Abstract
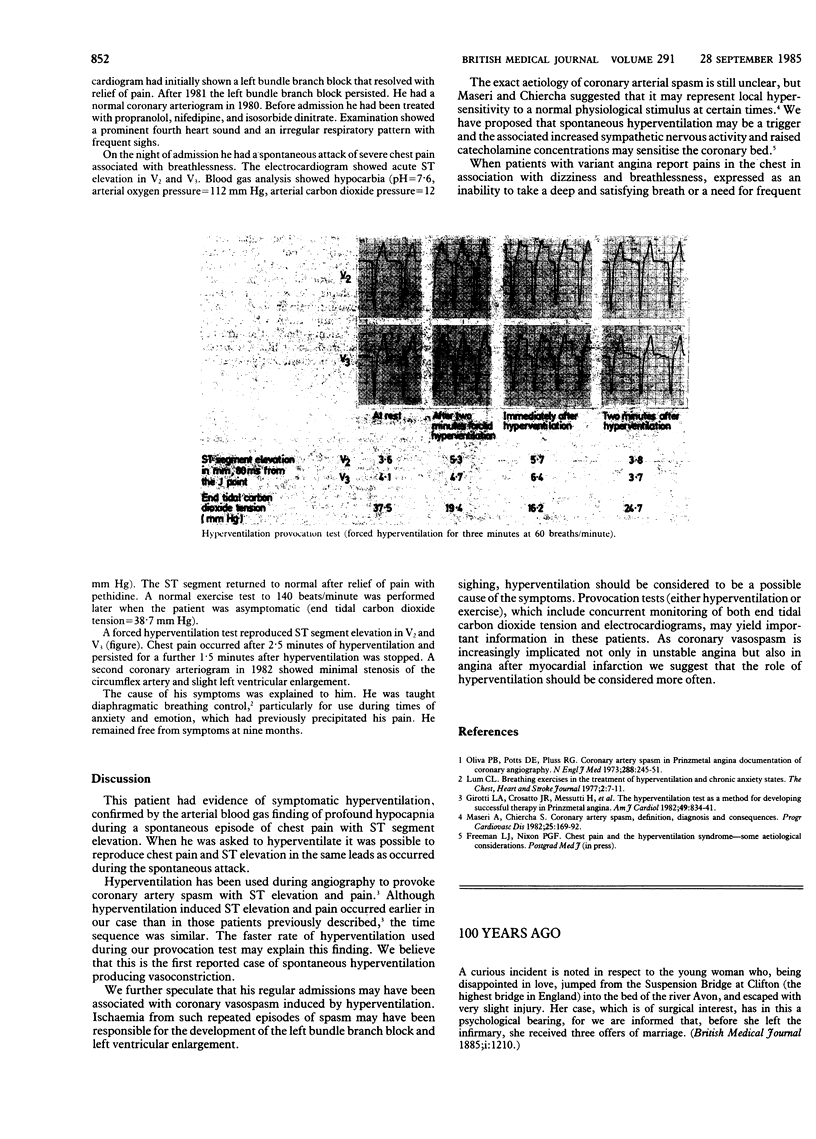
A case of coronary artery vasospasm was studied in a man with a four year history of angina. He had evidence of symptomatic hyperventilation during a spontaneous episode of chest pain. When asked to hyperventilate the pain in his chest and ST elevation were reproduced in the same leads as occurred during the spontaneous attack. This may be the first reported case of spontaneous hyperventilation producing vasoconstriction, and the patient's previous admissions to the coronary care unit may have been associated with coronary vasospasm induced by hyperventilation. When patients with variant angina report pains in the chest in association with dizziness and breathlessness hyperventilation should be considered to be a possible cause of the symptoms. As coronary vasospasm is increasingly implicated in angina after myocardial infarction the role of hyperventilation should be considered more often.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Girotti L. A., Crosatto J. R., Messuti H., Kaski J. C., Dyszel E., Rivas C. A., Araujo L. I., Vetulli H. D., Rosenbaum M. B. The hyperventilation test as a method for developing successful therapy in Prinzmetal's angina. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Mar;49(4):834–841. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)91966-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maseri A., Chierchia S. Coronary artery spasm: demonstration, definition, diagnosis, and consequences. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;25(3):169–192. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(82)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


