Abstract
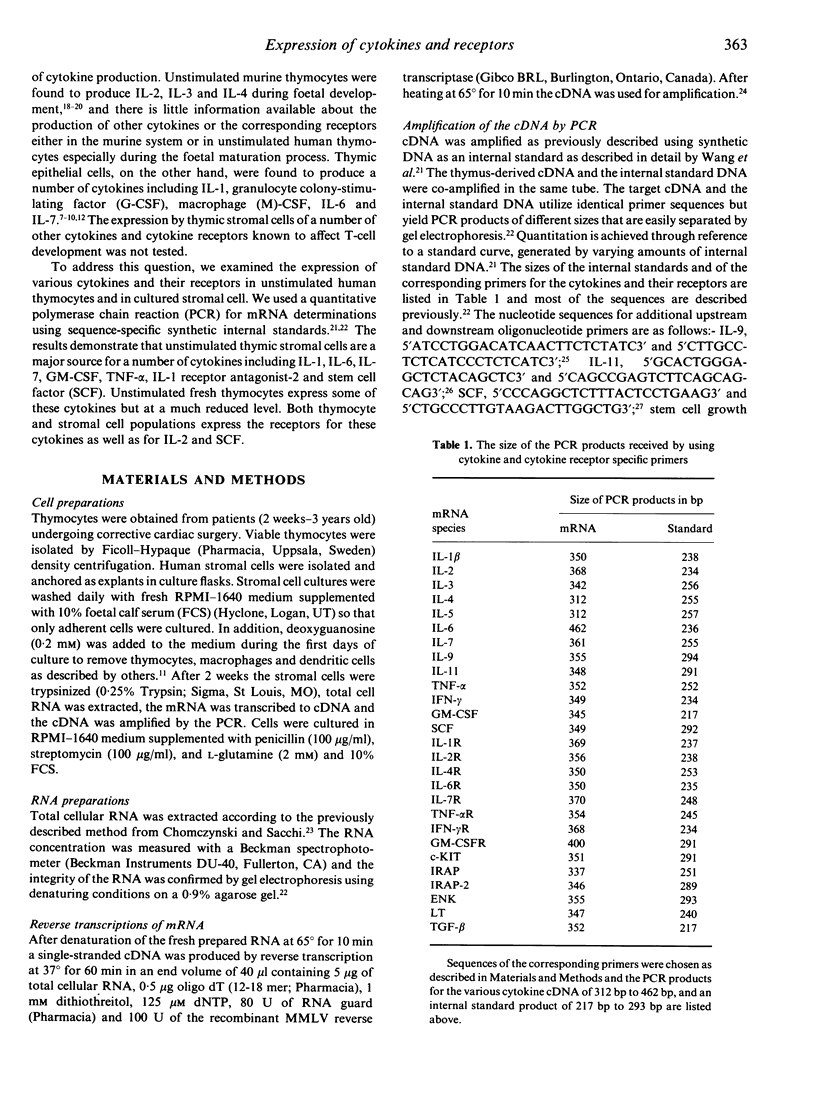
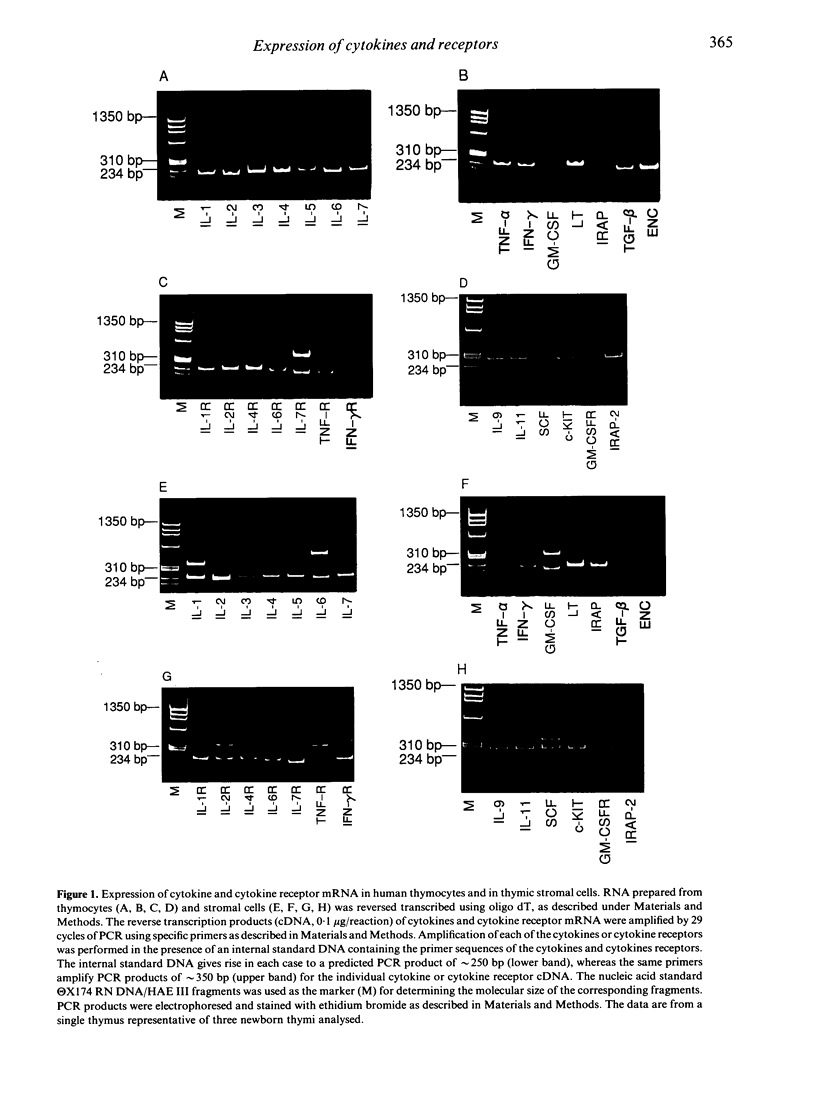
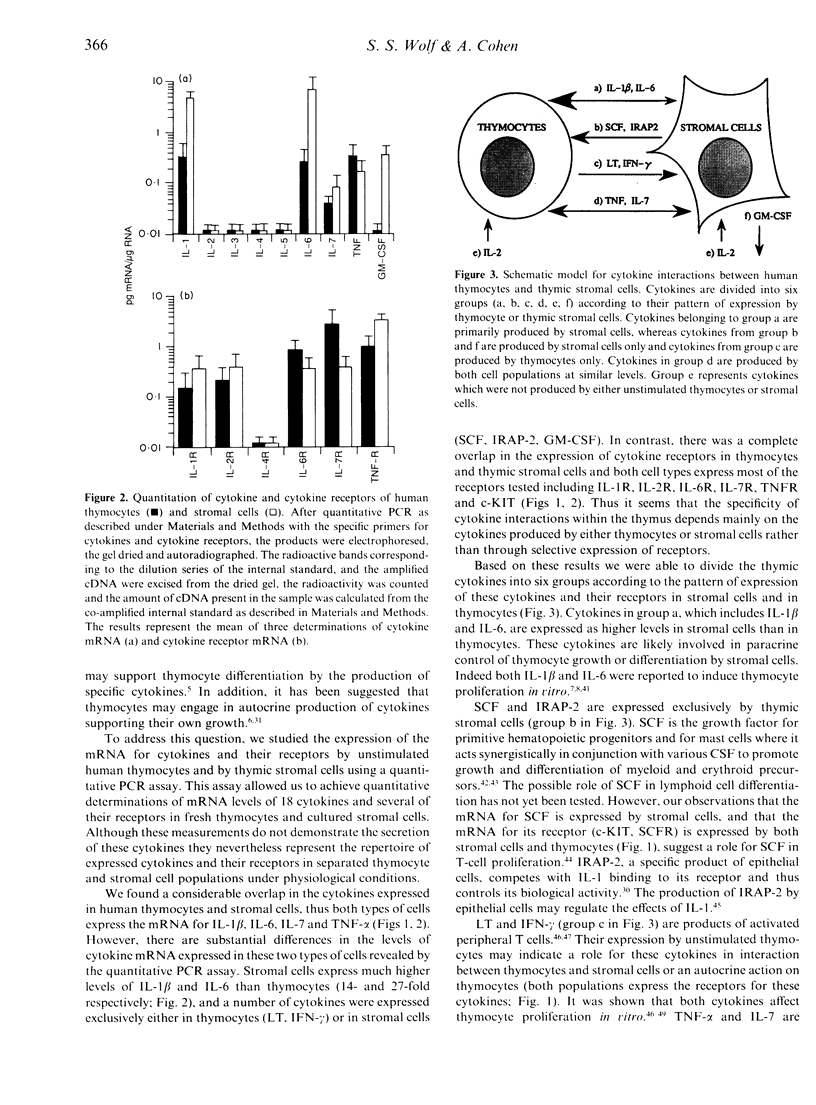
The repertoire of cytokine and cytokine receptor mRNA expressed by unstimulated human thymocytes and thymic stromal cells was explored by a quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using sequence specific internal standards. Of the 18 cytokines tested we found a considerable overlap in the expression of cytokines by human thymocytes and by thymic stromal cells; both cell types express the mRNA for interleukin-1 beta(IL-1, IL-6, IL-7 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). However, there are substantial differences in the levels of cytokine mRNA expressed in these two types of cells as revealed by the quantitative PCR assay. Stromal cells express considerably higher levels of IL-1 beta and IL-6 than thymocytes (14- and 27-fold respectively). In addition, a number of cytokines such as lymphotoxin and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), are expressed exclusively in thymocytes whereas others such as stem cell factor (SCF), IL-1 receptor antagonist-2 (IRAP-2) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) are produced only in stromal cells. There is a complete overlap in the expression of a group of cytokine receptors tested in thymocytes and thymic stromal cells; these include IL-1R, IL-2R, IL-6R, IL-7R, TNFR and stem cell growth factor receptor (c-KIT). The expression of specific cytokines by thymic stromal cells and the parallel expression of their receptors on thymocytes under physiological conditions, support the hypothesis that these cytokines participate in paracrine interactions between these two cell populations during thymocyte differentiation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Lyman S. D., Baird A., Wignall J. M., Eisenman J., Rauch C., March C. J., Boswell H. S., Gimpel S. D., Cosman D. Molecular cloning of mast cell growth factor, a hematopoietin that is active in both membrane bound and soluble forms. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90304-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson U., Sander B., Andersson J., Möller G. Concomitant production of different lymphokines in activated T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):2081–2084. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Smith M. F., Jr, Janson R. W., Joslin F. G. IL-1 receptor antagonist and IL-1 beta production in human monocytes are regulated differently. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1530–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendelac A., Schwartz R. H. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells acquire specific lymphokine secretion potentials during thymic maturation. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):68–71. doi: 10.1038/353068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertagnolli M., Herrmann S. IL-7 supports the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes from thymocytes. Multiple lymphokines required for proliferation and cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1706–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárcena A., Toribio M. L., Gutierrez-Ramos J. C., Kroemer G., Martínez C. Interplay between IL-2 and IL-4 in human thymocyte differentiation: antagonism or agonism. Int Immunol. 1991 May;3(5):419–425. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carding S. R., Hayday A. C., Bottomly K. Cytokines in T-cell development. Immunol Today. 1991 Jul;12(7):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90037-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carding S. R., Jenkinson E. J., Kingston R., Hayday A. C., Bottomly K., Owen J. J. Developmental control of lymphokine gene expression in fetal thymocytes during T-cell ontogeny. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3342–3345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Grunberger T., Vanek W., Dube I. D., Doherty P. J., Letarte M., Roifman C., Freedman M. H. Constitutive expression and role in growth regulation of interleukin-1 and multiple cytokine receptors in a biphenotypic leukemic cell line. Blood. 1991 Jul 1;78(1):94–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump W. L., 3rd, Owen-Schaub L. B., Grimm E. A. Synergy of human recombinant interleukin 1 with interleukin 2 in the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalloul A. H., Arock M., Fourcade C., Hatzfeld A., Bertho J. M., Debré P., Mossalayi M. D. Human thymic epithelial cells produce interleukin-3. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning S. M., Kurtzberg J., Le P. T., Tuck D. T., Singer K. H., Haynes B. F. Human thymic epithelial cells directly induce activation of autologous immature thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3125–3129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning S. M., Tuck D. T., Singer K. H., Haynes B. F. Human thymic epithelial cells function as accessory cells for autologous mature thymocyte activation. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):680–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers S., Smith K. A. Differentiation of T cell lymphokine gene expression: the in vitro acquisition of T cell memory. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):25–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer M., MacNeil I., Suda T., Cupp J. E., Shortman K., Zlotnik A. Cytokine production by mature and immature thymocytes. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3452–3456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Aggarwal B. B., Benton C. V., Bringman T. S., Henzel W. J., Jarrett J. A., Leung D. W., Moffat B., Ng P., Svedersky L. P. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human lymphotoxin, a lymphokine with tumour necrosis activity. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):721–724. doi: 10.1038/312721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez J. C., Palacios R. Heterogeneity of thymic epithelial cells in promoting T-lymphocyte differentiation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):642–646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Martin G., Van Le L., Morris J., Peace A., Bigler C. F., Jaffe G. J., Hammerberg C., Sporn S. A., Fong S. cDNA cloning of an intracellular form of the human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist associated with epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3681–3685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F. Human thymic epithelium and T cell development: current issues and future directions. Thymus. 1990 Nov-Dec;16(3-4):143–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herold K. C., Lancki D. W., Dunn D. E., Arai K., Fitch F. W. Activation of lymphokine genes during stimulation of cloned T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1533–1538. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori T., Cupp J., Wrighton N., Lee F., Spits H. Identification of a novel human thymocyte subset with a phenotype of CD3- CD4+ CD8 alpha + beta-1. Possible progeny of the CD3- CD4- CD8- subset. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4078–4084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Shiiba K., Shimizu Y., Suzuki R., Kumagai K. Generation of activated killer (AK) cells by recombinant interleukin 2 (rIL 2) in collaboration with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3124–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le P. T., Kurtzberg J., Brandt S. J., Niedel J. E., Haynes B. F., Singer K. H. Human thymic epithelial cells produce granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1211–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le P. T., Lazorick S., Whichard L. P., Haynes B. F., Singer K. H. Regulation of cytokine production in the human thymus: epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha regulate mRNA levels of interleukin 1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), IL-1 beta, and IL-6 in human thymic epithelial cells at a post-transcriptional level. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1147–1157. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le P. T., Lazorick S., Whichard L. P., Yang Y. C., Clark S. C., Haynes B. F., Singer K. H. Human thymic epithelial cells produce IL-6, granulocyte-monocyte-CSF, and leukemia inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3310–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le P. T., Tuck D. T., Dinarello C. A., Haynes B. F., Singer K. H. Human thymic epithelial cells produce interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2520–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Suggs S. V., Langley K. E., Lu H. S., Ting J., Okino K. H., Morris C. F., McNiece I. K., Jacobsen F. W., Mendiaz E. A. Primary structure and functional expression of rat and human stem cell factor DNAs. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90301-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marucha P. T., Zeff R. A., Kreutzer D. L. Cytokine-induced IL-1 beta gene expression in the human polymorphonuclear leukocyte: transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation by tumor necrosis factor and IL-1. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2603–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. The interleukins. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2379–2388. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. A., Dallman M. J. Analysis of cytokine gene expression during fetal thymic ontogeny using the polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):554–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki H., Ito M., Sudo T., Hattori M., Kano S., Katsura Y., Minato N. IL-7 promotes thymocyte proliferation and maintains immunocompetent thymocytes bearing alpha beta or gamma delta T-cell receptors in vitro: synergism with IL-2. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2917–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Schaub L. B., Gutterman J. U., Grimm E. A. Synergy of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 2 in the activation of human cytotoxic lymphocytes: effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 2 in the generation of human lymphokine-activated killer cell cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):788–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. R., Bennett F., Calvetti J. A., Kelleher K., Wood C. R., O'Hara R. M., Jr, Leary A. C., Sibley B., Clark S. C., Williams D. A. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding interleukin 11, a stromal cell-derived lymphopoietic and hematopoietic cytokine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7512–7516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Zlotnik A., Espevik T., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Palladino M. A., Jr Tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin is a growth factor for thymocytes. Synergistic interactions with other cytokines. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1472–1478. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Zlotnik A., Espevik T., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Palladino M. A., Jr Tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin is a growth factor for thymocytes. Synergistic interactions with other cytokines. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1472–1478. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom J., Fischer M., Mosmann T., Yokota T., DeLuca D., Schumacher J., Zlotnik A. Interferon-gamma is produced by activated immature mouse thymocytes and inhibits the interleukin 4-induced proliferation of immature thymocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4102–4108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renauld J. C., Goethals A., Houssiau F., Merz H., Van Roost E., Van Snick J. Human P40/IL-9. Expression in activated CD4+ T cells, genomic organization, and comparison with the mouse gene. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4235–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Singer K. H., Greenhouse J. J., Stanley S. K., Whichard L. P., Le P. T., Haynes B. F., Fauci A. S. Thymic microenvironment induces HIV expression. Physiologic secretion of IL-6 by thymic epithelial cells up-regulates virus expression in chronically infected cells. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Murray R., Guidos C., Zlotnik A. Growth-promoting activity of IL-1 alpha, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in combination with IL-2, IL-4, or IL-7 on murine thymocytes. Differential effects on CD4/CD8 subsets and on CD3+/CD3- double-negative thymocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3039–3045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. D., Morrissey P. J., Namen A. E., Conlon P. J., Widmer M. B. Effect of IL-7 on the growth of fetal thymocytes in culture. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1215–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T., Coussens L., Munemitsu S., Dull T. J., Chen E., Schlessinger J., Francke U., Ullrich A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3341–3351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Wypych J., McNiece I. K., Lu H. S., Smith K. A., Karkare S. B., Sachdev R. K., Yuschenkoff V. N., Birkett N. C., Williams L. R. Identification, purification, and biological characterization of hematopoietic stem cell factor from buffalo rat liver--conditioned medium. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubiaga A. M., Muñoz E., Huber B. T. Production of IL-1 alpha by activated Th type 2 cells. Its role as an autocrine growth factor. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3849–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Hera A., Marston W., Aranda C., Toribio M. L., Martinez C. Thymic stroma is required for the development of human T cell lineages in vitro. Int Immunol. 1989;1(5):471–478. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.5.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Hera A., Toribio M. L., Martinez C. Delineation of human thymocytes with or without functional potential by CD1-specific antibodies. Int Immunol. 1989;1(5):496–502. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.5.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen J. J., Comans-Bitter W. M., Wolvers-Tettero I. L., Borst J. Development of human T lymphocytes and their thymus-dependency. Thymus. 1990 Nov-Dec;16(3-4):207–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ewijk W. Immunohistology of lymphoid organs. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989 Jun;1(5):954–965. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ewijk W. T-cell differentiation is influenced by thymic microenvironments. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:591–615. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]