. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197104000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass N. M., Kirsch R. E., Tuff S. A., Saunders S. J. Radioimmunoassay of plasma ligandin: a sensitive index of experimental hepatocellular necrosis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):589–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. E., Gorden P., Robbins J. Hepatitis from methimazole during adrenal steroid therapy for malignant exophthalmos. JAMA. 1968 Nov 18;206(8):1787–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett G. J., Chapman B. J., Dyson E. H., Hayes J. D. Plasma glutathione S-transferase measurements after paracetamol overdose: evidence for early hepatocellular damage. Gut. 1985 Jan;26(1):26–31. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett G. J., Dyson E. H., Chapman B. J., Templeton A. J., Hayes J. D. Plasma glutathione S-transferase measurements by radioimmunoassay: a sensitive index of hepatocellular damage in man. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Feb 28;146(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett G. J., Hayes J. D. Development of specific radioimmunoassays for the measurement of human hepatic basic and N/A2b glutathione S-transferases. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Aug 31;141(2-3):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(84)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL A. R., Jr, SANDO D. E., LANG S. J. Propylthiouracil-induced agranulocytosis, toxic hepatitis, and death. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Feb 23;148(8):639–641. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.62930080001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James O., Lesna M., Roberts S. H., Pulman L., Douglas A. P., Smith P. A., Watson A. J. Liver damage after paracetamol overdose. Comparison of liver-function tests, fasting serum bile acids, and liver histology. Lancet. 1975 Sep 27;2(7935):579–581. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings P. E., O'Malley B. P., Griffin K. E., Northover B., Rosenthal F. D. Relevance of increased serum thyroxine concentrations associated with normal serum triiodothyronine values in hypothyroid patients receiving thyroxine: a case for "tissue thyrotoxicosis". Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Dec 15;289(6459):1645–1647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6459.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klion F. M., Segal R., Schaffner F. The effect of altered thyroid function on the ultrastructure of the human liver. Am J Med. 1971 Mar;50(3):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskelo K. Isoelectric focusing of glutathione S-transferases: comparison of the acidic transferases from human liver, kidney, lung, spleen and placenta. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;43(2):133–139. doi: 10.1080/00365518309168235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunzer M., Huang S. N., Ginsburg J., Ahmed M., Sherlock S. Jaundice due to carbimazole. Gut. 1975 Nov;16(11):913–917. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.11.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce C. J., Himsworth R. L. Total and free thyroid hormone concentrations in patients receiving maintenance replacement treatment with thyroxine. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Mar 3;288(6418):693–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6418.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe W. A., Challand G. S., Ratcliffe J. G. A critical evaluation of separation methods in radiommunoassay for total triiodothyronine and thyroxine in unextracted human serum. Ann Clin Biochem. 1974 Nov;11(6):224–229. doi: 10.1177/000456327401100166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan P. Thyroid hormones and the liver. Clin Gastroenterol. 1983 Sep;12(3):797–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M., Bass N. M., Campbell J. A., Kirsch R. E. Radioimmunoassay of human ligandin. Hepatology. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):162–169. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockman P. K., Beckett G. J., Hayes J. D. Identification of a basic hybrid glutathione S-transferase from human liver. Glutathione S-transferase delta is composed of two distinct subunits (B1 and B2). Biochem J. 1985 Apr 15;227(2):457–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2270457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


