Abstract
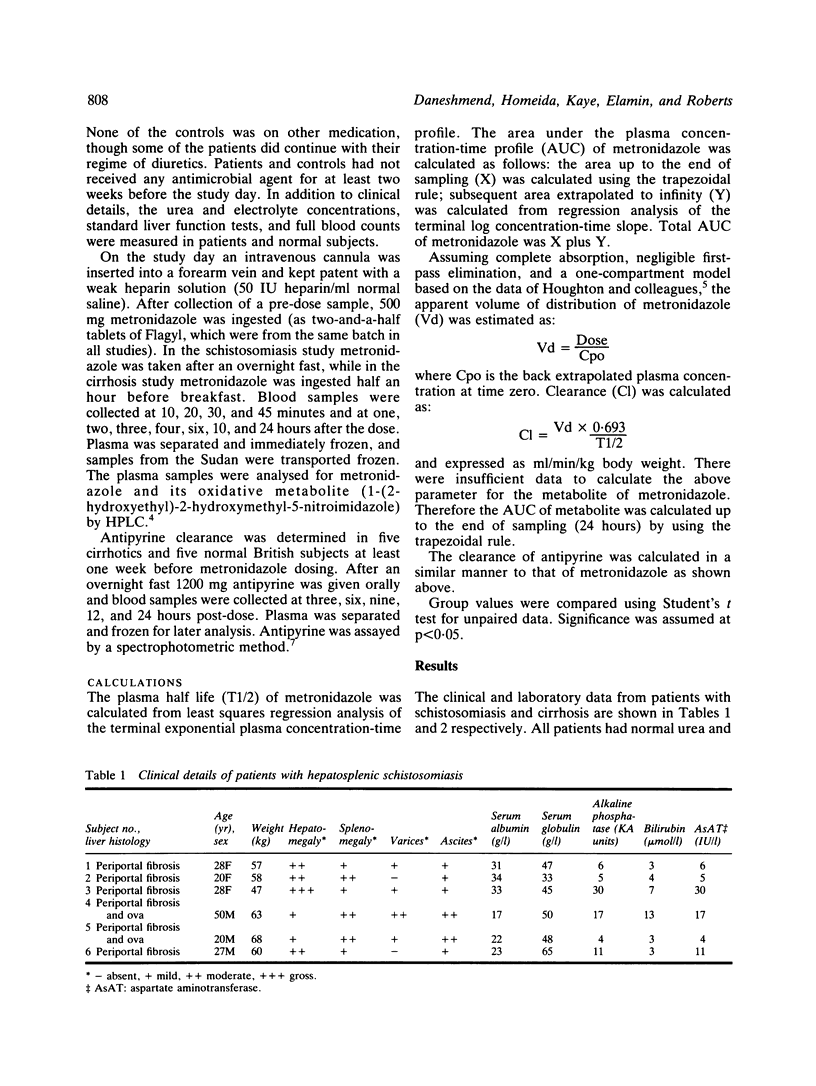
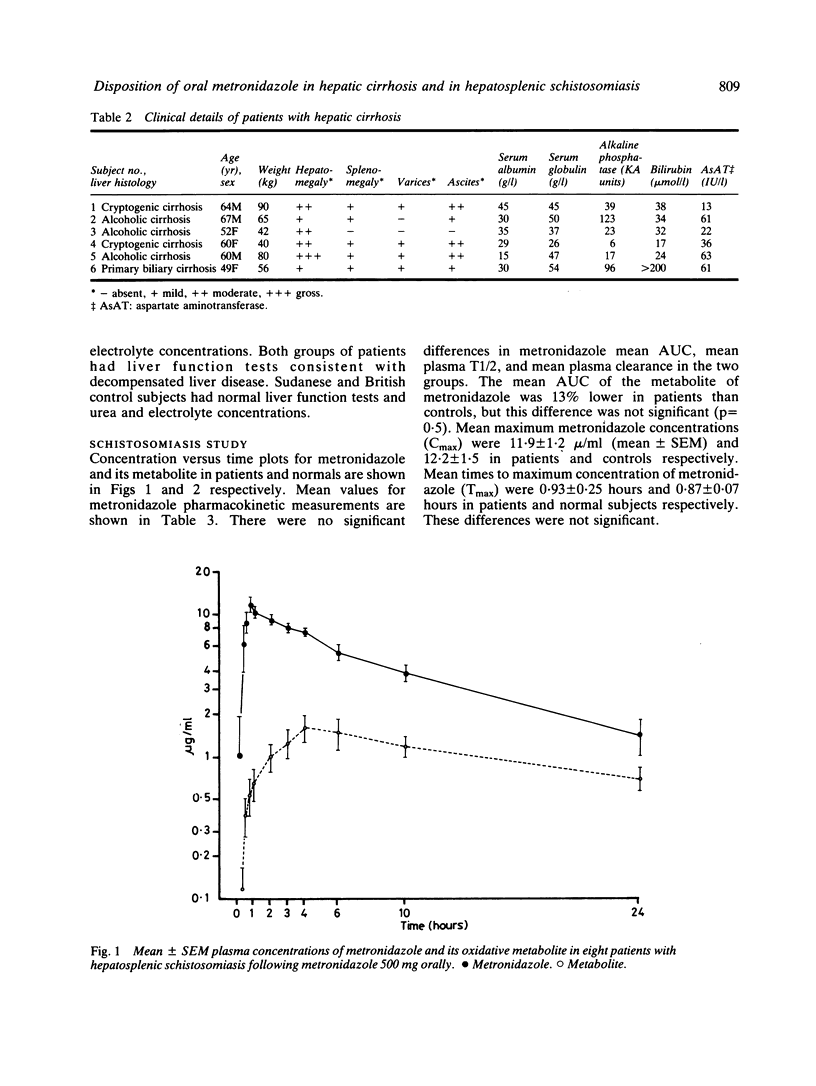
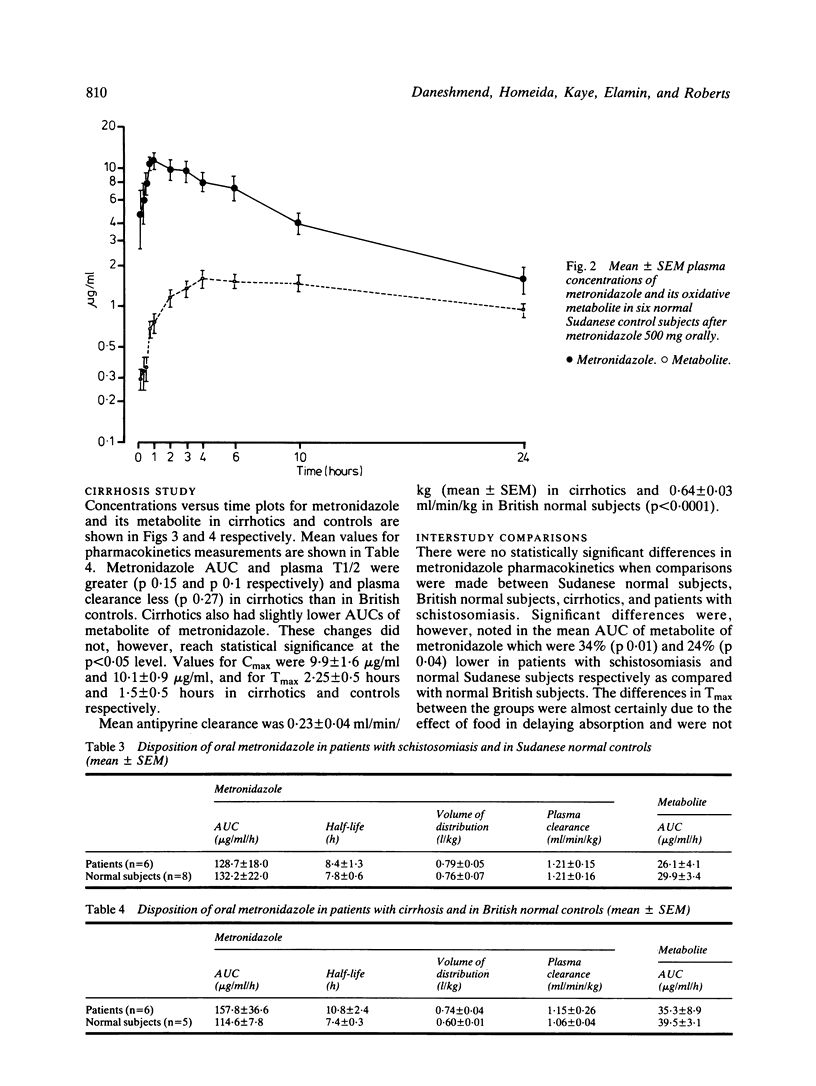
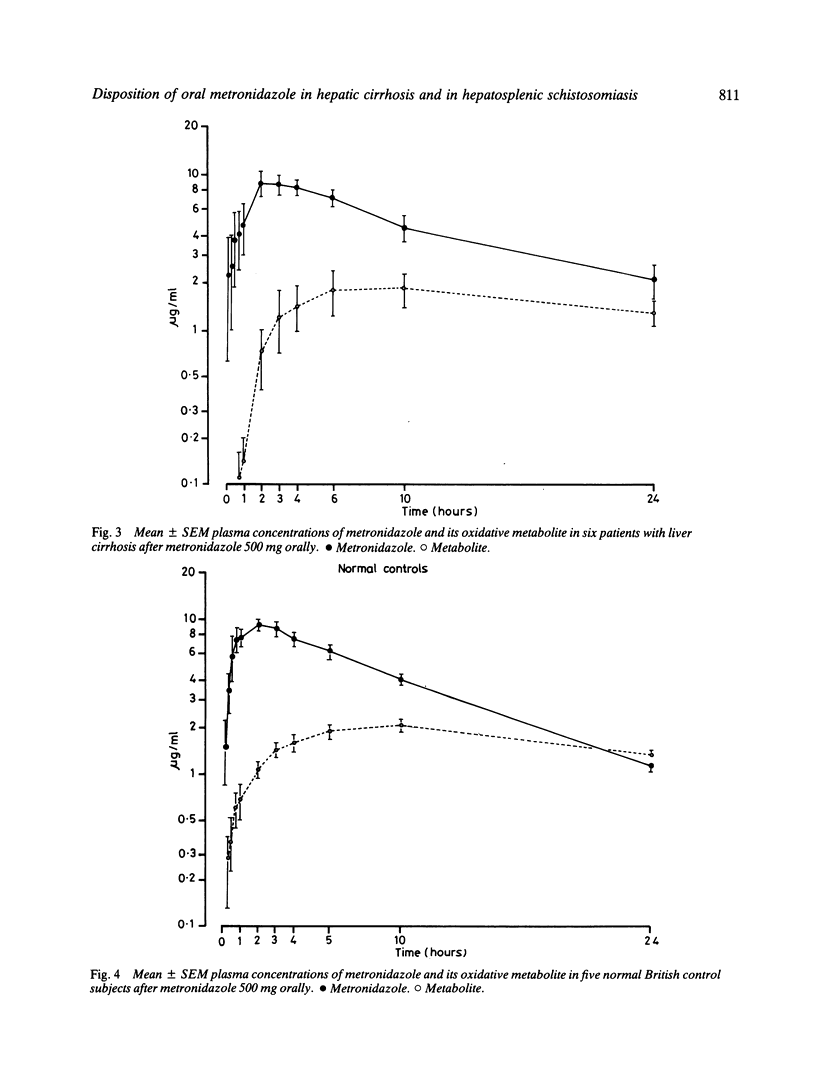
The pharmacokinetics of metronidazole 500 mg orally were determined in patients with hepatosplenic schistosomiasis and normal controls in the Sudan, and in cirrhotics and normal controls in Bristol. Plasma metronidazole levels were above the minimum inhibitory concentration of most susceptible anaerobic bacteria for four to six hours post-dose in all groups. Liver disease did not markedly influence the disposition of single oral doses of metronidazole. Cirrhotics showed some prolongation of metronidazole half-life, and somewhat greater metronidazole concentrations 24 hours after the dose. Concentrations of the oxidative metabolite of metronidazole were lower in Sudanese patients and normal controls than in normal British subjects. In chronic liver disease adjustment of metronidazole dosage is probably not required provided renal function is unimpaired.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brogden R. N., Heel R. C., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Metronidazole in anaerobic infections: a review of its activity, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1978 Nov;16(5):387–417. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197816050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha Y. N., Edwards R. Effect of Schistosoma mansoni infection on the hepatic drug-metabolizing capacity of mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Nov;199(2):432–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulaid A., Houghton G. W., Lewellen O. R., Smith J., Thorne P. S. Determination of metronidazole and its two major metabolites in biological fluids by high pressure liquid chromatography. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;6(5):430–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb04608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homeida M., Salih S. Y., Branch R. A. Drug metabolism in hepatosplenic schistosomiasis in the Sudan: a study with antipyrine. Gut. 1978 Sep;19(9):808–811. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.9.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton G. W., Smith J., Thorne P. S., Templeton R. The pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous metronidazole in man. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Sep;5(5):621–623. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.5.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton G. W., Thorne P. S., Smith J., Templeton R., Collier J. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of metronidazole in healthy female volunteers following either a single oral or intravenous dose. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;8(4):337–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., Law G. L., Parnell E. W. The metabolism of metronidazole (1-2'-hydroxyethyl-2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole). Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 May;15(5):515–519. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., McFadzean J. A., Ormerod W. E. The fate of metronidazole and tis implications in chemotherapy. Xenobiotica. 1975 Apr;5(4):223–235. doi: 10.3109/00498257509052069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye C. M., Sankey M. G., Thomas L. A. A rapid and specific semi-micro method involving high-pressure liquid chromatography for the assay of metronidazole in plasma, saliva, serum, urine and whole blood. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 May;9(5):528–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb05856.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Lindmark D. G., Müller M. Biliary and renal excretion, hepatic metabolism, and hepatic subcellular distribution of metronidazole in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(18):2247–2254. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander A., Kahlmeter G., Kamme C., Ursing B. Bioavailability of metronidazole in fasting and non-fasting healthy subjects and in patients with Crohn's disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Aug 17;12(1):69–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00561408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. H., Read A. E., Speller D. C. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy with metronidazole. Gut. 1982 Jan;23(1):1–7. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui W. H., Buttar H. S. Metronidazole: a comparative study on the intravaginal absorption, metabolism and disposition of a single product and commercial formulation. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1979 May;239(1):4–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stambaugh J. E., Feo L. G., Manthei R. W. The isolation and identification of the urinary oxidative metabolites of metronidazole in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jun;161(2):373–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


