Abstract
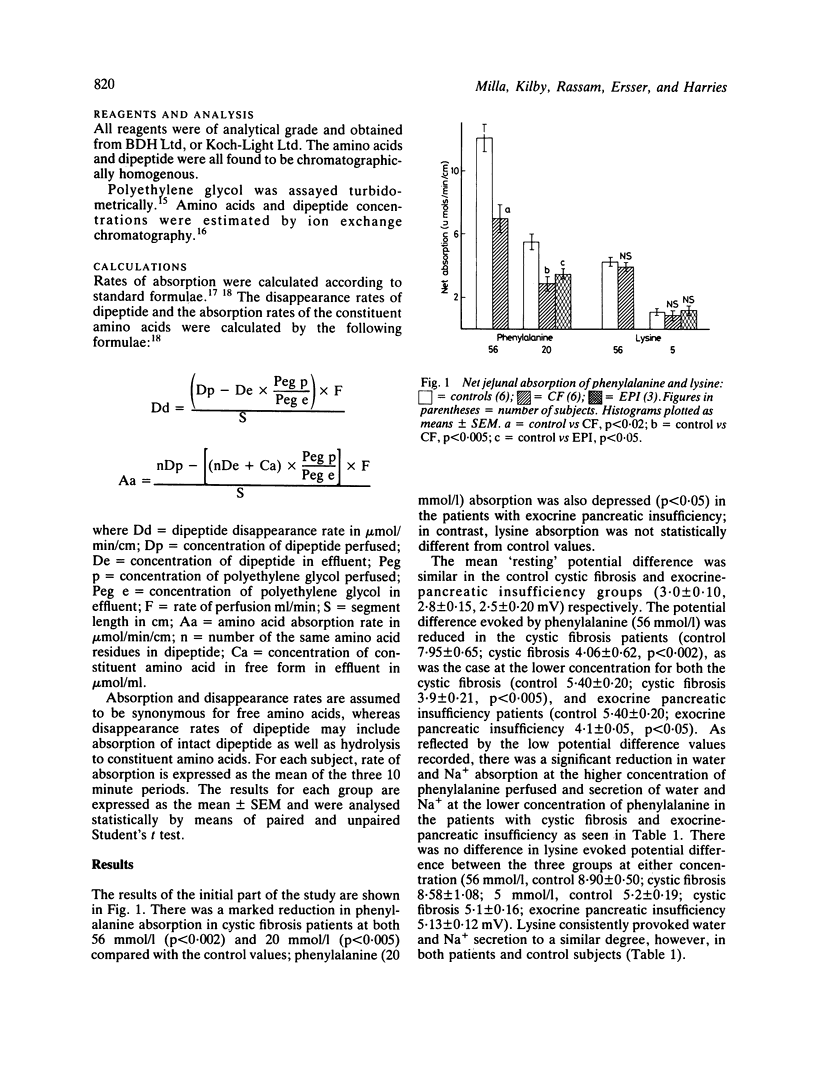
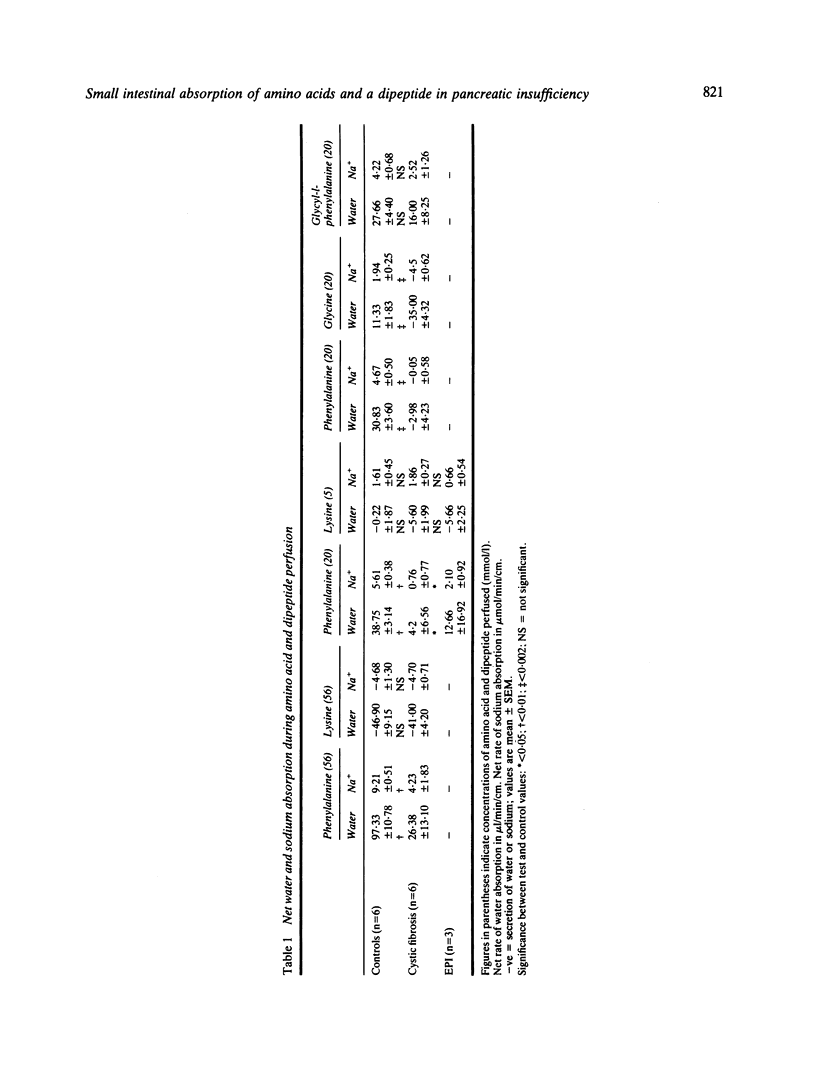
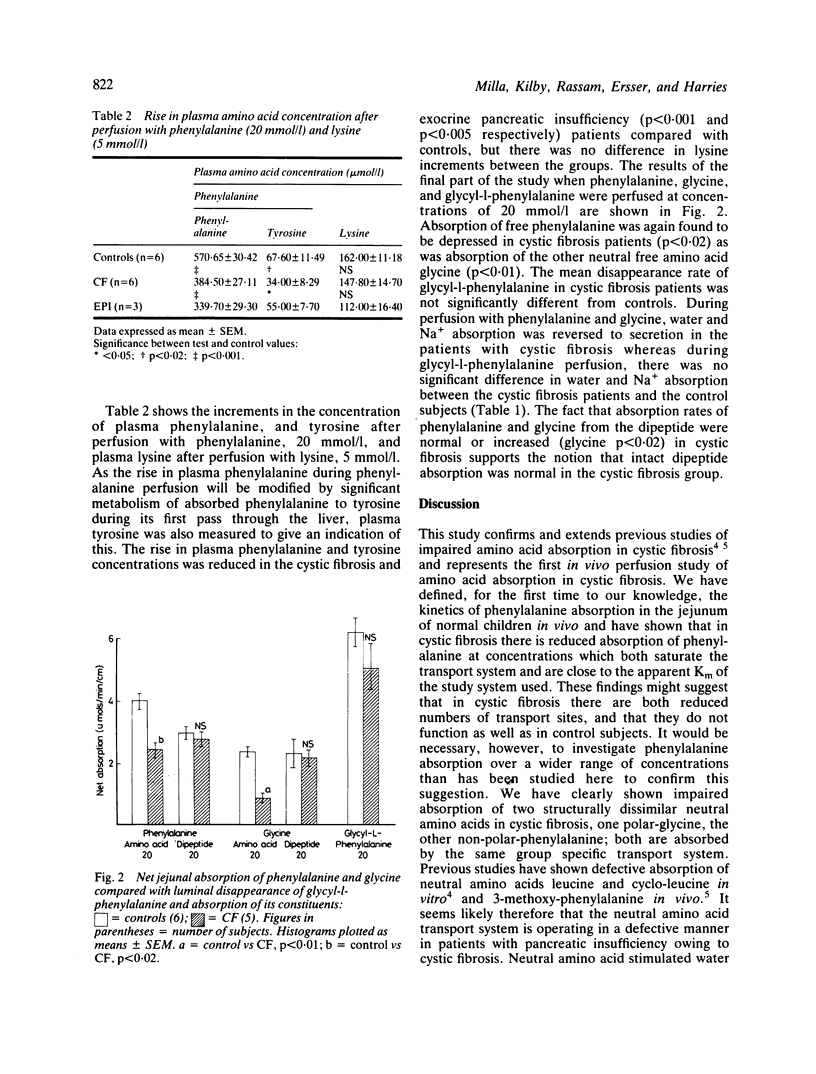
In this study a perfusion technique has been used to investigate in vivo jejunal absorption and transmural potential difference evoked by the neutral amino acids phenylalanine (56 or 20 mmol/l) and glycine (20 mmol/l), the dibasic amino acid lysine (56 or 5 mmol/l), and a dipeptide glycyl-l-phenylalanine (20 mmol/l) in 11 children with pancreatic insufficiency due to cystic fibrosis and in three children with other causes of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Net absorption and potential difference evoked by phenylalanine in both cystic fibrosis and pancreatic insufficiency, and net absorption of glycine in cystic fibrosis were significantly reduced; but the absorption of lysine and glycyl-l-phenylalanine was normal. Absorption of the constituent amino acids from the dipeptide was normal or increased in cystic fibrosis. Thus, these studies show a defect in active absorption of neutral amino acids in cystic fibrosis with pancreatic insufficiency and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. We speculate that pancreatic factors participate in neutral amino acid absorption.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adibi S. A. Intestinal transport of dipeptides in man: relative importance of hydrolysis and intact absorption. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2266–2275. doi: 10.1172/JCI106724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggett P. J., Cavanagh N. P., Matthew D. J., Pincott J. R., Sutcliffe J., Harries J. T. Shwachman's syndrome. A review of 21 cases. Arch Dis Child. 1980 May;55(5):331–347. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.5.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batt R. M., Bush B. M., Peters T. J. Biochemical changes in the jejunal mucosa of dogs with naturally occurring exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Gut. 1979 Aug;20(8):709–715. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.8.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellier M. D., Holdsworth C. D., Perrett D. Dibasic amino acid absorption in man. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):613–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON E. D., BONDY D. C., BROITMAN S. A., FORDTRAN J. S. Validity of polyethylene glycol in estimating intestinal water volume. Gastroenterology. 1963 Jun;44:761–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong W. K., Seetharam B., Alpers D. H. Effect of exchange exocrine pancreatic insufficiency on small intestine in the mouse. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jun;74(6):1277–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. M. Intestinal absorption of peptides. Physiol Rev. 1975 Oct;55(4):537–608. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1975.55.4.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCollum J. P., Muller D. P., Harries J. T. Test meal for assessing intraluminal phase of absorption in childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Nov;52(11):887–889. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.11.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milla P. J., Aggett P. J., Wolff O. H., Harries J. T. Studies in primary hypomagnesaemia: evidence for defective carrier-mediated small intestinal transport of magnesium. Gut. 1979 Nov;20(11):1028–1033. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.11.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin C. L., Roy C. C., Lasalle R., Bonin A. Small bowel mucosal dysfunction in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1976 Feb;88(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80984-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey F., Drillet F., Schmitz J., Rey J. Influence of flow rate on the kinetics of the intestinal absorption of glucose and lysine in children. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jan;66(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seakins J. W., Ersser R. S., Gibbons I. S. Studies on the origin of faecal amino acids in cystic fibrosis. Gut. 1970 Jul;11(7):600–609. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.7.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharam B., Grimme N., Goodwin C., Alpers D. H. Differential sensitivity of intestinal brush border enzymes to pancreatic and lysosomal proteases. Life Sci. 1976 Jan 1;18(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S., Lowenstein L. M., Wallace A. Comparison of the transport characteristics of L-lysine by rat intestine and kidney cortex. Gastroenterology. 1968 Sep;55(3):386–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmerling D. H., Forrer J. C., Prader A. Fecal fat and nitrogen in healthy children and in children with malabsorption or maldigestion. Pediatrics. 1970 Nov;46(5):690–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B., Kumar P. J., Perrett D., Clark M. L., Dawson A. M. Amino acid and peptide absorption in patients with coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis. Gut. 1974 Jan;15(1):1–8. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. Interrelationships between the absorptions of glucose, sodium and water by the normal human jejunum. Clin Sci. 1969 Feb;36(1):119–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


