Abstract
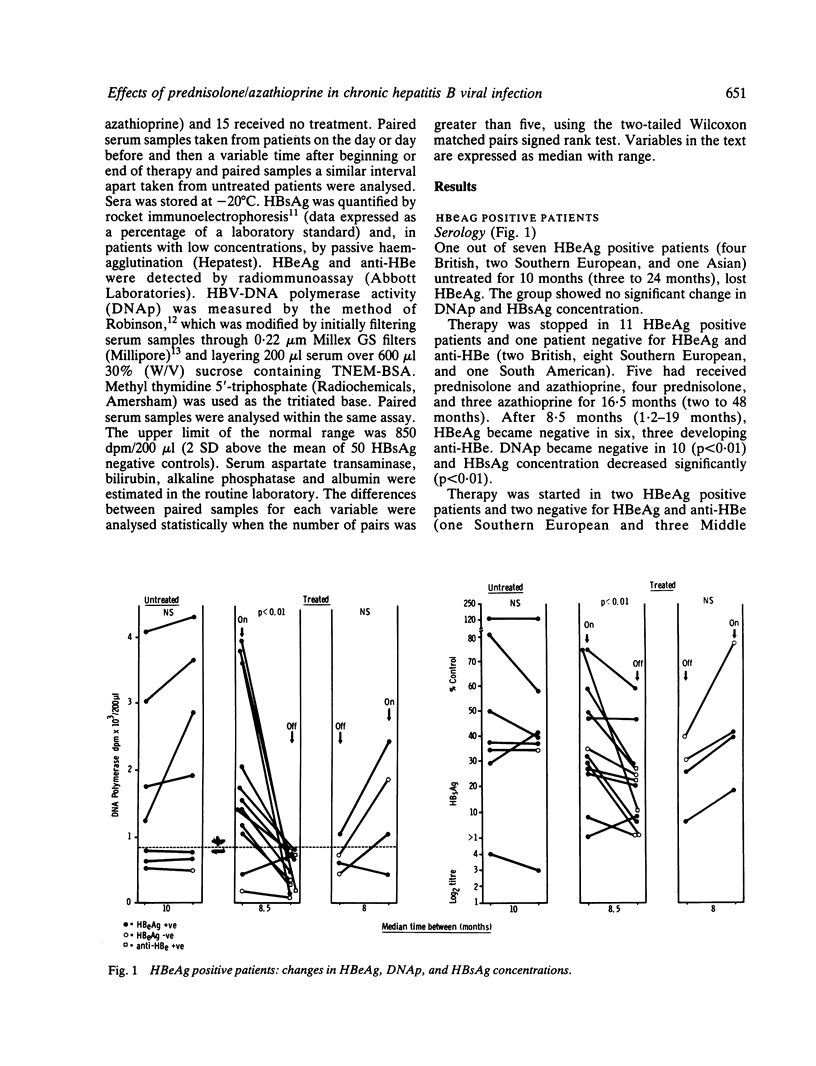
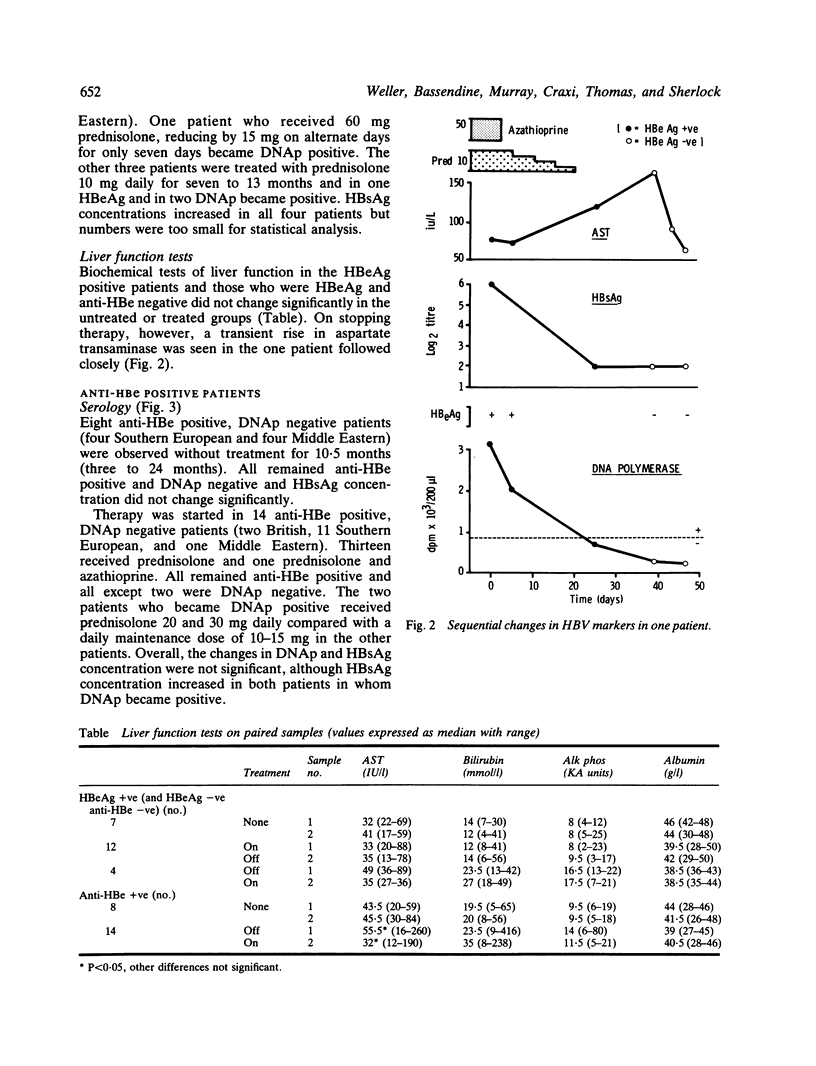
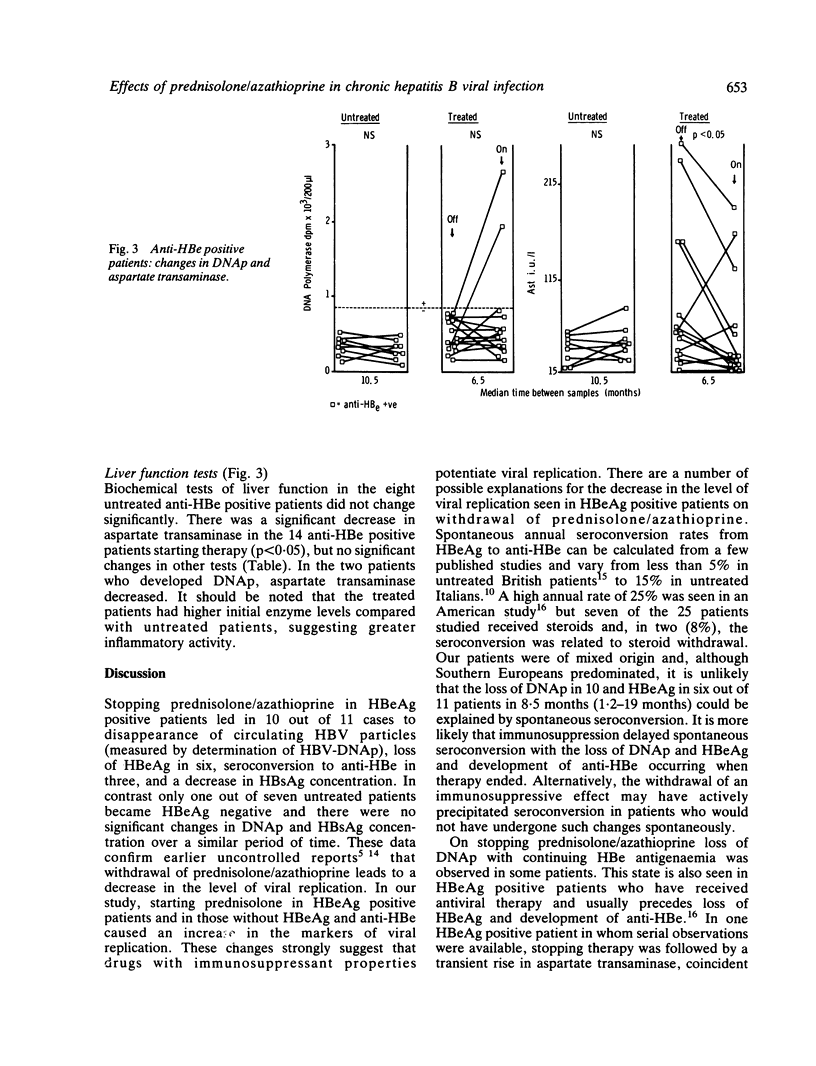
Changes in markers of hepatitis B viral replication and standard liver function tests were studied in 30 patients with HBsAg positive chronic liver disease starting or stopping prednisolone/azathioprine therapy, and compared with those occurring in 15 patients who did not receive therapy. On stopping prednisolone/azathioprine, 10 out of 11 HBeAg positive patients and one out of three patients negative for HBeAg and anti-HBe, lost HBV-DNA polymerase activity (p less than 0.01), five lost HBeAg, three developed anti-HBe and HBsAg concentration decreased (p less than 0.01). Only one out of seven untreated HBeAg positive patients lost HBeAg and there were no significant changes in DNA polymerase activity. In the anti-HBe positive patients, 14 starting therapy and eight untreated, there were no significant changes in the markers of viral replication - although two patients developed DNA polymerase activity on high maintenance doses of prednisolone - but a significant decrease (p less than 0.05) in aspartate transaminase in the treated group. It is concluded that the cessation of prednisolone/azathioprine therapy in HBeAg positive patients will result in a reduction in viral replication. In anti-HBe positive patients such therapy may be beneficial.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti A., Diana S., Sculard G. H., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Detection of a new antibody system reacting with Dane particles in hepatitis B virus infection. Br Med J. 1978 Oct 14;2(6144):1056–1058. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6144.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Seeff L. B., Kaplan P. M., McAuliffe V. J., Wright E. C., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Zimmerman H. J. Type B hepatitis: the infectivity of blood positive for e antigen and DNA polymerase after accidental needlestick exposure. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 21;295(17):909–913. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610212951701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. C., Mulligan R., Sherlock S. Controlled prospective trial of corticosteroid therapy in active chronic hepatitis. Q J Med. 1971 Apr;40(158):159–185. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.qjmed.a067264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Dusheiko G. M., Seeff L. B., Jones E. A., Waggoner J. G., Bales Z. B. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to antibody in chronic type B hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):744–748. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. C., Lai C. L., Trepo C., Wu P. C. Deleterious effect of prednisolone in HBsAg-positive chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):380–386. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray-Lyon I. M., Stern R. B., Williams R. Controlled trial of prednisone and azathioprine in active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):735–737. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Vido I., Schmidt F. W. Rapid withdrawal of immunosuppressive therapy in chronic active hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1323–1324. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92506-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrillo R. P., Gelb L. D., Wellinghoff W., Aach R. D. Filtration and immunoprecipitation in the elimination of DNA polymerase activity associated with bacterial contamination of sera positive for hepatitis B e antigen and its corresponding antibody. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):473–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrillo R. P., Gelb L., Campbell C., Wellinghoff W., Ellis F. R., Overby L., Aach R. D. Hepatitis B e antigen, DNA polymerase activity, and infection of household contacts with hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1319–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Realdi G., Alberti A., Rugge M., Bortolotti F., Rigoli A. M., Tremolada F., Ruol A. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. DNA and DNA polymerase in the core of the Dane particle of hepatitis B. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jul-Aug;270(1):151–159. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197507000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagnelli E., Manzillo G., Maio G., Pasquale G., Felaco F. M., Filippini P., Izzo C. M., Piccinino F. Serum levels of hepatitis B surface and core antigens during immunosuppressive treatment of HBsAg-positive chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1980 Aug 23;2(8191):395–397. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalm S. W., Summerskill W. H., Gitnick G. L., Elveback L. R. Contrasting features and responses to treatment of severe chronic active liver disease with and without hepatitis BS antigen. Gut. 1976 Oct;17(10):781–786. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.10.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway R. D., Summerskill W. H., Baggenstoss A. H., Geall M. G., Gitnićk G. L., Elveback I. R., Schoenfield L. J. Clinical, biochemical, and histological remission of severe chronic active liver disease: a controlled study of treatments and early prognosis. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):820–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. E., Neurath R. A., Beasley R. P., Szmuness W. HBeAg and anti-HBe detection by radioimmunoassay: correlation with vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus in Taiwan. J Med Virol. 1979;3(3):237–241. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viola L. A., Barrison I. G., Coleman J. C., Paradinas F. J., Fluker J. L., Evans B. A., Murray-Lyon I. M. Natural history of liver disease in chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carriers. Survey of 100 patients from Great Britain. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1156–1159. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90600-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogten A. J., Summerskill W. H., Gitnick G. L., Schalm S. W., Smith J. L., Murphy B. L., Maynard J. E. Behaviour of e antigen and antibody during chronic active liver disease. Relation to HB antigen-antibody system and prognosis. Lancet. 1976 Jul 17;2(7977):126–128. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92849-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


