Abstract
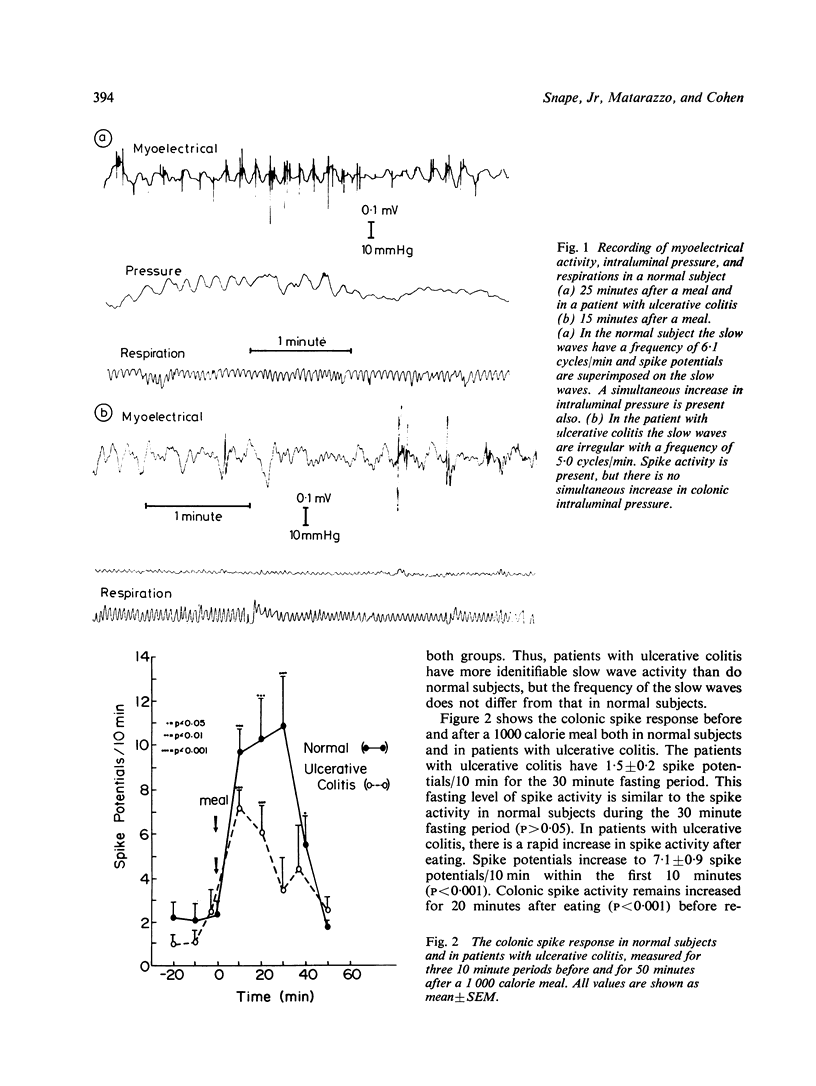
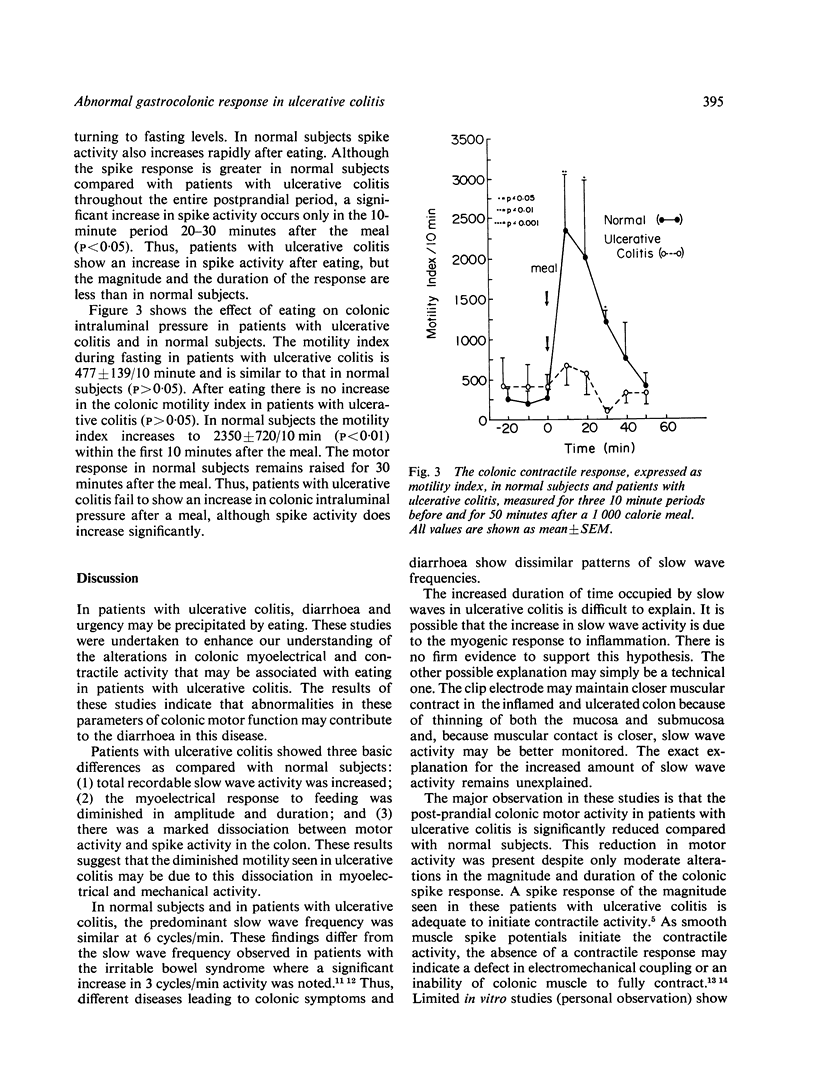
The purpose of these studies is to determine the colonic myoelectrical and contractile response after eating a 1000 calorie meal in patients with active ulcerative colitis. During fasting, slow waves are identifiable significantly more in patients with ulcerative colitis than in normal subjects (p < 0 . 01). The predominant slow wave frequency is 6 . 1 +/- 0 . 2 cycles/min, which is similar to the normal subjects. The slow waves are not altered by eating in either group. Minimal spike or contractile activity occurs during the fasting period both in patients with ulcerative colitis and in normal subjects. In patients with ulcerative colitis, spike activity increases rapidly after eating the 1000 calorie meal (P < 0 . 01), but the maximal response is decreased and shorter in duration than in normal subjects. There is no simultaneous increase in colonic contractility above fasting levels after the meal in patients with ulcerative colitis. This is strikingly different from the simultaneous increase in contractile and spike activity (P < 0 . 01) that occurs after eating in normal subjects. These studies suggest that in ulcerative colitis (1) the colonic smooth muscle slow wave activity is intact; and (2) a disturbance in the normal colonic contractile response to eating is present despite an adequate spike response. This lack of colonic contractility may contribute to the increase in diarrhoea that occurs in these patients after eating.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAUDHARY N. A., TRUELOVE S. C. Human colonic motility: a comparative study of normal subjects, patients with ulcerative colitis, and patients with the irritable colon syndrome. I. Resting patterns of motility. Gastroenterology. 1961 Jan;40:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL A. M., JONES F. A., ROWLANDS E. N. MOTILITY OF THE PELVIC COLON. IV. ABDOMINAL PAIN ASSOCIATED WITH COLONIC HYPERMOTILITY AFTER MEALS. Gut. 1965 Apr;6:105–112. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL A. M. The motility of the pelvic colon. II. Paradoxical motility in diarrhoea and constipation. Gut. 1962 Dec;3:342–348. doi: 10.1136/gut.3.4.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL E. E., CHAPMAN K. M. Electrical activity of the gastrointestinal tract as an indication of mechanical activity. Am J Dig Dis. 1963 Jan;8:54–102. doi: 10.1007/BF02233560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON M., SLEISENGER M. H., ALMY T. P., LEVINE S. Z. Studies of distal colonic motility in children. II. Propulsive activity in diarrheal states. Pediatrics. 1956 Jun;17(6):820–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdstock D. J., Misiewicz J. J. Factors controlling colonic motility: colonic pressures and transit after meals in patients with total gastrectomy, pernicious anaemia or duodenal ulcer. Gut. 1970 Feb;11(2):100–110. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.2.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERN F., Jr, ALMY T. P., ABBOT F. K., BOGDONOFF M. D. The motility of the distal colon in nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1951 Nov;19(3):492–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRIGGS E. A., CODE C. F., BARGEN J. A., CURTISS R. K., HIGHTOWER N. C., Jr Motility of the pelvic colon and rectum of normal persons and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1951 Nov;19(3):480–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Carlson G. M., Cohen S. Colonic myoelectric activity in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):326–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Carlson G. M., Cohen S. Human colonic myoelectric activity in response to prostigmin and the gastrointestinal hormones. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Oct;22(10):881–887. doi: 10.1007/BF01076164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Matarazzo S. A., Cohen S. Effect of eating and gastrointestinal hormones on human colonic myoelectrical and motor activity. Gastroenterology. 1978 Sep;75(3):373–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tansy M. F., Kendall F. M. Experimental and clinical aspects of gastrocolic reflexes. Am J Dig Dis. 1973 Jun;18(6):521–531. doi: 10.1007/BF01076606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I., Darby C., Hammond P., Basu P. Is there a myoelectrical abnormality in the irritable colon syndrome? Gut. 1978 May;19(5):391–395. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.5.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANGEL A. G., DELLER D. J. INTESTINAL MOTILITY IN MAN. 3. MECHANISMS OF CONSTIPATION AND DIARRHEA WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE IRRITABLE COLON SYNDROME. Gastroenterology. 1965 Jan;48:69–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller S. L., Misiewicz J. J., Kiley N. Effect of eating on motility of the pelvic colon in constipation or diarrhoea. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):805–811. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.10.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


