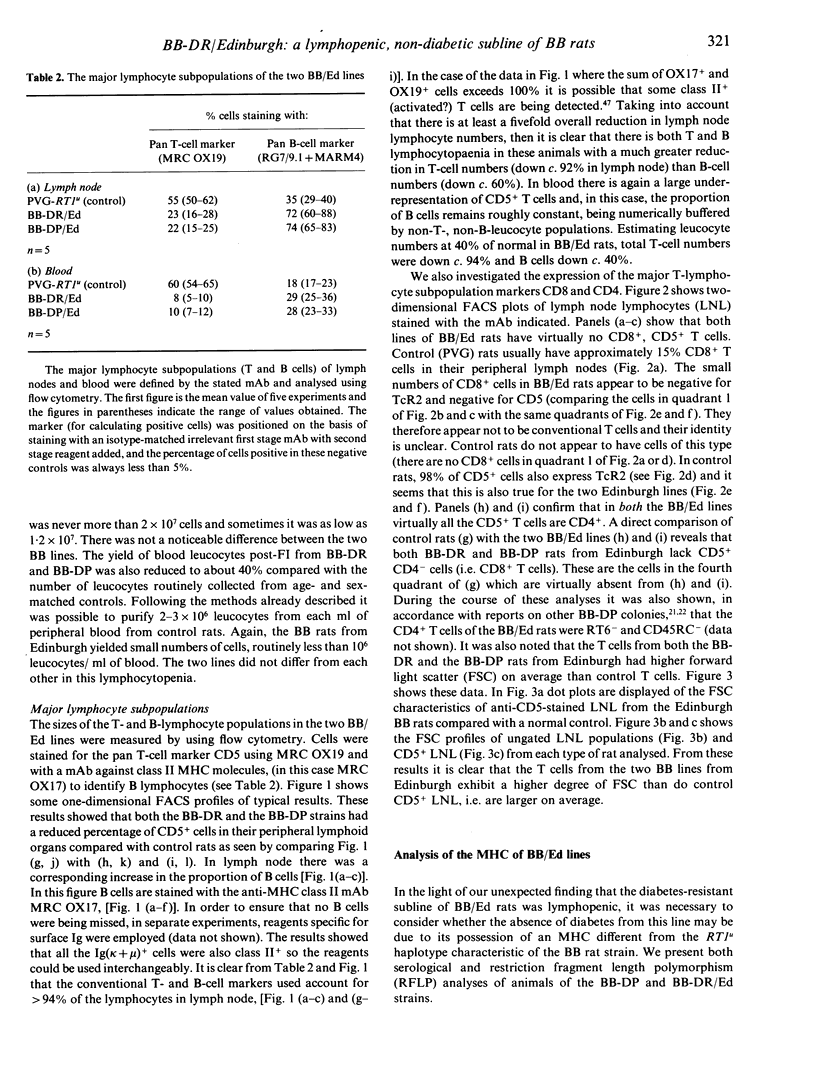
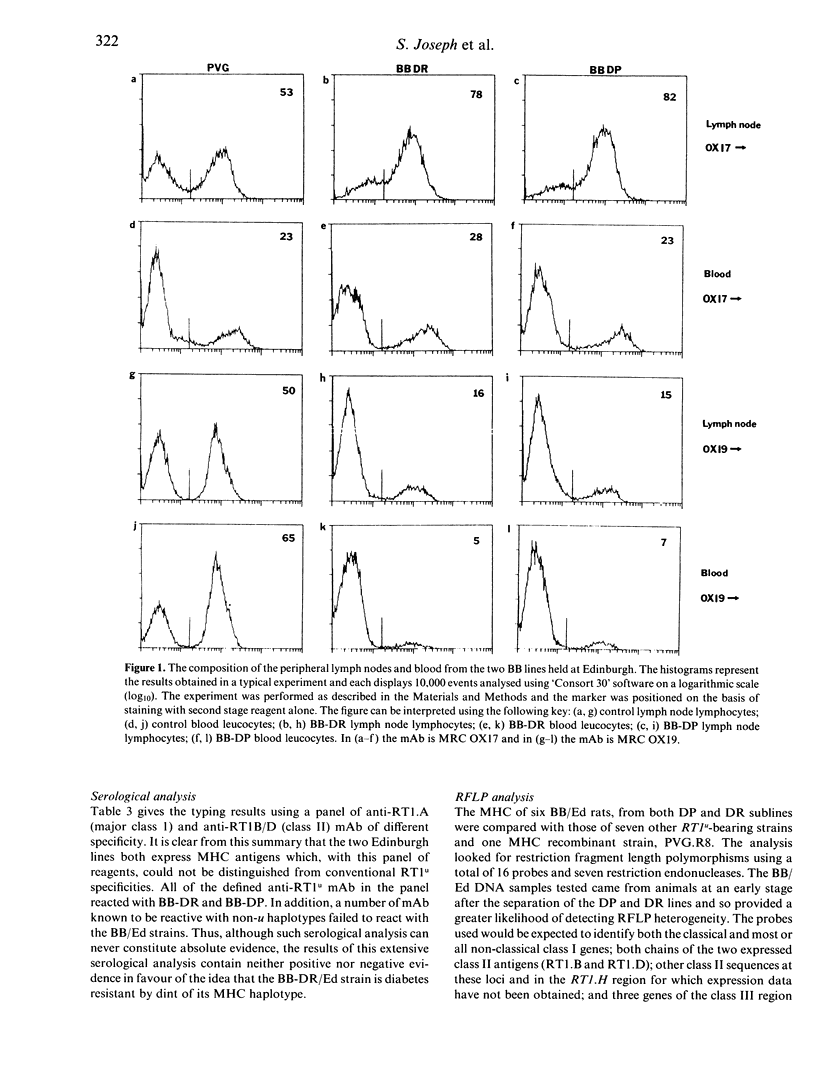
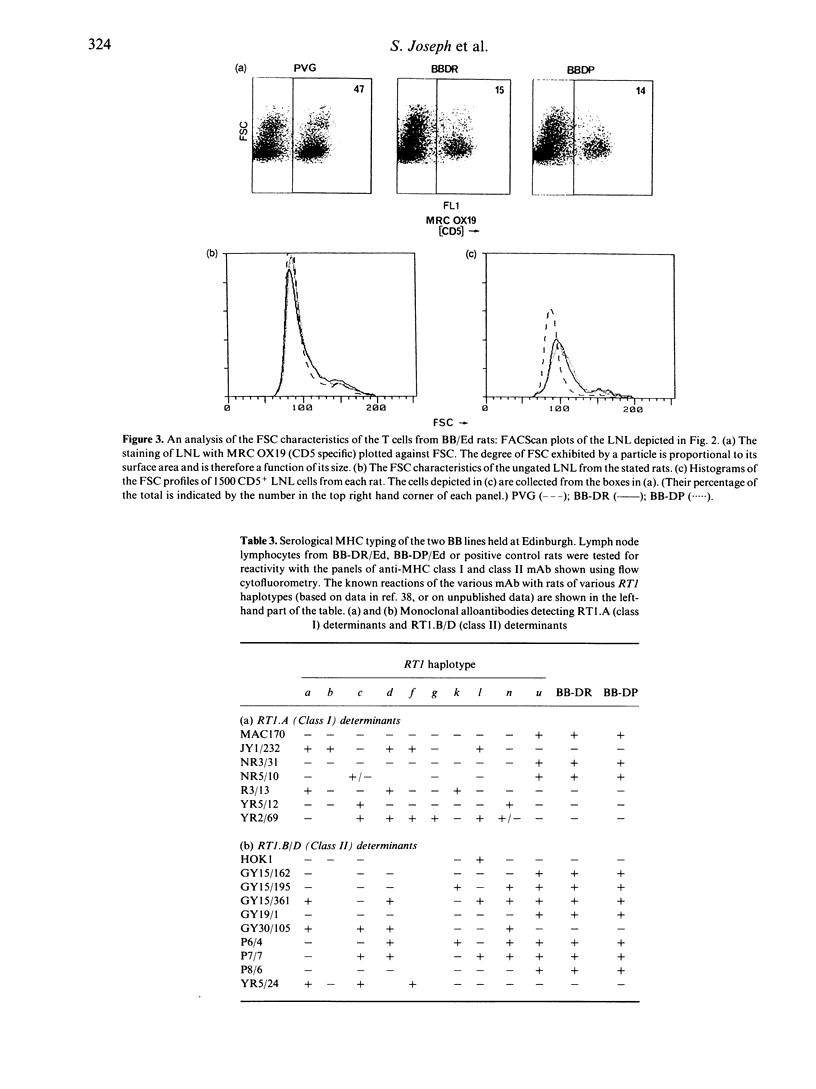
Abstract
Diabetes-prone (DP) and diabetes-resistant (DR) sublines of the BB rat have been established in Edinburgh, U.K., separately from other existing colonies. In an examination of the lymphoid status of the two lines, BB-DP/Ed and BB-DR/Ed, it has been found that both lines have very low T-cell numbers, depressed B-lymphocyte numbers and a complete absence of peripheral CD8+ T cells, all features characteristic of the previously described genetic lymphopenia lesion. It was also noted that the peripheral T cells of both BB/Ed lines were larger than normal. The DP/Ed and DR/Ed lines were indistinguishable in all these respects, and furthermore, they were both shown to type as RT1u at the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). The genetic combination of lymphopenia and RT1u without expression of diabetes is not present in other extant BB lines and makes BB-DR/Ed a uniquely useful control strain for BB rat studies as well as a valuable genetic resource for the further genetic analysis of diabetes susceptibility in rats.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellgrau D., Lagarde A. C. Cytotoxic T-cell precursors with low-level CD8 in the diabetes-prone Biobreeding rat: implications for generation of an autoimmune T-cell repertoire. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):313–317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellgrau D., Naji A., Silvers W. K., Markmann J. F., Barker C. F. Spontaneous diabetes in BB rats: evidence for a T cell dependent immune response defect. Diabetologia. 1982 Oct;23(4):359–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00253745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. Isolation of cDNA clones for human complement component C2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1212–1215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan D. J., Chisholm P. M. Co-expression of CD4 and CD8 molecules and de novo expression of MHC class II antigens on activated rat T cells. Immunology. 1986 Dec;59(4):621–625. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Kryspin-Sörensen I., Dyrberg T., Lernmark A., Kastern W. A deletion in a rat major histocompatibility complex class I gene is linked to the absence of beta 2-microglobulin-containing serum molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5630–5633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. W. A list of monoclonal antibodies specific for alloantigens of the rat. J Immunogenet. 1987 Apr-Jun;14(2-3):163–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1987.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler L., Guberski D. L., Like A. A. Genetic analysis of the BB/W diabetic rat. Can J Genet Cytol. 1983 Feb;25(1):7–15. doi: 10.1139/g83-002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappel C. I., Chappel W. R. The discovery and development of the BB rat colony: an animal model of spontaneous diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1983 Jul;32(7 Suppl 1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(83)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colle E., Guttmann R. D., Fuks A. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is associated with genes that map to the right of the class I RT1.A locus of the major histocompatibility complex of the rat. Diabetes. 1986 Apr;35(4):454–458. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.4.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colle E., Guttmann R. D., Seemayer T. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus syndrome in the rat. I. Association with the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1237–1242. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. F., Parish C. R. A procedure for removing red cells and dead cells from lymphoid cell suspensions. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jun;7(2-3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A. G., Hood L. E., Howard J. C., Windle M., Winoto A. The class II genes of the rat MHC. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3268–3274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder M. E., Maclaren N. K. Identification of profound peripheral T lymphocyte immunodeficiencies in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1723–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto T., McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Mouse monoclonal antibodies against rat major histocompatibility antigens. Two Ia antigens and expression of Ia and class I antigens in rat thymus. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Mar;12(3):237–243. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner D. L., Handler E. S., Nakano K., Mordes J. P., Rossini A. A. Absence of the RT-6 T cell subset in diabetes-prone BB/W rats. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):148–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner D. L., Mordes J. P., Handler E. S., Angelillo M., Nakamura N., Rossini A. A. Depletion of RT6.1+ T lymphocytes induces diabetes in resistant biobreeding/Worcester (BB/W) rats. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):461–475. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttmann R. D., Colle E., Michel F., Seemayer T. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus syndrome in the rat. II. T lymphopenia and its association with clinical disease and pancreatic lymphocytic infiltration. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1732–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther E., Kiesel U., Kolb H., Krawczak M., Rothermel E., Wurst W. Genetic analysis of susceptibility to diabetes mellitus in F2-hybrids between diabetes-prone BB and various MHC-recombinant congenic rat strains. J Autoimmun. 1991 Jun;4(3):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Clark M., Waldmann H. Therapeutic potential of rat monoclonal antibodies: isotype specificity of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity with human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3056–3061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Buse J. B., Rifai R., Pelletier D., Milford E. L., Carpenter C. B., Eisenbarth G. S., Williams R. M. Two genes required for diabetes in BB rats. Evidence from cyclical intercrosses and backcrosses. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1629–1636. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R., Rassi N., Crump T., Haynes B., Eisenbarth G. S. The BB diabetic rat. Profound T-cell lymphocytopenia. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):887–889. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies W. A., Green J. R., Williams A. F. Authentic T helper CD4 (W3/25) antigen on rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):117–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. A., Scollay R. Analysis of recent thymic emigrants with subset- and maturity-related markers. Int Immunol. 1990;2(5):419–425. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloeting I., Vogt L. Coat colour phenotype, leucopenia, and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in BB rats. Transplant Proc. 1990 Dec;22(6):2574–2575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klöting I., Stark O. Genetic studies of IDDM in BB rats: the incidence of diabetes in F2 and first backcross hybrids allows rejection of the recessive hypothesis. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1987 Aug;89(3):312–318. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1210656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryspin-Sørensen I., Dyrberg T., Kastern W. Genetic heterogeneity in the major histocompatibility complex of various BB rat sublines. Diabetologia. 1986 May;29(5):307–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00452068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Guberski D. L., Butler L. Diabetic BioBreeding/Worcester (BB/Wor) rats need not be lymphopenic. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3254–3258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markholst H., Eastman S., Wilson D., Andreasen B. E., Lernmark A. Diabetes segregates as a single locus in crosses between inbred BB rats prone or resistant to diabetes. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):297–300. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Arthur R. P., Dallman M. J., Green J. R., Spickett G. P., Thomas M. L. Functions of rat T-lymphocyte subsets isolated by means of monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:57–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Germain R. N. Efficient cell surface expression of class II MHC molecules in the absence of associated invariant chain. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1478–1489. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Like A. A., Chappel C. I., Murray F. T., Marliss E. B. The spontaneously diabetic Wistar rat. Metabolic and morphologic studies. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):100–112. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhale W. J., Farmer A., Irvine W. J. Thyroiditis in T cell-depleted rats. Influence of strain, radiation dose, adjuvants and antilymphocyte serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Sep;21(3):362–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prins J. B., Herberg L., Den Bieman M., van Zutphen L. F. Genetic variation within and between lines of diabetes-prone and non-diabetes-prone BB rats; allele distribution of 8 protein markers. Lab Anim. 1991 Jul;25(3):207–211. doi: 10.1258/002367791780808446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson K. A., McMaster W. R. Complete structure of a rat RT1 E beta chain: extensive conservation of MHC class II beta chains. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4095–4099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinzer R., Hedrich H. J., Wonigeit K. T cell differentiation in athymic nude rats (rnu/rnu): demonstration of a distorted T cell subset structure by flow cytometry analysis. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Oct;19(10):1841–1847. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemayer T. A., Tannenbaum G. S., Goldman H., Colle E. Dynamic time course studies of the spontaneously diabetic BB Wistar rat. III. Light-microscopic and ultrastructural observations of pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Am J Pathol. 1982 Feb;106(2):237–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Bhattacharya A., Cardoza J. T., Sanchez-Madrid F. Monoclonal antibodies specific for rat IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b subclasses, and kappa chain monotypic and allotypic determinants: reagents for use with rat monoclonal antibodies. Hybridoma. 1982;1(3):257–273. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Young J. A., Kelly A. P., Austin P. J., Carson S., Meunier H., So A., Erlich H. A., Spielman R. S., Bodmer J. Structure, sequence and polymorphism in the HLA-D region. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:5–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varey A. M., Dean B. M., Walker R., Bone A. J., Baird J. D., Cooke A. Immunological responses of the BB rat colony in Edinburgh. Immunology. 1987 Jan;60(1):131–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woda B. A., Like A. A., Padden C., McFadden M. L. Deficiency of phenotypic cytotoxic-suppressor T lymphocytes in the BB/W rat. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):856–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]