Abstract
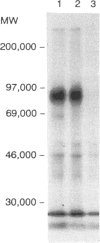
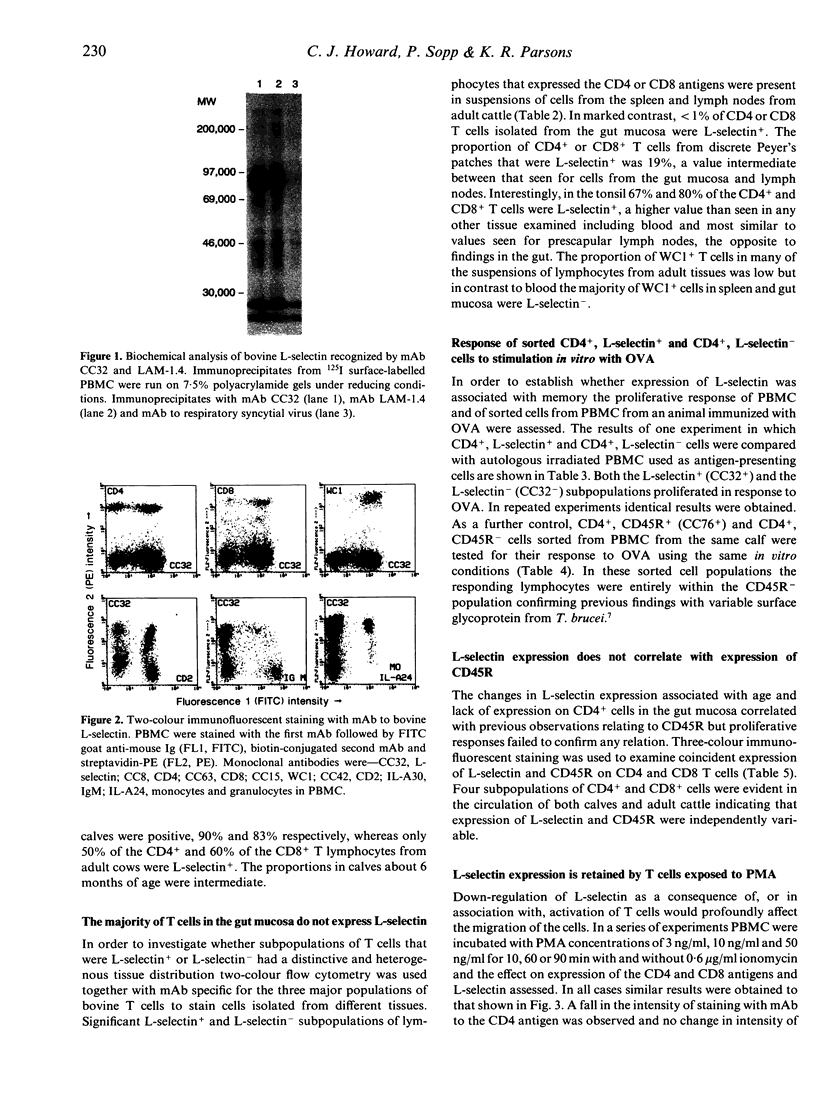
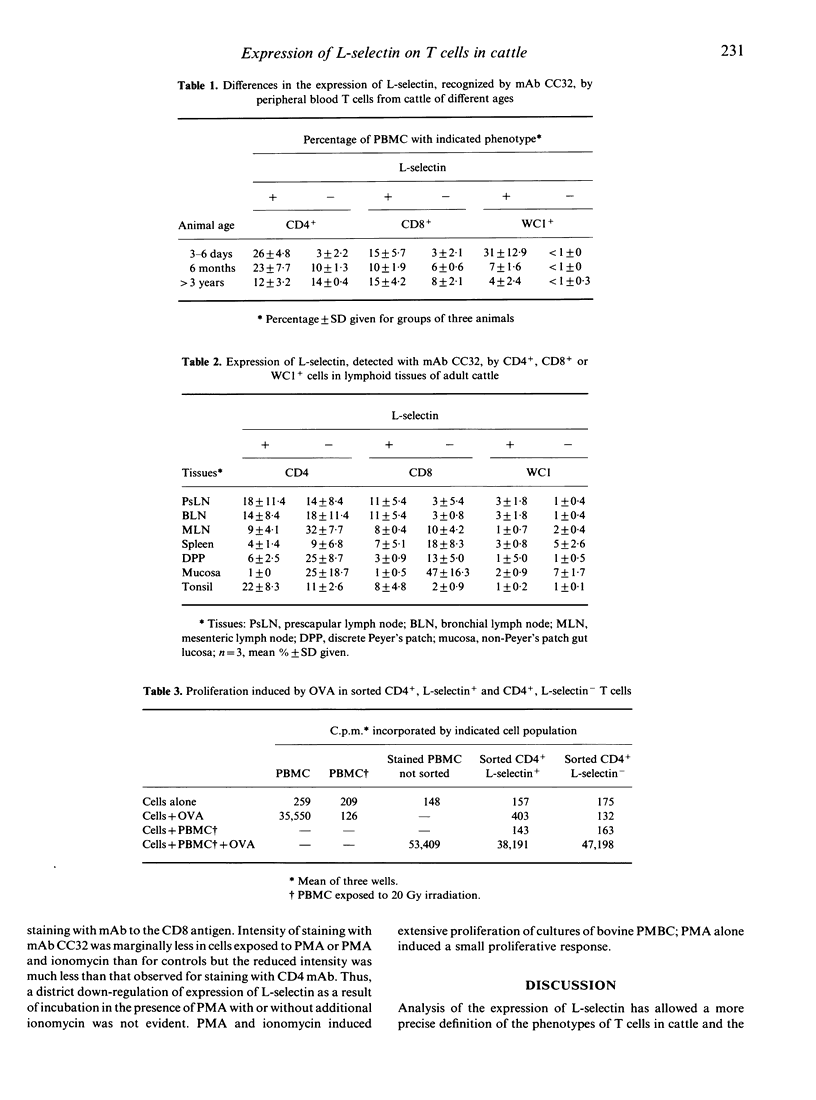
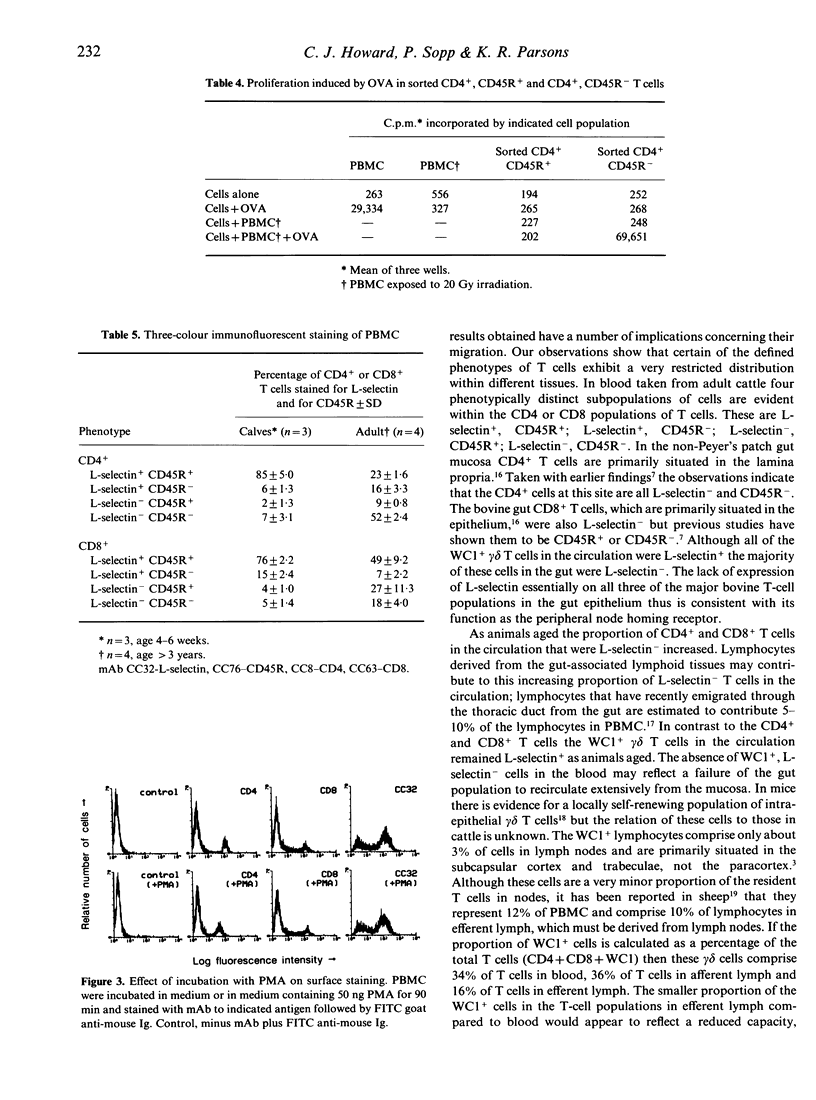
L-selectin (LECAM-1, LAM-1) was expressed by a high proportion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, as well as almost all of the gamma delta T-cell receptor (TcR)+ (WC1+) T cells, isolated from blood, lymph nodes or tonsils. CD4+ T cells in the lamina propria of the gut villi and CD8+ T cells in the villous epithelium as well as the majority of WC1+ T cells in the gut mucosa were L-selectin-. The proportion of T cells from Peyer's patches that synthesized the molecule was intermediate between the value for blood and gut mucosa. Expression of L-selectin therefore marks T cells in cattle with a distinct tissue distribution that correlates with its function as the peripheral node homing receptor. The proportion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the circulation that were L-selectin+ decreased with age. Unlike CD45R, expression of L-selectin was not related to CD4 T-cell memory as judged by proliferation in transformation assays to soluble antigen. Three-colour immunofluorescent staining demonstrated four subpopulations of CD4 and CD8 T lymphocytes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) that were CD45R+, L-selectin+; CD45R+, L-selectin-; CD45R-, L-selectin+; CD45R-, L-selectin-. CD4(4) memory cells were CD45R- and L-selectin+ or L-selectin-. Taken with earlier studies the reported observations demonstrated that only one of the four phenotypes of the CD4+ T cells in blood is present in the lamina propria of the gut villi and these are CD45R-, L-selectin-. Two of the four phenotypes of CD8+ T cells were present in the gut epithelium; these were CD45R+, L-selectin- or CD45R-, L-selectin-. Expression of the bovine molecule was not rapidly down-regulated on T cells following activation by exposure to phorbol myristate acetate.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bührer C., Berlin C., Thiele H. G., Hamann A. Lymphocyte activation and expression of the human leucocyte-endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (Leu-8/TQ1 antigen). Immunology. 1990 Nov;71(3):442–448. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., MacHugh N. D., Bensaid A., Dunlap S., Baldwin C. L., Kaushal A., Iams K., Howard C. J., Morrison W. I. Identification of a bovine surface antigen uniquely expressed on CD4-CD8- T cell receptor gamma/delta+ T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):809–817. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. A., Davis W. C., MacHugh N. D., Emery D. L., Kaushal A., Morrison W. I. Differentiation antigens on bovine mononuclear phagocytes identified by monoclonal antibodies. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Oct;19(3-4):325–340. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):30–34. doi: 10.1038/304030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The mouse gut T lymphocyte, a novel type of T cell. Nature, origin, and traffic in mice in normal and graft-versus-host conditions. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1661–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Jablonski-Westrich D., Jonas P., Thiele H. G. Homing receptors reexamined: mouse LECAM-1 (MEL-14 antigen) is involved in lymphocyte migration into gut-associated lymphoid tissue. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Dec;21(12):2925–2929. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann B., Weissman I. L. Peyer's patch-specific lymphocyte homing receptors consist of a VLA-4-like alpha chain associated with either of two integrin beta chains, one of which is novel. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1735–1741. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Parsons K. R., Jones B. V., Sopp P., Pocock D. H. Two monoclonal antibodies (CC17, CC29) recognizing an antigen (Bo5) on bovine T lymphocytes, analogous to human CD5. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Sep;19(2):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Sopp P., Parsons K. R., McKeever D. J., Taracha E. L., Jones B. V., MacHugh N. D., Morrison W. I. Distinction of naive and memory BoCD4 lymphocytes in calves with a monoclonal antibody, CC76, to a restricted determinant of the bovine leukocyte-common antigen, CD45. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2219–2226. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr The immune system evolved to discriminate infectious nonself from noninfectious self. Immunol Today. 1992 Jan;13(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90198-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Jutila M. A., Butcher E. C. Identification of a human peripheral lymph node homing receptor: a rapidly down-regulated adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2244–2248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leukocyte antigens in cattle, sheep and goats. Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Leukocyte Antigens in Cattle, Sheep and Goats. Hannover, Germany, 25 July 1989. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jan;27(1-3):1–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Kimpton W. G., Brandon M. R., Cahill R. N. Lymphocyte subsets show marked differences in their distribution between blood and the afferent and efferent lymph of peripheral lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1755–1765. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D., Powrie F. Memory CD4+ T cells in man form two distinct subpopulations, defined by their expression of isoforms of the leucocyte common antigen, CD45. Immunology. 1990 Aug;70(4):427–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naessens J., Newson J., McHugh N., Howard C. J., Parsons K., Jones B. Characterization of a bovine leucocyte differentiation antigen of 145,000 MW restricted to B lymphocytes. Immunology. 1990 Apr;69(4):525–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naessens J., Newson J., Williams D. J., Lutje V. Identification of isotypes and allotypes of bovine immunoglobulin M with monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1988 Apr;63(4):569–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons K. R., Howard C. J., Jones B. V., Sopp P. Investigation of bovine gut associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) using monoclonal antibodies against bovine lymphocytes. Vet Pathol. 1989 Sep;26(5):396–408. doi: 10.1177/030098588902600505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Newman W., Tanaka Y., Shaw S. Lymphocyte interactions with endothelial cells. Immunol Today. 1992 Mar;13(3):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90151-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopp P., Howard C. J., Parsons K. R. Investigating monoclonal antibodies to bovine "null" cell antigens using two-colour immunofluorescence. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jan;27(1-3):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(91)90095-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini O., Kansas G. S., Reimann K. A., Mackay C. R., Tedder T. F. Function and evolutionary conservation of distinct epitopes on the leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (TQ-1, Leu-8) that regulate leukocyte migration. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):942–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Bradley L. M., Croft M., Tonkonogy S., Atkins G., Weinberg A. D., Duncan D. D., Hedrick S. M., Dutton R. W., Huston G. Helper T-cell subsets: phenotype, function and the role of lymphokines in regulating their development. Immunol Rev. 1991 Oct;123:115–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada S., Koide J., Engleman E. G. Differences in surface phenotype between cytolytic and non-cytolytic CD4+ T cells. MHC class II-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes lack Leu 8 antigen and express CD2 in high density. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3038–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Matsuyama T., Rothstein D., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Human antigen-specific memory T cells express the homing receptor (LAM-1) necessary for lymphocyte recirculation. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1351–1355. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Penta A. C., Levine H. B., Freedman A. S. Expression of the human leukocyte adhesion molecule, LAM1. Identity with the TQ1 and Leu-8 differentiation antigens. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):532–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann J., Pabst R. Lymphocyte subsets in the blood: a diagnostic window on the lymphoid system? Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):406–410. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90160-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]