Abstract
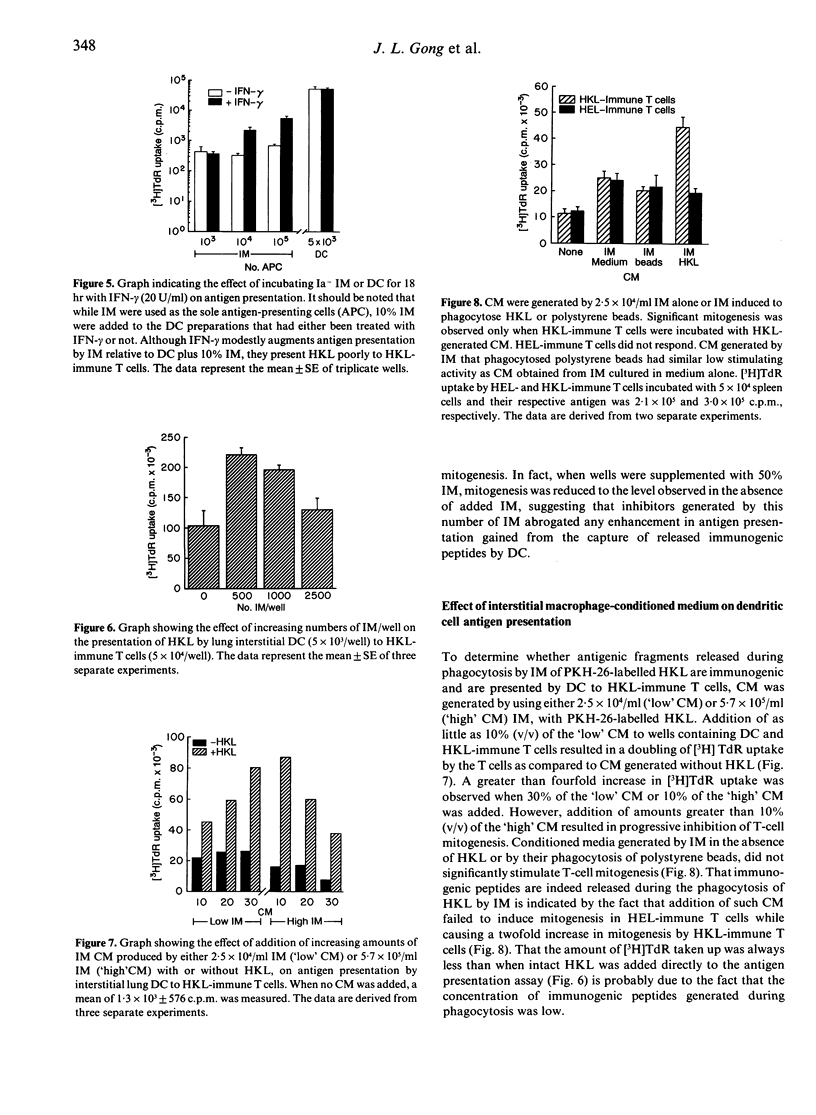
When the protective structural and functional barriers of the lung are breached, immune responses must be generated in order to contain invading micro-organisms. This requires the presence of accessory cells capable of phagocytosing and presenting immunogenic peptides to either naive or sensitized T cells. In contrast to dendritic cells (DC) present in the airway epithelium, those within the lung parenchyma do not readily engulf particulates and, therefore, other mechanisms must account for their apparent ability to present immunogenic peptides derived from micro-organisms. The purpose of the present study was to determine the extent to which interstitial macrophages (IM) interact with lung DC to process and present antigenic peptides, derived from particulate, heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes (HKL), to HKL-immune T cells. Results show that highly purified Ia- lung IM avidly phagocytose fluorescent-labelled HKL, but they do not present antigen to primed T cells. Their ability to present antigen is only modestly increased following interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) stimulation. Conversely, mature DC isolated from the lung interstitium do not phagocytose fluorescent-labelled HKL. In antigen presentation assays, however, addition of 10% (2.5 x 10(3)/ml) Ia- IM to DC and HKL results in a two- to threefold increase in antigen presentation by DC to HKL-immune T cells. Conditioned medium (CM), generated by 2.5 x 10(4)/ml IM induced to phagocytose HKL, when administered to DC and HKL-sensitized T cells without added intact HKL, resulted in brisk mitogenesis, a response that did not occur in T cells sensitized to an irrelevant antigen. Conditioned medium derived from larger numbers of IM was inhibitory. When IM phagocytosed inert polystyrene beads, the resulting CM induced modest T-cell mitogenesis, suggesting that small amounts of cytokines were released. The results indicate that in small numbers, IM augment DC function, in part, by the release of antigenic peptides which are then presented by DC to T cells. When present in numbers greater than 50% of DC, however, they inhibit DC function, probably due to the release of soluble inhibitors.
Full text
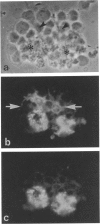
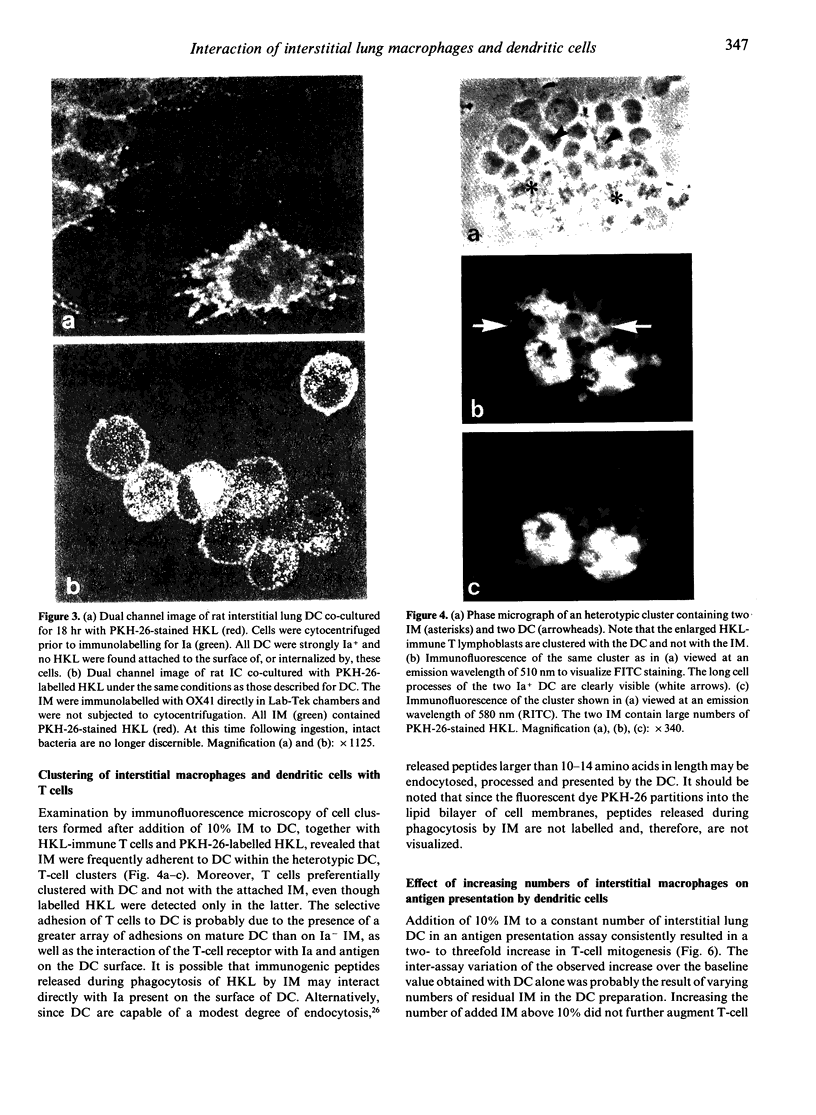
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Beller D. I., Braun J., Unanue E. R. The handling of Listeria monocytogenes by macrophages: the search for an immunogenic molecule in antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):323–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsden A., Lawn C. Y., Roy S., Sunshine G. H., Leskowitz S. Hapten-specific T-cell response to azobenzenearsonate-N-acetyl-L-tyrosine in the Lewis rat. IV. Rat dendritic cells present soluble and insoluble azobenzenearsonate conjugates to T cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jul;93(2):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden D. H., Adamson I. Y. The pulmonary interstitial cell as immediate precursor of the alveolar macrophage. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):521–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers W. E., Ruhoff M. S., Goodell E. M. Conditioned medium from activated rat macrophages and the recombinant factors, IL-1 beta and GM-CSF, enhance the accessory activity of dendritic cells. Immunobiology. 1990 Jun;180(4-5):362–384. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(11)80299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry D., Kulkarni P., Lipscomb M. F. The migration of bronchoalveolar macrophages into hilar lymph nodes. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):321–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley M., Inaba K., Steinman R. M. Dendritic cells are the principal cells in mouse spleen bearing immunogenic fragments of foreign proteins. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):383–386. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruijn M. L., Nieland J. D., Harding C. V., Melief C. J. Processing and presentation of intact hen egg-white lysozyme by dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2347–2352. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler A. A., Carey P. D., Walsh C. J., Sessler C. N., Mumaw V. R., Bechard D. E., Leeper-Woodford S. K., Fisher B. J., Blocher C. R., Byrne T. K. In situ pulmonary vascular perfusion for improved recovery of pulmonary intravascular macrophages. Microvasc Res. 1991 May;41(3):328–344. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(91)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenthal P. S., Steinman R. M. The distinct surface of human blood dendritic cells, as observed after an improved isolation method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7698–7702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giloh H., Sedat J. W. Fluorescence microscopy: reduced photobleaching of rhodamine and fluorescein protein conjugates by n-propyl gallate. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1252–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.7112126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong J. L., McCarthy K. M., Telford J., Tamatani T., Miyasaka M., Schneeberger E. E. Intraepithelial airway dendritic cells: a distinct subset of pulmonary dendritic cells obtained by microdissection. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):797–807. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen A. G., Muggenburg B. A., Snipes M. B., Bice D. E. The role of macrophages in particle translocation from lungs to lymph nodes. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1277–1280. doi: 10.1126/science.4071052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havenith C. E., Breedijk A. J., Betjes M. G., Calame W., Beelen R. H., Hoefsmit E. C. T cell priming in situ by intratracheally instilled antigen-pulsed dendritic cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;8(3):319–324. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heufler C., Koch F., Schuler G. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin 1 mediate the maturation of murine epidermal Langerhans cells into potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):700–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G. Down-regulation of immune responses in the lower respiratory tract: the role of alveolar macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Feb;63(2):261–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Oliver J., Bilyk N., McMenamin C., McMenamin P. G., Kraal G., Thepen T. Downregulation of the antigen presenting cell function(s) of pulmonary dendritic cells in vivo by resident alveolar macrophages. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):397–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Schon-Hegrad M. A., Oliver J. MHC class II antigen-bearing dendritic cells in pulmonary tissues of the rat. Regulation of antigen presentation activity by endogenous macrophage populations. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):262–274. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horan P. K., Slezak S. E. Stable cell membrane labelling. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):167–168. doi: 10.1038/340167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye P. M., Chain B. M., Feldmann M. Nonphagocytic dendritic cells are effective accessory cells for anti-mycobacterial responses in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1930–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kradin R. L., McCarthy K. M., Gifford J., Schneeberger E. E. Antigen-independent binding of T-cells by dendritic cells and alveolar macrophages in the rat. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jan;139(1):207–211. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kradin R. L., McCarthy K. M., Xia W. J., Lazarus D., Schneeberger E. E. Accessory cells of the lung. I. Interferon-gamma increases Ia+ dendritic cells in the lung without augmenting their accessory activities. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Mar;4(3):210–218. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kradin R. L., Xia W., McCarthy K., Schneeberger E. E. FcR+/- subsets of Ia+ pulmonary dendritic cells in the rat display differences in their abilities to provide accessory co-stimulation for naive (OX-22+) and sensitized (OX-22-) T cells. Am J Pathol. 1993 Mar;142(3):811–819. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPherson G. G. Properties of lymph-borne (veiled) dendritic cells in culture. I. Modulation of phenotype, survival and function: partial dependence on GM-CSF. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):102–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Identification of Ia glycoproteins in rat thymus and purification from rat spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):426–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki H., Osawa T. Accessory functions and mutual cooperation of murine macrophages and dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Dec;13(12):984–989. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito K., Inaba K., Hirayama Y., Inaba-Miyama M., Sudo T., Muramatsu S. Macrophage factors which enhance the mixed leukocyte reaction initiated by dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1834–1839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi P., Steinman R. M., Bhardwaj N. Dendritic cells efficiently immunoselect mycobacterial-reactive T cells in human blood, including clonable antigen-reactive precursors. Immunology. 1992 Jun;76(2):217–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard A. M., Lipscomb M. F. Characterization of murine lung dendritic cells: similarities to Langerhans cells and thymic dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):159–167. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puré E., Inaba K., Crowley M. T., Tardelli L., Witmer-Pack M. D., Ruberti G., Fathman G., Steinman R. M. Antigen processing by epidermal Langerhans cells correlates with the level of biosynthesis of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules and expression of invariant chain. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1459–1469. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. P., White T. M., Mason D. W. Macrophage heterogeneity in the rat as delineated by two monoclonal antibodies MRC OX-41 and MRC OX-42, the latter recognizing complement receptor type 3. Immunology. 1986 Feb;57(2):239–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani N., Koide S., Crowley M., Witmer-Pack M., Livingstone A. M., Fathman C. G., Inaba K., Steinman R. M. Presentation of exogenous protein antigens by dendritic cells to T cell clones. Intact protein is presented best by immature, epidermal Langerhans cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samlowski W. E., Robertson B. A., Draper B. K., Prystas E., McGregor J. R. Effects of supravital fluorochromes used to analyze the in vivo homing of murine lymphocytes on cellular function. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Nov 5;144(1):101–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sertl K., Takemura T., Tschachler E., Ferrans V. J., Kaliner M. A., Shevach E. M. Dendritic cells with antigen-presenting capability reside in airway epithelium, lung parenchyma, and visceral pleura. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):436–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. I. Morphology, quantitation, tissue distribution. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1142–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Antigen-presenting function of the macrophage. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:395–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van oud Alblas A. B., van Furth R. Origin, Kinetics, and characteristics of pulmonary macrophages in the normal steady state. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1504–1518. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]