Abstract
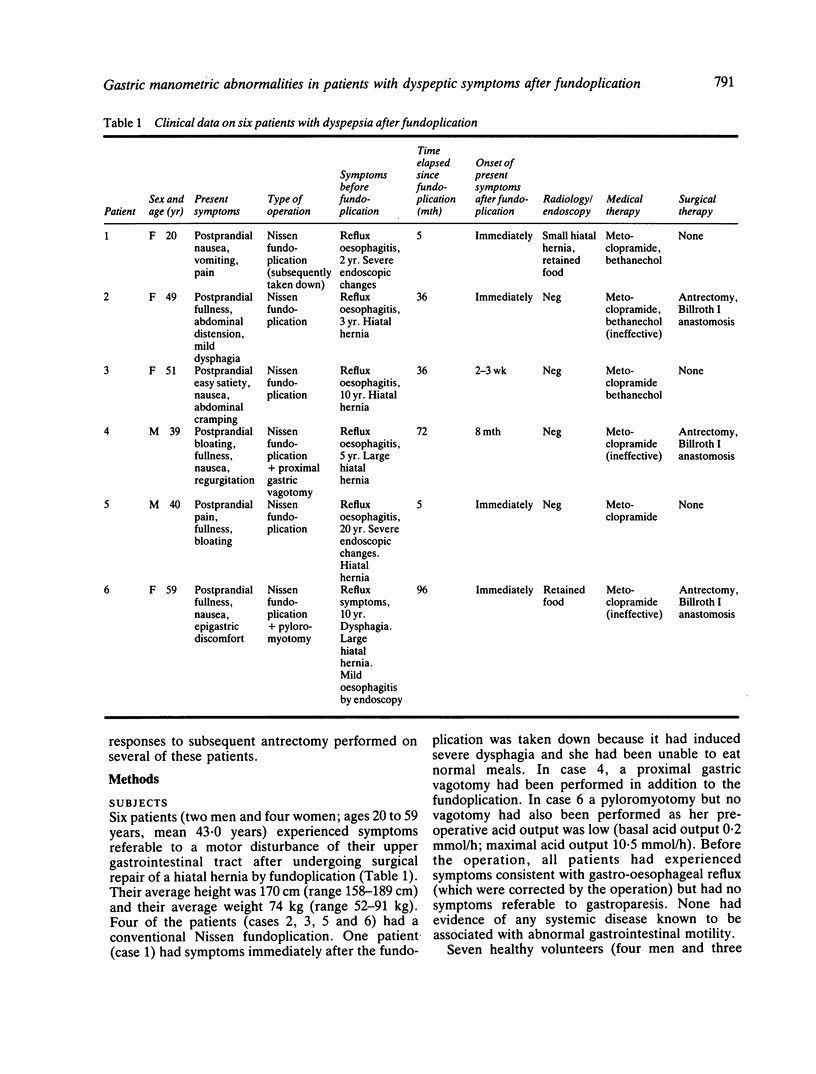
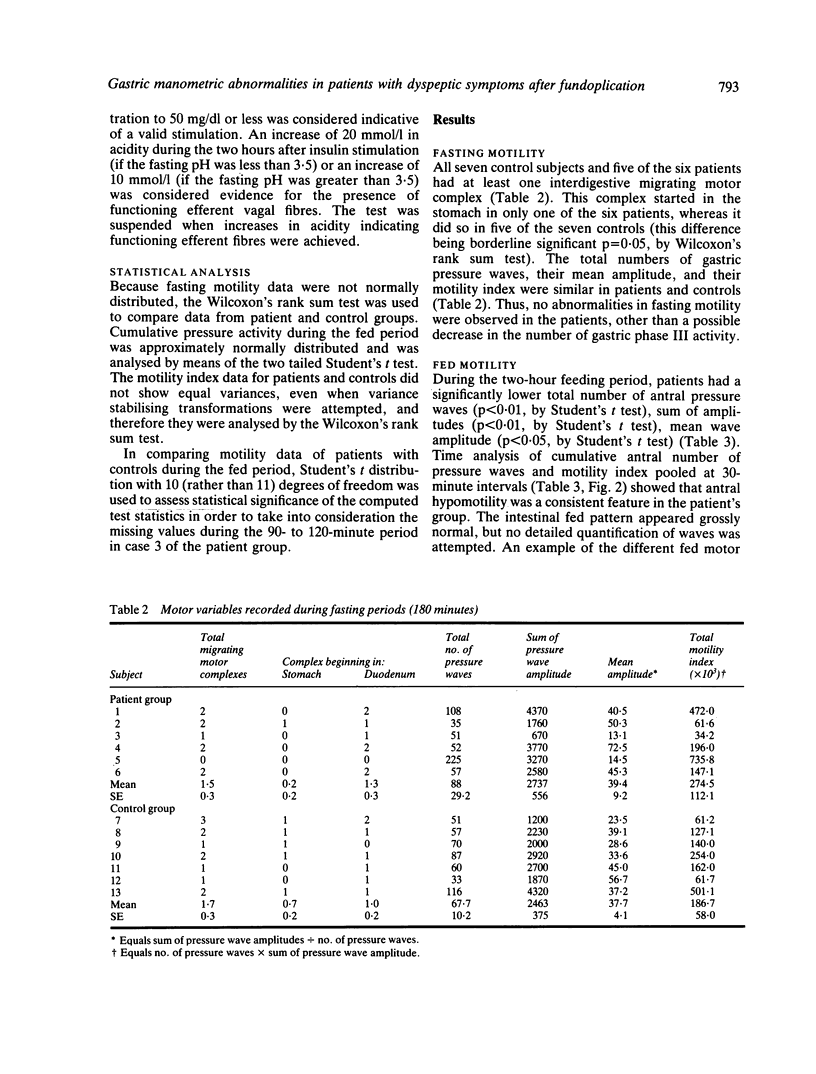
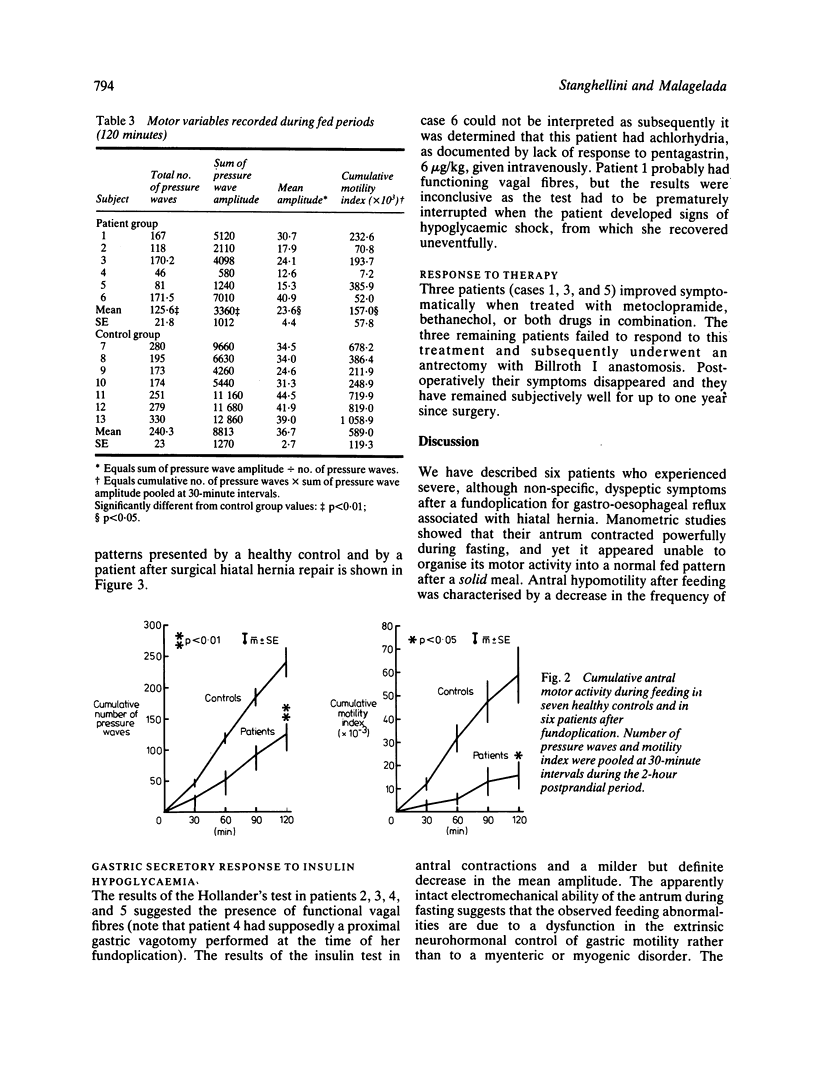
We describe six patients in whom severe dyspeptic symptoms developed after fundoplication. The symptoms began immediately after operation (three patients) or shortly thereafter (three and eight months). There were no other known predisposing factors to gastroparesis. Seven, age-matched, healthy volunteers served as controls. Pressure activity from antrum (two sites), duodenum (two sites), and jejunum (one site) was recorded by a low compliance perfusion system connected to external strain gauge transducers. Activity was recorded for three hours during fasting and for two hours after the ingestion of a solid and a liquid meal. To determine whether an inadvertent vagotomy had been performed, basal acid output and the response to insulin (Hollander's test) were measured on a separate day. Manometric studies revealed postprandial hypomotility in these patients, whereas fasting antral and intestinal activities were normal. Acid output increased in all patients during insulin induced hypoglycaemia. In three patients, an antrectomy was subsequently performed, and they were relieved of their symptoms. We conclude that, after fundoplication, symptoms associated with postprandial antral hypomotility may develop in some patients. The pathophysiologic mechanism is unknown, but a positive acid response to insulin induced hypoglycaemia does not support the occurrence of incidental vagotomy. We do not know the prevalence of this motor abnormality among asymptomatic patients with prior fundoplication. A favourable symptomatic response to antrectomy in several of our patients, however, suggests that the symptoms were related to antral motor dysfunction.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndorfer R. C., Stef J. J., Dodds W. J., Linehan J. H., Hogan W. J. Improved infusion system for intraluminal esophageal manometry. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jul;73(1):23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGIN W. F., JORDAN P. H., Jr Gastric atonia and delayed gastric emptying after vagotomy for obstructing ulcer. Am J Surg. 1959 Oct;98:612–616. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(59)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldi F., Corinaldesi R., Ferrarini F., Stanghellini V., Miglioli M., Barbara L. Gastric secretion and emptying of liquids in reflex esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Oct;26(10):886–889. doi: 10.1007/BF01309491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker M. C., Cobden I., Axon A. T. Proximal stomach and antrum in stomach emptying. Gut. 1979 Apr;20(4):309–311. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.4.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Code C. F., Marlett J. A. The interdigestive myo-electric complex of the stomach and small bowel of dogs. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):289–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke A. R. Control of gastric emptying and motility. Gastroenterology. 1975 Apr;68(4 Pt 1):804–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison J. S., Grundy D. Modulation of single vagal efferent fibre discharge by gastrointestinal afferents in the rat. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:69–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan I. A., Harding L. K., Keighley M. R., Griffin D. W., Collis J. L. Abnormalities of gastric emptying and pyloric reflux in uncomplicated hiatus hernia. Br J Surg. 1977 Dec;64(12):847–848. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800641203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois A., Gross H. A., Ebert M. H., Castell D. O. Altered gastric emptying and secretion in primary anorexia nervosa. Gastroenterology. 1979 Aug;77(2):319–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois A., Gross H. A., Richter J. E., Ebert M. H. Effect of bethanechol on gastric functions in primary anorexia nervosa. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Jul;26(7):598–600. doi: 10.1007/BF01367671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk D. L., Anuras S., Christensen J. Chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1978 May;74(5 Pt 1):922–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grivel M. L., Ruckebusch Y. The propagation of segmental contractions along the small intestine. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):611–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann G., Johnson V. Management of prolonged gastric retention after vagotomy and drainage. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970 Jun;130(6):1044–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillemand B. Evacuation gastrique et sclérose latérale amyotrophique. Lille Med. 1979 Jan;24(1):13–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane F. B., Dimagno E. P., Malagelada J. R. Duodenogastric reflux in humans: its relationship to fasting antroduodenal motility and gastric, pancreatic, and biliary secretion. Gastroenterology. 1981 Oct;81(4):726–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latchis L. S., Canter J. W., Shorb P. E., Jr Delayed gastric emptying following operations for peptic ulcer. Am Surg. 1972 Apr;38(4):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis T. D., Daniel E. E. Gastroduodenal motility in a case of dystrophia myotonica. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jul;81(1):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Rees W. D., Mazzotta L. J., Go V. L. Gastric motor abnormalities in diabetic and postvagotomy gastroparesis: effect of metoclopramide and bethanechol. Gastroenterology. 1980 Feb;78(2):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeroff J. C., Schreiber D. S., Trier J. S., Blacklow N. R. Abnormal gastric motor function in viral gastroenteritis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):370–373. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miolan J. P., Roman C. Discharge of efferent vagal fibers supplying gastric antrum: indirect study by nerve suture technique. Am J Physiol. 1978 Oct;235(4):E366–E373. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.4.E366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAISH J. M., CAPPER W. M., BROWN N. J. Intestinal pseudoobstruction with steatorrhoea. Gut. 1960 Mar;1:62–66. doi: 10.1136/gut.1.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahai F. Pseudo-obstruction of the small bowel. Bristol Med Chir J. 1969 Oct;84(312):209–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen T. S., Eigenbrodt E. H., Keoshian L. A., Bunker C., Johnson L. Alterations in muscular and electrical activity of the stomach following vagotomy. Arch Surg. 1967 Jun;94(6):821–835. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1967.01330120075015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees W. D., Go V. L., Malagelada J. R. Antroduodenal motor response to solid-liquid and homogenized meals. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1438–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saleh J. W., Lebwohl P. Metoclopramide-induced gastric emptying in patients with anorexia nervosa. Am J Gastroenterol. 1980 Aug;74(2):127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. P., Staley C. J., Hammond J. B. Carcinoma of the esophagus involving the vagus nerves associated with gastric retention simulating pyloric obstruction. A case report. Am J Dig Dis. 1968 Sep;13(9):842–846. doi: 10.1007/BF02233102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. D., Stewart J. J., Bass P. The effect of parietal cell and truncal vagotomy on gastric and duodenal contractile activity of the unanesthetized dog. Ann Surg. 1974 Jun;179(6):853–858. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197406000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur B. G., Kelly K. A. Effect of proximal gastric, complete gastric, and truncal vagotomy on canine gastric electric activity, motility, and emptying. Ann Surg. 1973 Sep;178(3):295–303. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197309000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You C. H., Lee K. Y., Chey W. Y., Menguy R. Electrogastrographic study of patients with unexplained nausea, bloating, and vomiting. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):311–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


