Abstract
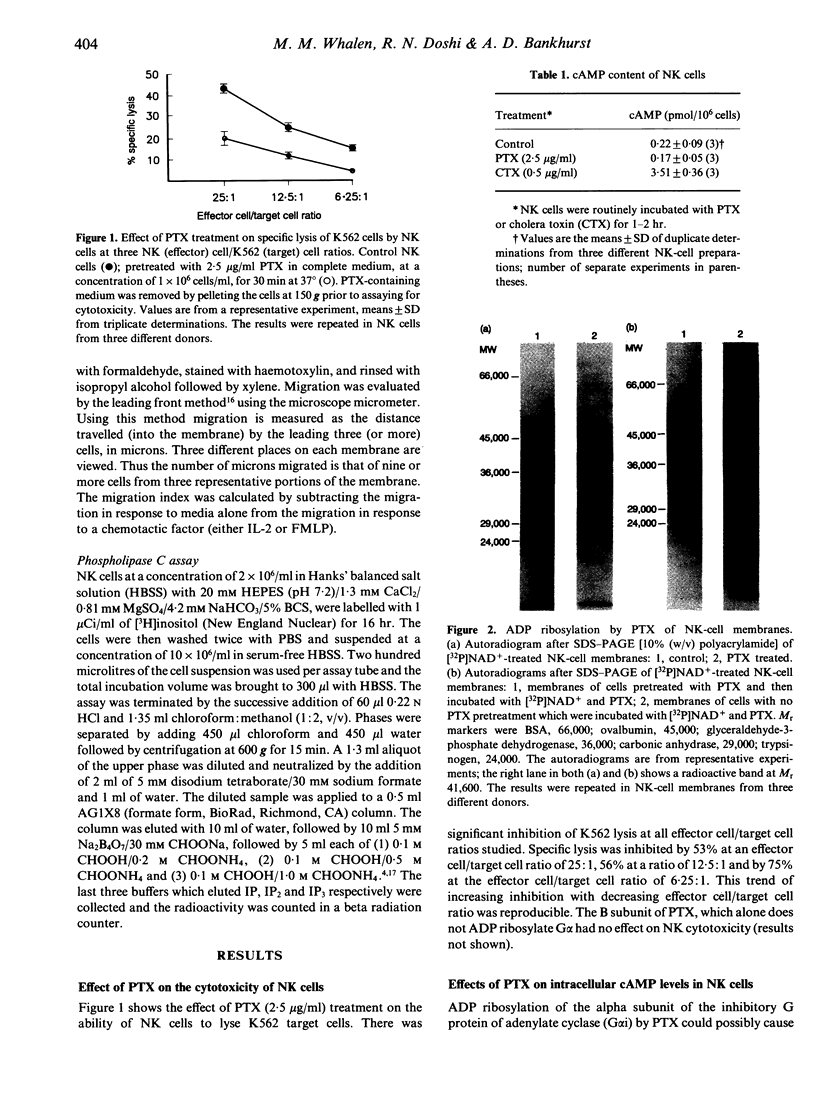
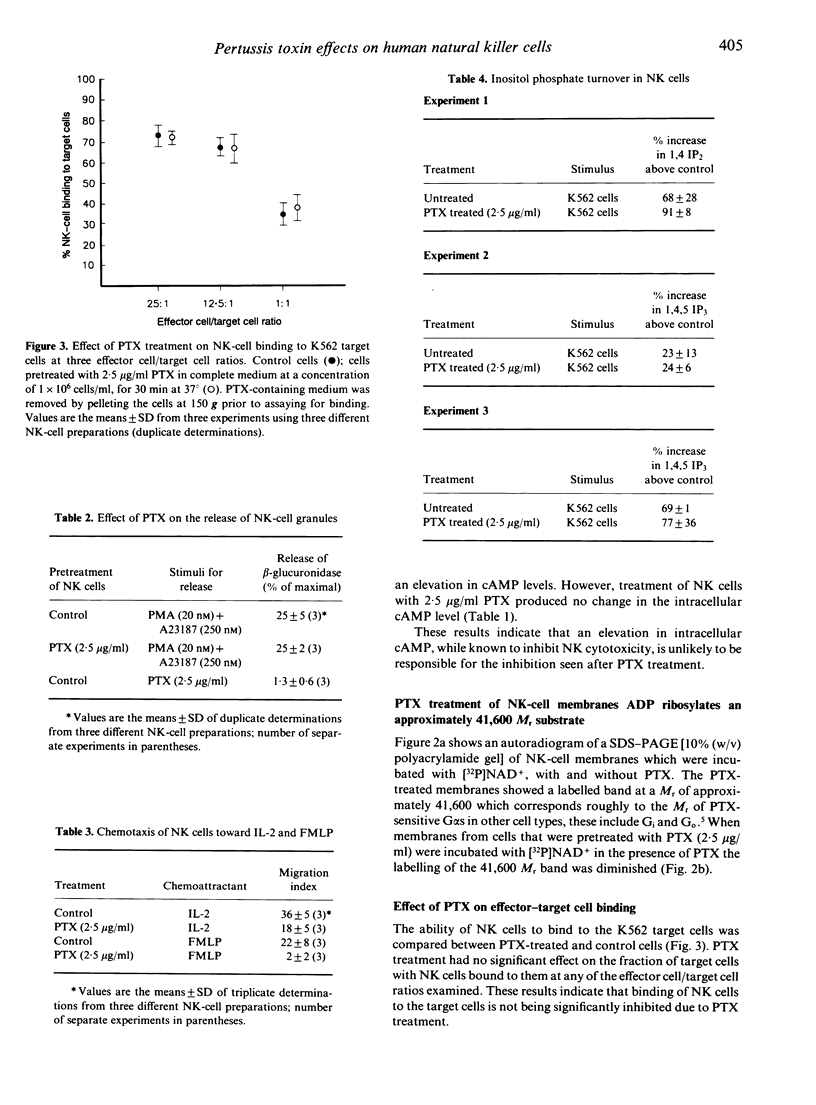
Membranes from highly purified natural killer (NK) cells were ADP ribosylated by treatment with pertussis toxin (PTX). PTX treatment resulted in a single band of 32P incorporation at M(r) 41,600. PTX treatment of NK cells diminished their ability to lyse K562 tumour cells by about 50%. However PTX treatment had no measurable effect on cAMP levels in NK cells. PTX pretreatment also had no effect on the ability of target cells to induce phosphoinositide turnover or on the ability of the NK cells to conjugate with the K562 tumour cells. Movement toward the chemoattractants interleukin-2 (IL-2) and formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine (FMLP) was significantly inhibited indicating that a PTX substrate in NK cells may be involved in the transduction of signals which are involved in cell motility.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Peñarrubia P., Koster F. T., Kelley R. O., McDowell T. D., Bankhurst A. D. Antibacterial activity of human natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):99–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore W., Weiner L. P. The effects of pertussis toxin and cholera toxin on mitogen-induced interleukin-2 production: evidence for G protein involvement in signal transduction. Cell Immunol. 1988 May;113(2):235–250. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Herberman R. B., Maluish A., Strong D. M. Cyclic AMP as a mediator of prostaglandin E-induced suppression of human natural killer cell activity. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1350–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves S. S., Bramhall J., Bonavida B. Studies on the lethal hit stage of natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. I. Both phorbol ester and ionophore are required for release of natural killer cytotoxic factors (NKCF), suggesting a role for protein kinase C activity. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1977–1984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Reynolds C. W., Ortaldo J. R. Mechanism of cytotoxicity by natural killer (NK) cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:651–680. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Zaytoun A. M., Fauci A. S. Mechanisms of human cell-mediated cytotoxicity. I. Modulation of natural killer cell activity by cyclic nucleotides. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Katada T., Ui M. Coupling of the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein to chemotactic peptide receptors in neutrophil membranes and its uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6761–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Klein M. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer cell system. IV. Modulation by cyclic nucleotides. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2785–2790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Austen K. F., Wasserman S. I. Immunologic release of beta-hexosaminidase and beta-glucuronidase from purified rat serosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1445–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbitt W. L., Jr, Mathews P. M., Bankhurst A. D. Natural killer cell in systemic lupus erythematosus. Defects in effector lytic activity and response to interferon and interferon inducers. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1230–1239. doi: 10.1172/JCI110872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullberg M., Jondal M., Lanefelt F., Fredholm B. B. Inhibition of human NK cell cytotoxicity by induction of cyclic AMP depends on impaired target cell recognition. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Apr;17(4):365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Durant D. A., Potter J. W. Migration of human helper/inducer T cells in response to supernatants from Con A-stimulated suppressor/cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):697–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen M. M., Bankhurst A. D. Effects of beta-adrenergic receptor activation, cholera toxin and forskolin on human natural killer cell function. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):327–331. doi: 10.1042/bj2720327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windebank K. P., Abraham R. T., Powis G., Olsen R. A., Barna T. J., Leibson P. J. Signal transduction during human natural killer cell activation: inositol phosphate generation and regulation by cyclic AMP. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3951–3957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]