Abstract
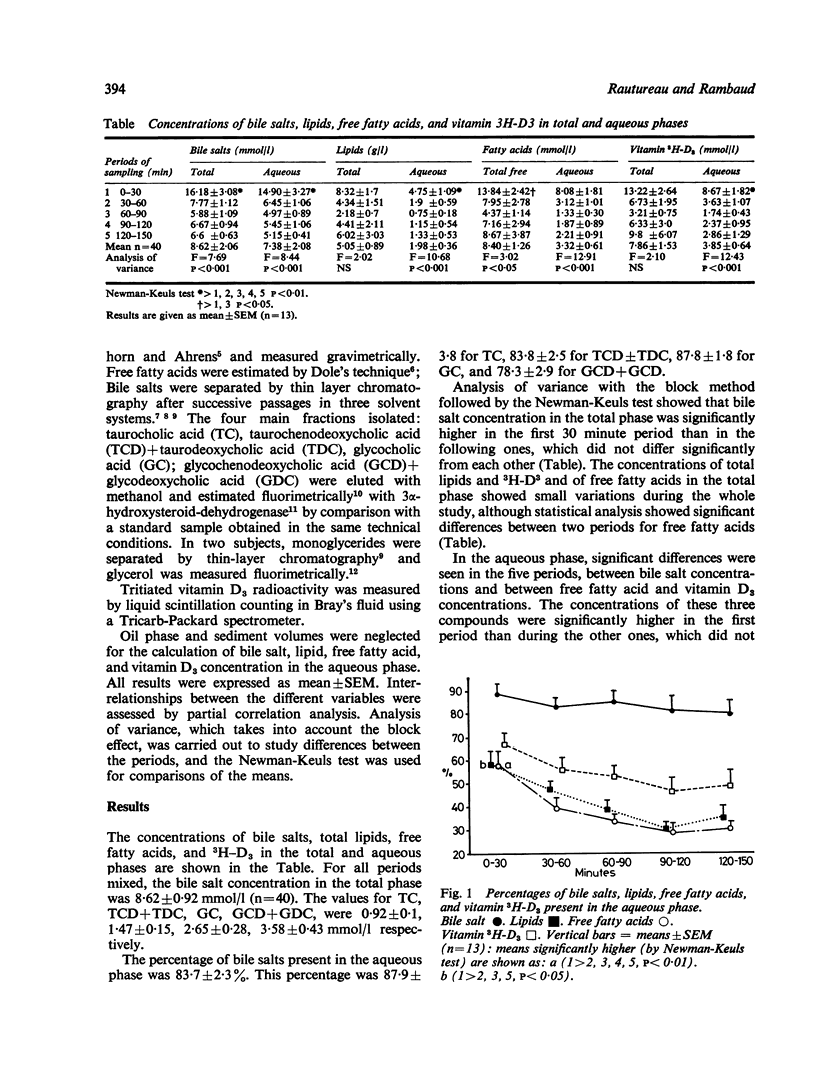
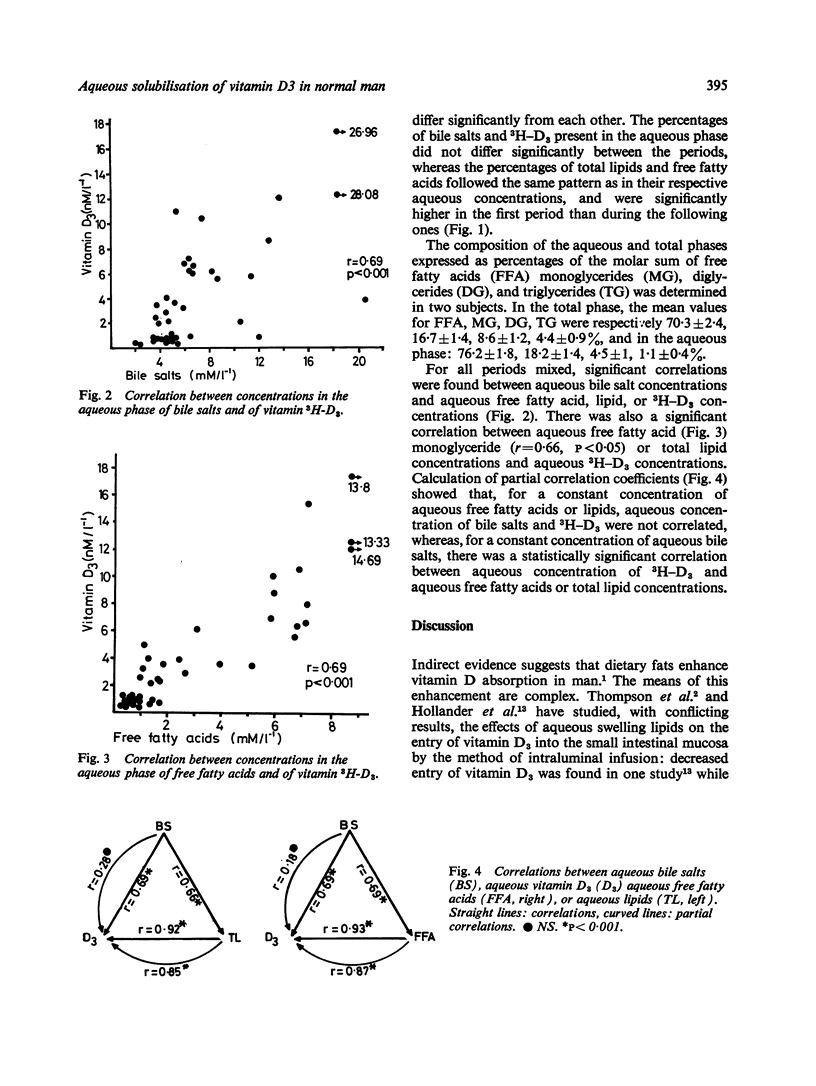
Jejunal aqueous solubilisation of vitamin D3 was assessed in eight normal subjects, after ingestion of a standard liquid test meal. Percentages and total concentrations of vitamin D3 in the aqueous phase were significantly higher in the first post-prandial 30 minutes than during the following two hours, as were bile salts, total lipids, and free fatty acids. As shown by partial correlation analysis, a statistically significant relationship was found between aqueous concentrations of free fatty acids and of vitamin D3 in the jejunal content during all the 2 1/2 hours of the study. From these data it is concluded that, in healthy man, vitamin D3 is solubilised in vivo in mixed micelles only, and is governed in the aqueous phase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLANKENHORN D. H., AHRENS E. H., Jr Extraction, isolation, and identification of hydrolytic products of triglyceride digestion in man. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):69–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B., DAHLQVIST A., LUNDH G., SJOVALL J. Studies of intestinal digestion and absorption in the human. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1521–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI103549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley B. W., Murphy G. M., Bouchier I. A., Sherlock S. Diminished micellar phase lipid in patients with chronic nonalcoholic liver disease and steatorrhea. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jun;58(6):781–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgström B. Bile salts--their physiological functions in the gastrointestinal tract. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Jul-Aug;196(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1974.tb00958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. Micelle formation by bile salts. Physical-chemical and thermodynamic considerations. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):506–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMagno E. P., Go W. L., Summerskill W. H. Impaired cholecystokinin-pancreozymin secretion, intraluminal dilution, and maldigestion of fat in sprue. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jul;63(1):25–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAENSHIRT H., KOSS F. W., MORIANZ K. [Studies on the quantitative evaluation of thin-layer chromatography. 2. Separation and determination of bile acids]. Arzneimittelforschung. 1960 Nov;10:943–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., BORGSTROEM B. THE INTRALUMINAL PHASE OF FAT DIGESTION IN MAN: THE LIPID CONTENT OF THE MICELLAR AND OIL PHASES OF INTESTINAL CONTENT OBTAINED DURING FAT DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION. J Clin Invest. 1964 Feb;43:247–257. doi: 10.1172/JCI104909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander D., Muralidhara K. S., Zimmerman A. Vitamin D-3 intestinal absorption in vivo: influence of fatty acids, bile salts, and perfusate pH on absorption. Gut. 1978 Apr;19(4):267–272. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.4.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRITCHEVSKY D., MARTAK D. S., ROTHBLAT G. H. Detection of bile acids in thin-layer chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1963 May;5:388–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. Y. Artifacts in ultracentrifugal estimation of aqueous fatty acid concentration. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):745–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A., Siurala M. Bile salts, sterols, sterol esters, glycerides and fatty acids in micellar and oil phases of intestinal contents during fat digestion in man. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1971 Jan;9(1):47–52. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1971.9.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modai M., Theodor E. Intestinal contents in patients with viral hepatitis after a lipid meal. Gastroenterology. 1970 Mar;58(3):379–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. M., Billing B. H., Baron D. N. A fluorimetric and enzymatic method for the estimation of serum total bile acids. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Oct;23(7):594–598. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.7.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Borgström B. Absorption and metabolism of lecithin and lysolecithin by intestinal slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):240–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pié A., Giner A. Solvents for thin layer chromatography of blood serum lipids. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):402–403. doi: 10.1038/212402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter H. P., Saunders D. R. Isolation of the aqueous phase of human intestinal contents during the digestion of a fatty meal. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jun;60(6):997–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost A., Rambaud J. C., Miravet L., Bordier P., Hioco D., Paolaggi J., Camus J. P., Lievre J. A., de Sèze S., Bernier J. J. Les ostéomalacies révélatrices de la maladie coeliaque de l'adulte. A propos de sept observations. Nouv Presse Med. 1972 May 13;1(20):1329–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid W. C., Phillips S. F., Summerskill W. H. Jejunal secretion of electrolytes and water in nontropical sprue. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 May;73(5):772–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds W. J., Hofmann A. F., Theodor E. Absorption of cholesterol from a micellar solution: intestinal perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):874–890. doi: 10.1172/JCI105587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons F., Bouchier I. A. Intraluminal bile salt concentrations and fat digestion after cholecystectomy. S Afr Med J. 1972 Dec 30;46(52):2089–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Lewis B., Booth C. C. Absorption of vitamin D3-3H in control subjects and patients with intestinal malabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):94–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI105327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Ockner R. K., Isselbacher K. J. Effect of mixed micellar lipid on the absorption of cholesterol and vitamin D3 into lymph. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):87–95. doi: 10.1172/JCI105977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


