Abstract
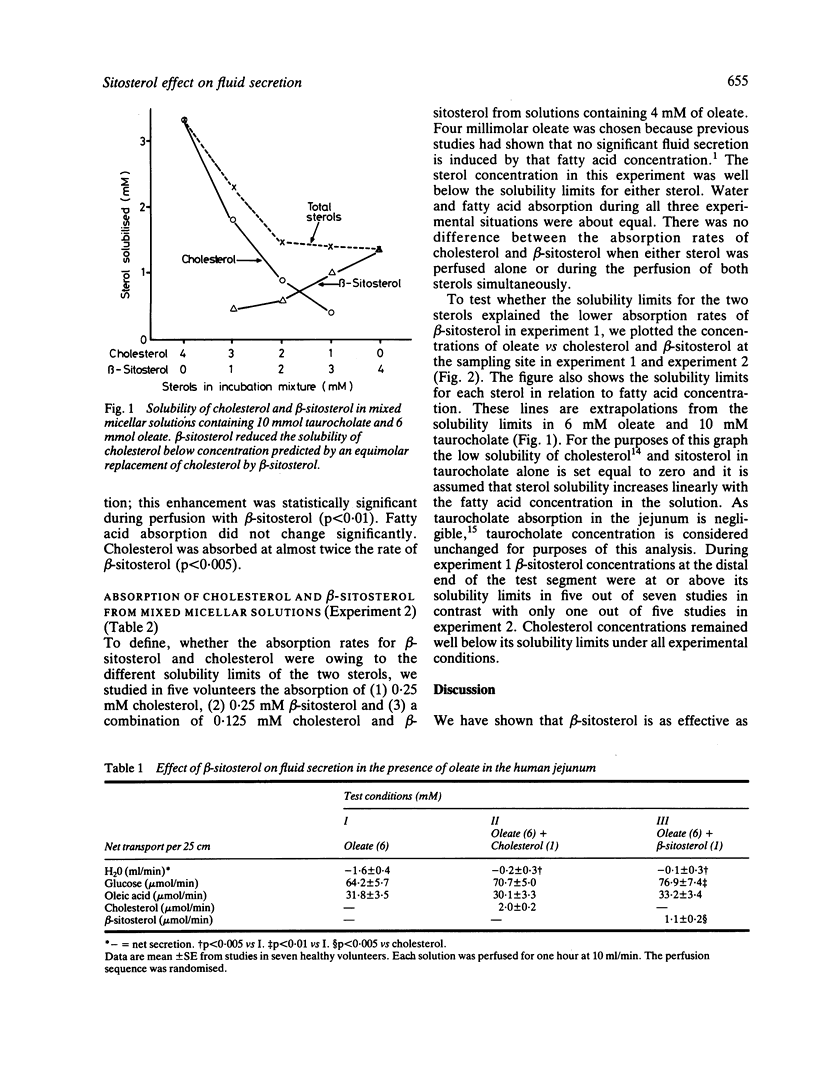
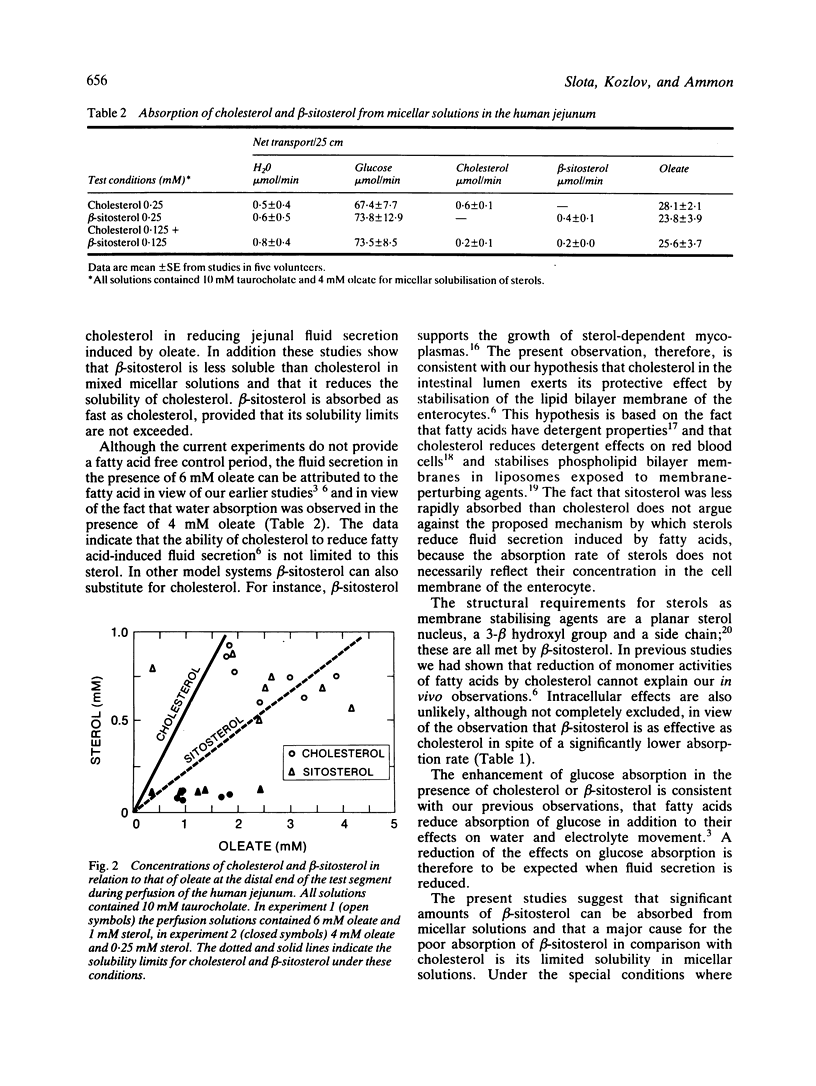
Jejunal fluid secretion induced by perfusion with oleic acid can be reduced by the addition of cholesterol. The present study was performed to test the specificity of this effect by comparing the effects of cholesterol with that of a plant sterol, beta-sitosterol during perfusion of the jejunum in healthy volunteers. In addition, we compared the solubilities of cholesterol and beta-sitosterol in micellar solutions and their jejunal absorption rates. One millimolar beta-sitosterol was as effective as 1 mM cholesterol in reducing jejunal fluid secretion induced by 6 mM oleate (n = 7). In mixed micellar solutions consisting of 10 mM taurocholate and 6 mM oleate, solubility of beta-sitosterol is about one third of cholesterol solubility. When cholesterol was gradually replaced by beta-sitosterol in the incubation mixture, beta-sitosterol reduced cholesterol solubility to a greater extent than would be expected from an equimolar replacement of cholesterol by beta-sitosterol. Absorption of beta-sitosterol was limited by its solubility in mixed micellar solutions and both sterols were absorbed at equal rates as long as their solubility limits were not exceeded (n = 5).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammon H. V., Phillips S. F. Inhibition of ileal water absorption by intraluminal fatty acids. Influence of chain length, hydroxylation, and conjugation of fatty acids. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):205–210. doi: 10.1172/JCI107539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Thomas P. J., Phillips S. F. Effects of long chain fatty acids on solute absorption: perfusion studies in the human jejunum. Gut. 1977 Oct;18(10):805–813. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.10.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Thomas P. J., Phillips S. F. Effects of oleic and ricinoleic acids on net jejunal water and electrolyte movement. Perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):374–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI107569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright-Asare P., Binder H. J. Stimulation of colonic secretion of water and electrolytes by hydroxy fatty acids. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broor S. L., Slota T., Ammon H. V. Cholesterol reduces the effects of dihydroxy bile acids and fatty acids on water and solute transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):920–925. doi: 10.1172/JCI109746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., De Kruyff B. The function of sterols in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):109–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Wilson J. D. Regulation of cholesterol metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 21;282(21):1179–1183. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005212822105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunwald C. Quantitative analysis of free phytosterols by gas chromatography using stationary phase OV-101. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:16–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F. THE FUNCTION OF BILE SALTS IN FAT ABSORPTION. THE SOLVENT PROPERTIES OF DILUTE MICELLAR SOLUTIONS OF CONJUGATED BILE SALTS. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:57–68. doi: 10.1042/bj0890057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nes W. R. Role of sterols in membranes. Lipids. 1974 Aug;9(8):596–612. doi: 10.1007/BF02532509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang K. Y., Miller K. W. Cholesterol modulates the effects of membrane perturbers in phospholipid vesicles and biomembranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 20;511(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampone A. J., Machida C. M. Mode of action of lecithin in suppressing cholesterol absorption. J Lipid Res. 1981 Jul;22(5):744–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Grundy S. M. Metabolism of beta-sitosterol in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):952–967. doi: 10.1172/JCI106315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozawa S., Araki Y., Utsumi K., Oda T. Stabilizing effects of cholesterol on changes in membrane permeability and potential induced in red blood cells by lysolecithin. Physiol Chem Phys. 1979;11(2):161–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds W. J., Hofmann A. F., Theodor E. Absorption of cholesterol from a micellar solution: intestinal perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):874–890. doi: 10.1172/JCI105587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbiah M. T. Significance of dietary plant sterols in man and experimental animals. Mayo Clin Proc. 1971 Aug;46(8):549–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén C., Borgström B. Absorption and lymphatic transport of cholesterol and sitosterol in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1969 Mar;10(2):179–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén C., Borgström B. Absorption and lymphatic transport of cholesterol in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):596–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén C., Borgström B. Intestinal absorption and lymphatic transport of cholesterol in the rat: influence of the fatty acid chain length of the carrier triglyceride. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jul;10(4):351–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén C. Influence of blood supply on lipid uptake from micellar solutions by the rat small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 2;203(3):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamesue N., Inoue T., Juniper K., Jr Solubility of cholesterol in bile salt-lecithin model systems. Am J Dig Dis. 1973 Aug;18(8):670–678. doi: 10.1007/BF01072038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangedahl T. N., Thistle J. L., Hofmann A. F., Matseshe J. W. Effect of beta-sitosterol alone or in combination with chenic acid on cholesterol saturation of bile and cholesterol absorption in gallstone patients. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1341–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Sandberg R. J., Phillips S. F. A comparison of stable and 14 C-labelled polyethylene glycol as volume indicators in the human jejunum. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):812–815. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.10.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


