Abstract
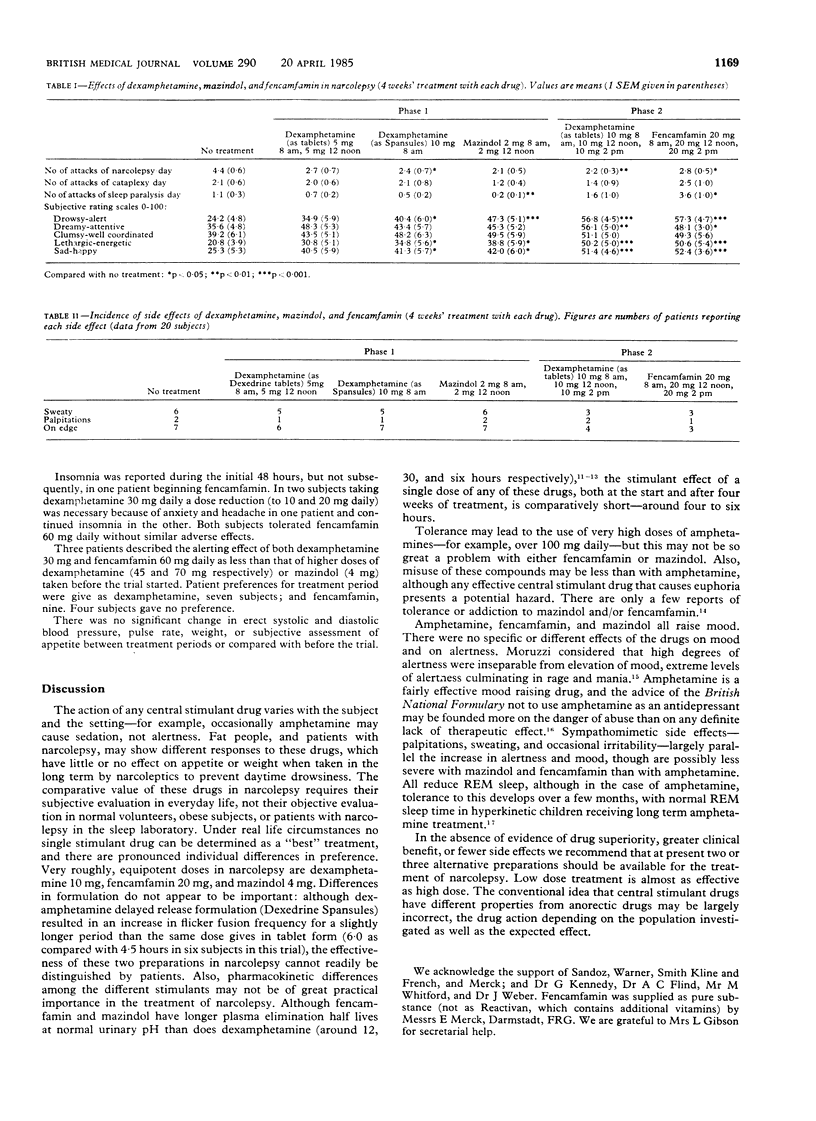
Twenty patients with the narcoleptic syndrome were treated separately with dexamphetamine sulphate tablets 10 and 30 mg, Dexedrine Spansules 10 mg, mazindol 4 mg, and fencamfamin hydrochloride 60 mg daily. Each drug was given for four weeks and the effects compared. In these dosages the reported frequency of attacks of narcolepsy was roughly halved with each treatment, dexamphetamine 30 mg daily being only slightly more potent than 10 mg. The subjective effects of Dexedrine tablets and Spansules could not be distinguished by most patients. Effects on mood, alertness, and sympathomimetic side effects were largely inseparable with all these drugs, but a decrease in appetite was not reported by patients with narcolepsy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKETT A. H., ROWLAND M., TURNER P. INFLUENCE OF URINARY PH ON EXCRETION OF AMPHETAMINE. Lancet. 1965 Feb 6;1(7380):303–303. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock D. Anorectic drugs: use in general practice. Drugs. 1976;11(5):378–393. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197611050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALY D. D., YOSS R. E. The treatment of narcolepsy with methyl phenylpiperidylacetate: a preliminary report. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1956 Nov 14;31(23):620–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogerty J. H., Penberthy C., Iorio L. C., Trapold J. H. Pharmacological analysis of a new anorexic substance: 5-hydroxy-5(4'-chlorophenyl)-2, 3-dihydro-5H-imidazo-(2, 1-a) isoindole (Mazindol). Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1975 Apr;214(2):285–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLIDAY A. R., DEVERY W. J. Effects of drugs on the performance of a task by fatigued subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1962 Jan-Feb;3:5–15. doi: 10.1002/cpt1962315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges A. AN. 448 on critical flicker frequency and heart rate in man. S Afr Med J. 1972 Feb 5;46(6):139–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmstrand J., Jonsson J. Subjective effects of two anorexigenic agents--fenfluramine and AN 448 in normal subjects. Postgrad Med J. 1975;51 (Suppl 1):183–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moruzzi G. The sleep-waking cycle. Ergeb Physiol. 1972;64:1–165. doi: 10.1007/3-540-05462-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday B., Kendall M. J., Mitchard M. A single dose study of trazodone with an assessment of its effect on mood and arousal. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;2(1):19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1975.tb00466.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes J. D., Schachter M. Mazindol in the treatment of narcolepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1979 Oct;60(4):250–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1979.tb02976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M., Parkes J. D. Fluvoxamine and clomipramine in the treatment of cataplexy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Feb;43(2):171–174. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sroufe L. A., Stewart M. A. Treating problem children with stimulant drugs. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 23;289(8):407–413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308232890806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vree T. B., van Rossum J. M. Suppression of renal excretion of fencamfamine in man. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969 Aug;7(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


