Abstract
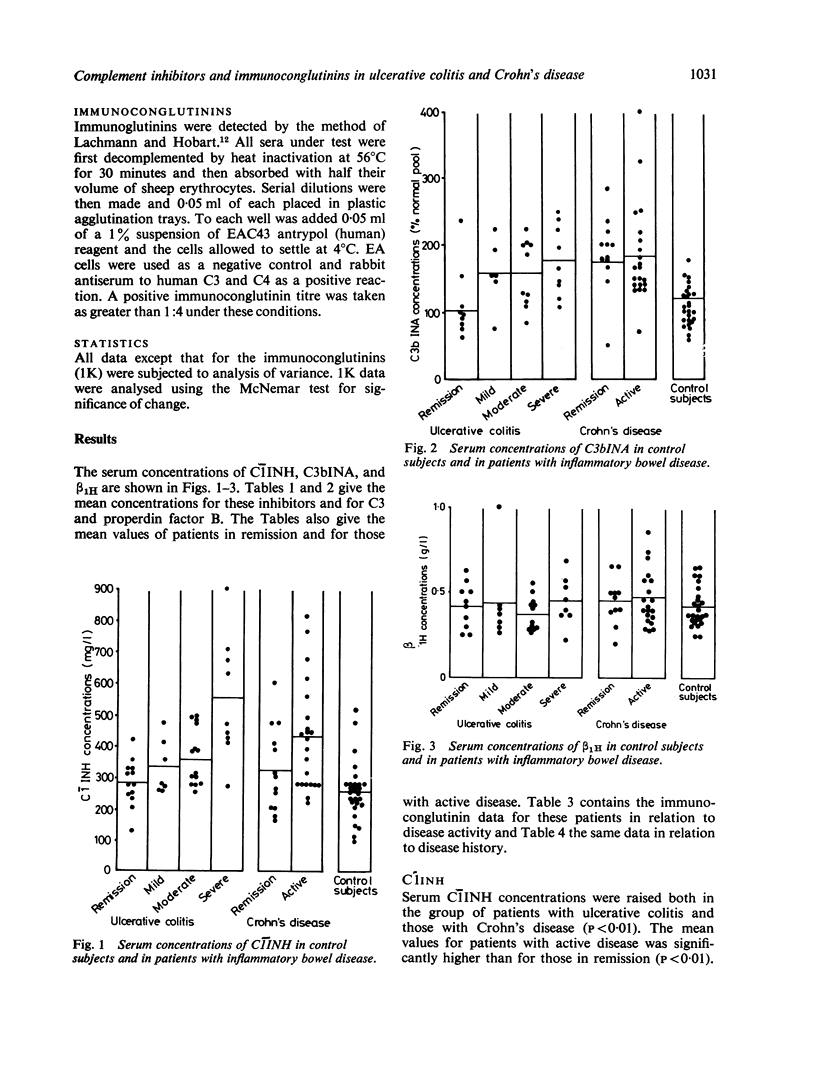
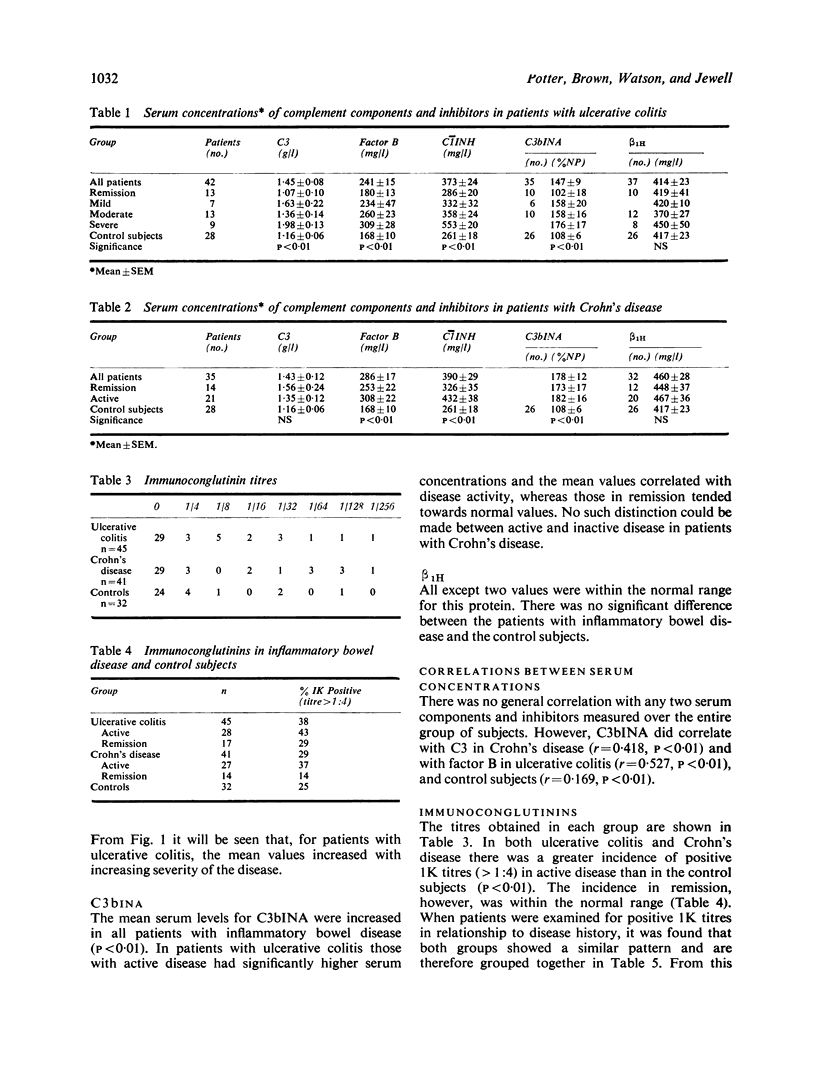
The serum concentrations of the complement inactivators C1INH, C3bINA and beta 1H have been determined in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease and their correlation with C3 and properdin factor B examined. The incidence of immunoconglutinins (1K) in these patients was investigated. Raised serum concentrations of C1INH and C3bINA have been found in patients with active disease, but no significant alteration was found in serum concentration of beta 1H. An increasing incidence of positive 1K titres was found with increased length of disease history. These results suggest continuing complement activation in these diseases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamkin D., Stitzel A., Urmson J., Farnett M. L., Post E., Spitzer R. Activity of the alternative pathway of complement in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1978 Oct;93(4):604–608. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80895-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baklien K., Brandtzaeg P. Comparative mapping of the local distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease of the colon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Nov;22(2):197–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard J., Shiner M. Evidence of cytotoxicity in ulcerative colitis from immunofluorescent staining of the rectal mucosa. Lancet. 1974 May 25;1(7865):1014–1017. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90416-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen G. E., Kirsner J. B. Positive epinephrine skin test for "circulating endotoxin" in inflammatory disease of the intestine. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Dec;44(6):642–647. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.6.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Scott D. M., Pussell B. A., Peters D. K. Metabolism of human beta 1H: studies in man and experimental animals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):397–404. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Dombal F. T., Burton I. L., Clamp S. E., Goligher J. C. Short-term course and prognosis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):435–443. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe W. F., Booth C. C., Brown D. L. Evidence for complement-binding immune complexes in adult coeliac disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1973 Feb 24;1(7800):402–403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein P. A., Kaplan S. R., Thayer W. R., Jr The alternate complement pathway in inflammatory bowel disease. Quantitation of the C3 proactivator (factor B) protein. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebbers J. O., Otto H. F. Evidence for local immune complexes in ulcerative colitis. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1978 May-Jun;41(5-6):329–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Pickering R. J., Naff G., Snyderman R., Mergenhagen S. E., Good R. A. Decreased properdin activity in acute glomerulonephritis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(6):592–598. doi: 10.1159/000230780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Shin H. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Interactions of the complement system with endotoxic lipopolysaccharide: consumption of each of the six terminal complement components. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1049–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Potter B. J., Jewell D. P. C3 metabolism in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jun;28(3):490–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Potter B. J., Jewell D. P. Humoral immune system in inflammatory bowel disease: I. Complement levels. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):749–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Potter B. J., Jewell D. P. Immune complexes in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Aug;29(2):187–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell D. P., MacLennan I. C. Circulating immune complexes in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalwinsky D. K., Urmson J. R., Stitzel A. E., Spitzer R. E. Activation of the alternative pathway of complement in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Nov;88(5):745–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Ten Bensel R. Serial complement component alterations in acute glomerulonephritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Feb;4(2):191–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake A. M., Stitzel A. E., Urmson J. R., Walker W. A., Spitzer R. E. Complement alterations in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1374–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H., Binder V., Daugharty H., Svehag S. E. Circulating immune complexes in ulcerative colitis. I. Correlation to disease activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jan;31(1):72–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter B. J., Hodgson H. J., Mee A. S., Jewell D. P. Clq metabolism in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Gut. 1979 Nov;20(11):1012–1019. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.11.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUELOVE S. C., WITTS L. J. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis; final report on a therapeutic trial. Br Med J. 1955 Oct 29;2(4947):1041–1048. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4947.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teisberg P., Gjone E. Humoral immune system activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(5):545–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M., Eastwood M. A. Proceedings: Serum complement components C3 and C4 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1974 Oct;15(10):835–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


