Abstract
In this study a perfusion technique has been used to investigate jejunal secretion in response to the dibasic amino acid L-arginine. L-arginine at 5, 15, and 40 mmol/l in isotonic saline solutions induced net intestinal secretion of water and Na+. The structurally similar dibasic amino acid L-lysine caused net absorption at 5 and 15 mmol/l, and only modest net secretion of water and Na+ at 40 mmol/l, although absorption rates of the two amino acids were similar. D-arginine (15 mmol/l) was without effect on net water and Na+ absorption. L-arginine 15 mmol/l inhibited glucose-stimulated water and Na+ absorption when perfused in the same intestinal segment, but was without effect when perfused in separate jejunal or ileal segments. Parenteral chlorpromazine inhibited L-arginine induced jejunal water and Na+ secretion. Jejunal secretion induced by L-arginine thus appears not to be due to passive osmotic water flow, nor to release of circulating secretagogues. Stimulation of a mucosal secretory process is most likely to be the mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
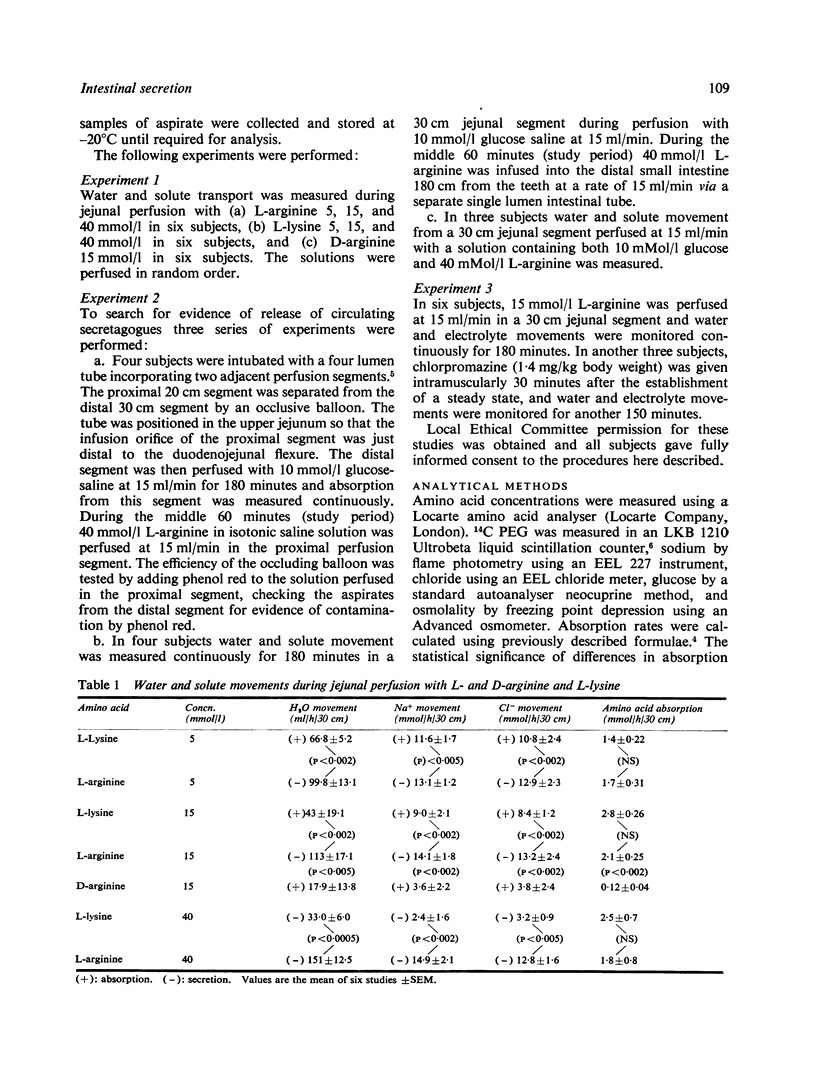
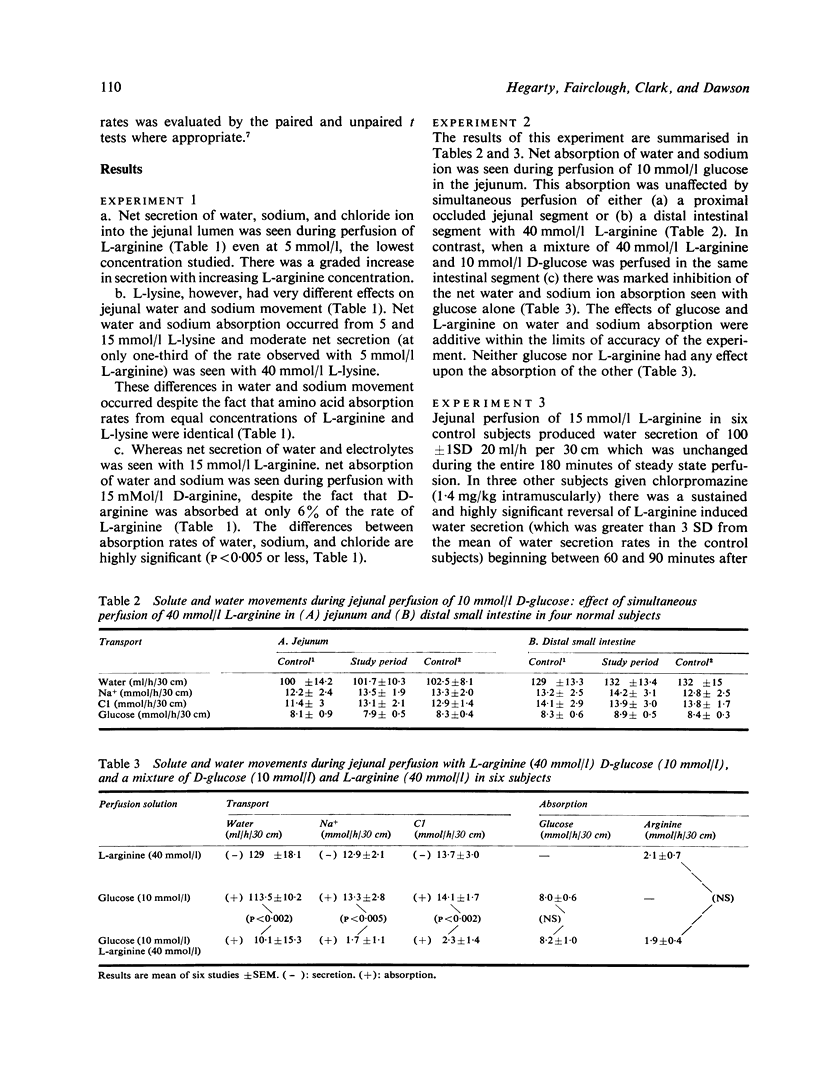
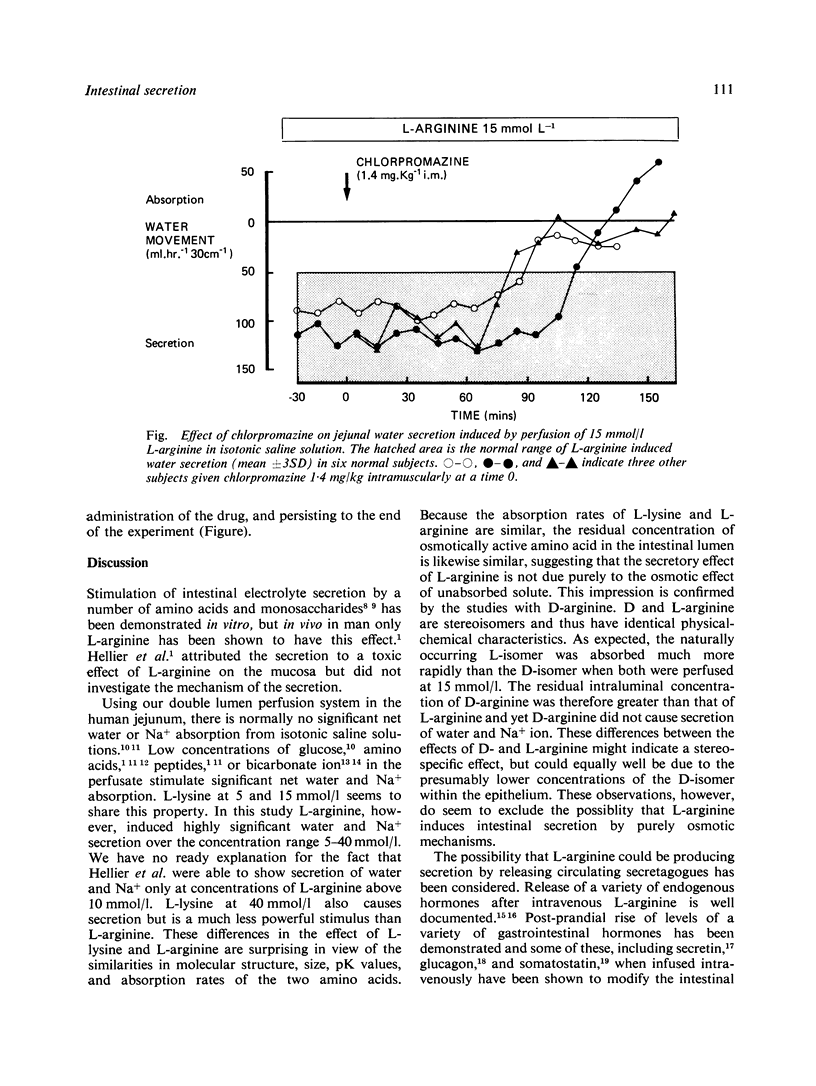
- Adibi S. A. Leucine absorption rate and net movements of sodium and water in human jejunum. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Jun;28(6):753–757. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. R., Santa Ana C. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Inhibition of water and electrolyte absorption by polyethylene glycol (PEG). Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellier M. D., Thirumalai C., Holdsworth C. D. The effect of amino acids and dipeptides on sodium and water absorption in man. Gut. 1973 Jan;14(1):41–45. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks T., Turnberg L. A. The effect of glucagon and secretion on salt and water transport in the human jejunum. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):854–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks T., Turnberg L. A. The influence of secretin on ion transport in the human jejunum. Gut. 1973 Jun;14(6):485–490. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.6.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lange S., Lönnroth I. Reversal of cyclic AMP-mediated intestinal secretion in mice by chlorpromazine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1103–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilundain A., Naftalin R. J. Role of Ca(2+)-dependent regulator protein in intestinal secretion. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):446–448. doi: 10.1038/279446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejs G. J., Browne R., Raskin P. Effect of intravenous somatostatin on jejunal absorption of glucose, amino acids, water, and electrolytes. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jan;78(1):26–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwant W. O., Seeman P. The displacement of membrane calcium by a local anesthetic (chlorpromazine). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):338–349. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwant W. O., van Steveninck J. The influence of chlorpromazine on human erythrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Oct;17(10):2215–2223. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Lillicrap D. A., Rabinowitz D. Effect of arginine on serum-levels of human growth-hormone. Lancet. 1965 Oct 2;2(7414):668–670. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90399-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G. Effects of sugar and amino acid transport on transepithelial fluxes of sodium and chloride of short circuited rat jejunum. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):699–717. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poitras P., Modigliani R., Bernier J. J. Effect of a combination of gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, glucagon, and gastric inhibitory polypeptide on jejunal absorption in man. Gut. 1980 Apr;21(4):299–304. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.4.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Binder H. J., Curran P. F. Electrolyte secretion by the guinea pig ileum in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1972 Sep;223(3):531–537. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani G. H., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Holmgren J., Lönnroth I. Chlorpromazine reduces fluid-loss in cholera. Lancet. 1979 Feb 24;1(8113):410–412. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90885-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Kwant W. O., Goldberg M., Chau-Wong M. The effects of ethanol and chlorpromazine on the passive membrane permeability to Na + . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B., Fairclough P. D., Park N. J., Lane A. E., Webb J. P., Clark M. L., Dawson A. M. A study of relations between the absorption of amino acids, dipeptides, water and electrolytes in the normal human jejunum. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Nov;49(5):401–408. doi: 10.1042/cs0490401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. Effect of bicarbonate on sodium absorption by the human jejunum. Nature. 1968 Apr 20;218(5138):267–268. doi: 10.1038/218267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. Further studies on the perfusion method for measuring intestinal absorption in man: the effects of a proximal occlusive balloon and a mixing segment. Gut. 1970 Nov;11(11):947–954. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.11.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. Interrelationships between the absorptions of glucose, sodium and water by the normal human jejunum. Clin Sci. 1969 Feb;36(1):119–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Field M. In vitro antisecretory effects of trifluoperazine and other neuroleptics in rabbit and human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jun;78(6):1545–1553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Fordtran J. S., Carter N. W., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):548–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI106265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Sandberg R. J., Phillips S. F. A comparison of stable and 14 C-labelled polyethylene glycol as volume indicators in the human jejunum. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):812–815. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.10.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. P., Barbezat G. O., Clain J. E. Jejunal secretion in response to a duodenal mixed nutrient perfusion. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jan;76(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


