Abstract
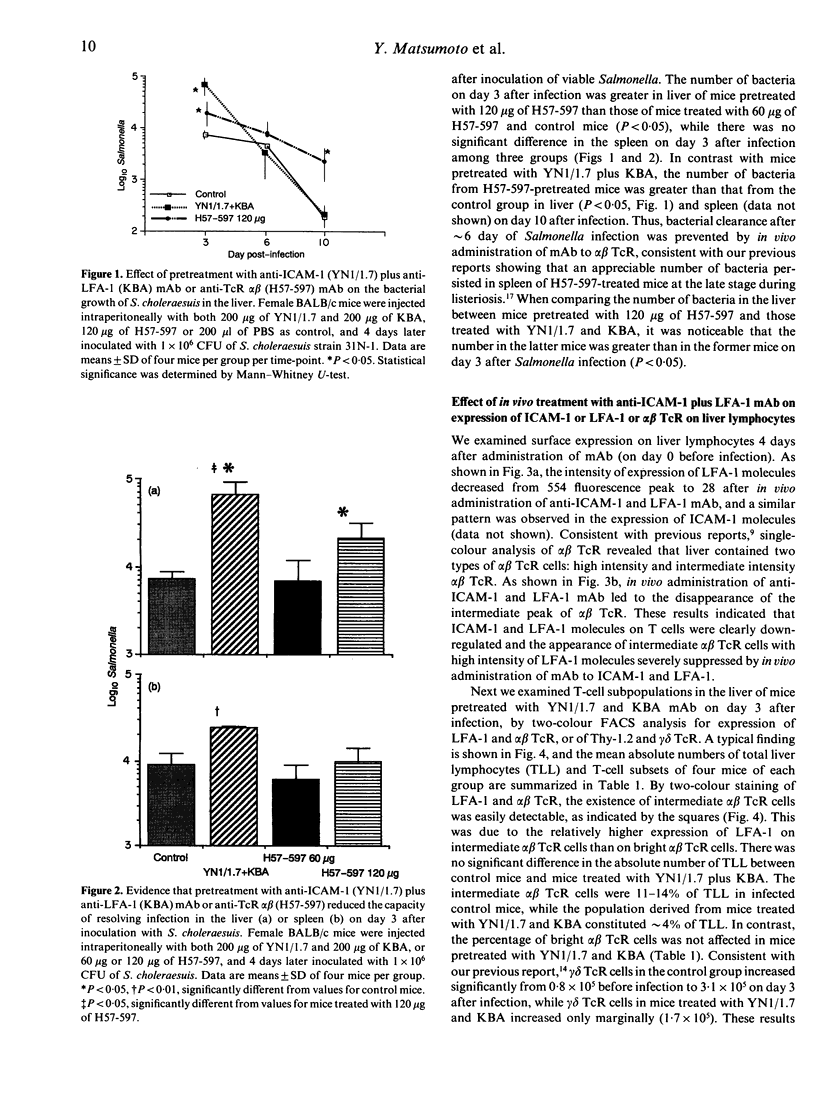
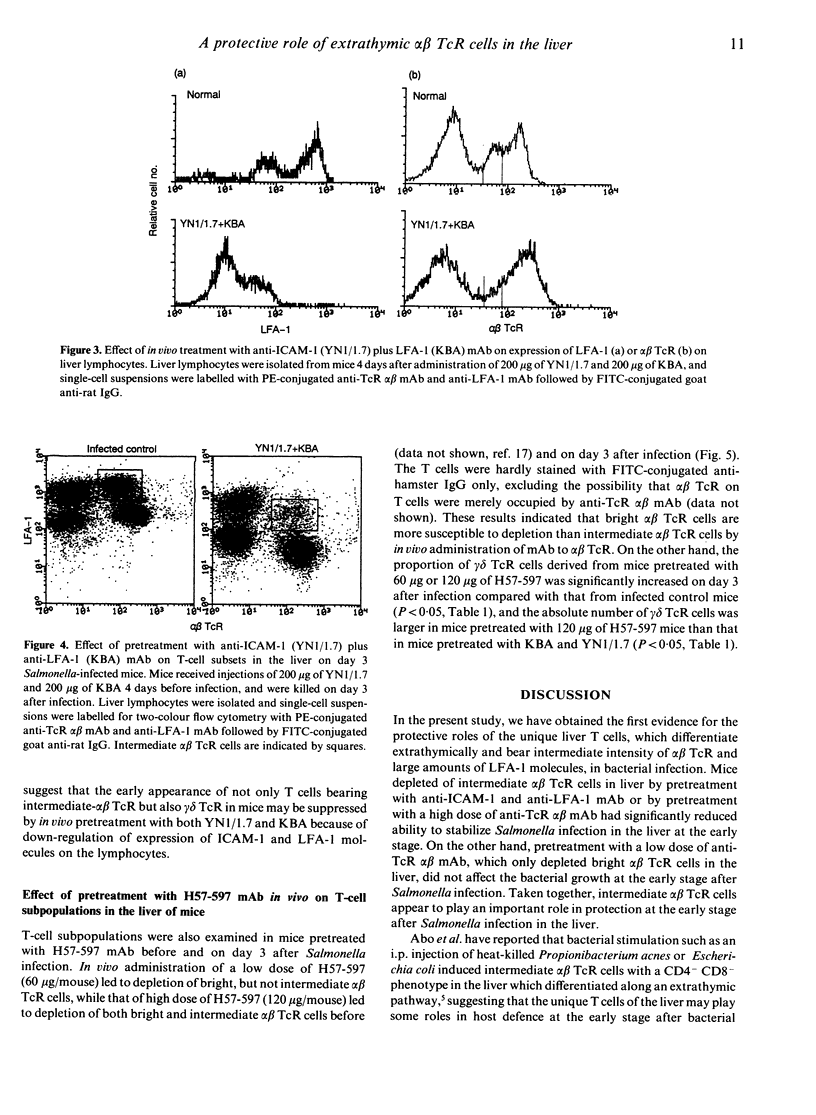
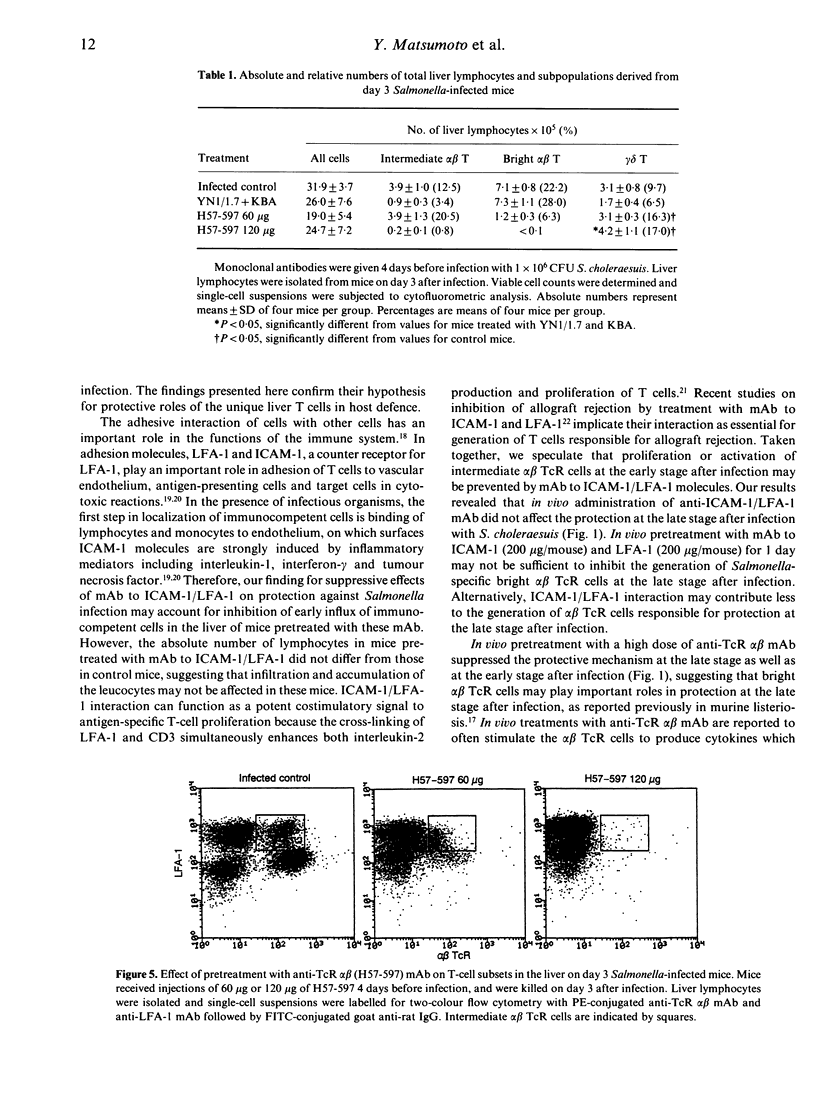
The liver comprises unique T cells differentiating extrathymically and expressing an intermediate intensity of alpha beta T-cell receptor (TcR) and a high intensity of leucocyte function antigen-1 (LFA-1). To elucidate the functional roles of the intermediate alpha beta TcR cells in host defence against bacterial infection, we examined the effects of depletion of the intermediate alpha beta TcR cells by in vivo administration of monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1)/LFA-1 and alpha beta TcR on the bacterial growth in the liver after infection with Salmonella chorelaesuis in mice. Pretreatment with mAb to LFA-1 (200 micrograms/mouse) together with mAb to ICAM-1 (200 micrograms/mouse), which could preferentially deplete the intermediate alpha beta TcR cells and gamma delta TcR cells in the liver, resulted in a severely reduced ability to resolve acute phase of Salmonella infection in the liver. Pretreatment with a low dose of anti-alpha beta TcR mAb (60 micrograms/mouse), which depleted only bright alpha beta TcR cells, did not affect the bacterial growth in the liver at the early stage after Salmonella infection, while the depleting of both intermediate and bright alpha beta TcR cells by pretreatment with a high dose of anti-alpha beta TcR mAb (120 micrograms/mouse) allowed the bacteria to multiply exaggeratedly in the liver at this stage. These results suggest that intermediate alpha beta TcR cells may play an important role in protection at the early stage after Salmonella infection in liver and that the interaction of ICAM-1/LFA-1 is critically involved in protective roles of extrathymic T cells bearing intermediate alpha beta TcR in liver at the early stage after Salmonella infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Ohteki T., Seki S., Koyamada N., Yoshikai Y., Masuda T., Rikiishi H., Kumagai K. The appearance of T cells bearing self-reactive T cell receptor in the livers of mice injected with bacteria. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):417–424. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angerman C. R., Eisenstein T. K. Comparative efficacy and toxicity of a ribosomal vaccine, acetone-killed cells, lipopolysaccharide, and a live cell vaccine prepared from Salmonella typhhimurium. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.575-582.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. T-cell receptor cross-linking transiently stimulates adhesiveness through LFA-1. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):619–624. doi: 10.1038/341619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emoto M., Danbara H., Yoshikai Y. Induction of gamma/delta T cells in murine salmonellosis by an avirulent but not by a virulent strain of Salmonella choleraesuis. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):363–372. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromatsu K., Matsuzaki G., Tauchi Y., Yoshikai Y., Nomoto K. Sequential analysis of T cells in the liver during murine listerial infection. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):568–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochadel J. F., Keller K. F. Protective effects of passively transferred immune T- or B-lymphocytes in mice infected with Salmonella typhimurium. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):813–823. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe M., Yagita H., Okumura K., Ihara A. Specific acceptance of cardiac allograft after treatment with antibodies to ICAM-1 and LFA-1. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1125–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.1347662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Abo T., Sugawara S., Kanno A., Kumagai K. Age-related variation in the proportion and activity of murine liver natural killer cells and their cytotoxicity against regenerating hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):315–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Haraguchi Y., Tsuchimoto M., Terakado N., Danbara H. Evidence of correlation between 50-kilobase plasmid of Salmonella choleraesuis and its virulence. Microb Pathog. 1988 Feb;4(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Larson R. S., Corbi A. L., Dustin M. L., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A. The leukocyte integrins. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:149–182. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita E., Kashiba S. Immunogenicity of the ribosomal fraction of Salmonella typhimurium: analysis of humoral immunity. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.197-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohteki T., Abo T., Seki S., Kobata T., Yagita H., Okumura K., Kumagai K. Predominant appearance of gamma/delta T lymphocytes in the liver of mice after birth. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1733–1740. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama R., Abo T., Seki S., Ohteki T., Sugiura K., Kusumi A., Kumagai K. Estrogen administration activates extrathymic T cell differentiation in the liver. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):661–669. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röcken M., Urban J. F., Shevach E. M. Infection breaks T-cell tolerance. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):79–82. doi: 10.1038/359079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki S., Abo T., Masuda T., Ohteki T., Kanno A., Takeda K., Rikiishi H., Nagura H., Kumagai K. Identification of activated T cell receptor gamma delta lymphocytes in the liver of tumor-bearing hosts. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):409–415. doi: 10.1172/JCI114726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki S., Abo T., Ohteki T., Sugiura K., Kumagai K. Unusual alpha beta-T cells expanded in autoimmune lpr mice are probably a counterpart of normal T cells in the liver. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1214–1221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki S., Abo T., Sugiura K., Ohteki T., Kobata T., Yagita H., Okumura K., Rikiishi H., Masuda T., Kumagai K. Reciprocal T cell responses in the liver and thymus of mice injected with syngeneic tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;137(1):46–60. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90055-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Dustin M. L., Kishimoto T. K., Marlin S. D. The lymphocyte function-associated LFA-1, CD2, and LFA-3 molecules: cell adhesion receptors of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:223–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy S. P., Mackaness G. B. The effect of cytotoxic agents on the primary immune response to Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1969 Jul 1;130(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Ohtsuka K., Kimura M., Ikarashi Y., Ohmori K., Kusumi A., Ohteki T., Seki S., Abo T. Details of an isolation method for hepatic lymphocytes in mice. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Feb 5;146(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90223-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


