Abstract
Rabbit kidney tissue contains antigens which are tissue-specific and species restricted, as well as other antigens which are shared by different organs of the animal. The stability of these antigens was investigated as a function of temperature, in order to explore the possibility of thermal fractionation. It was observed that one rabbit kidney-specific autoantigen was destroyed at 56° and another at 65°. A third antigen, which is restricted to the rabbit species but is non-tissue specific, was destroyed at 72°. Ultracentrifugal analysis of the saline extract at different concentrations showed the presence of several components, whose extrapolated values at zero concentration were found to be 4.2S, 6.2S, 10S, 19S, and 80S. The first two components were the most prominent.
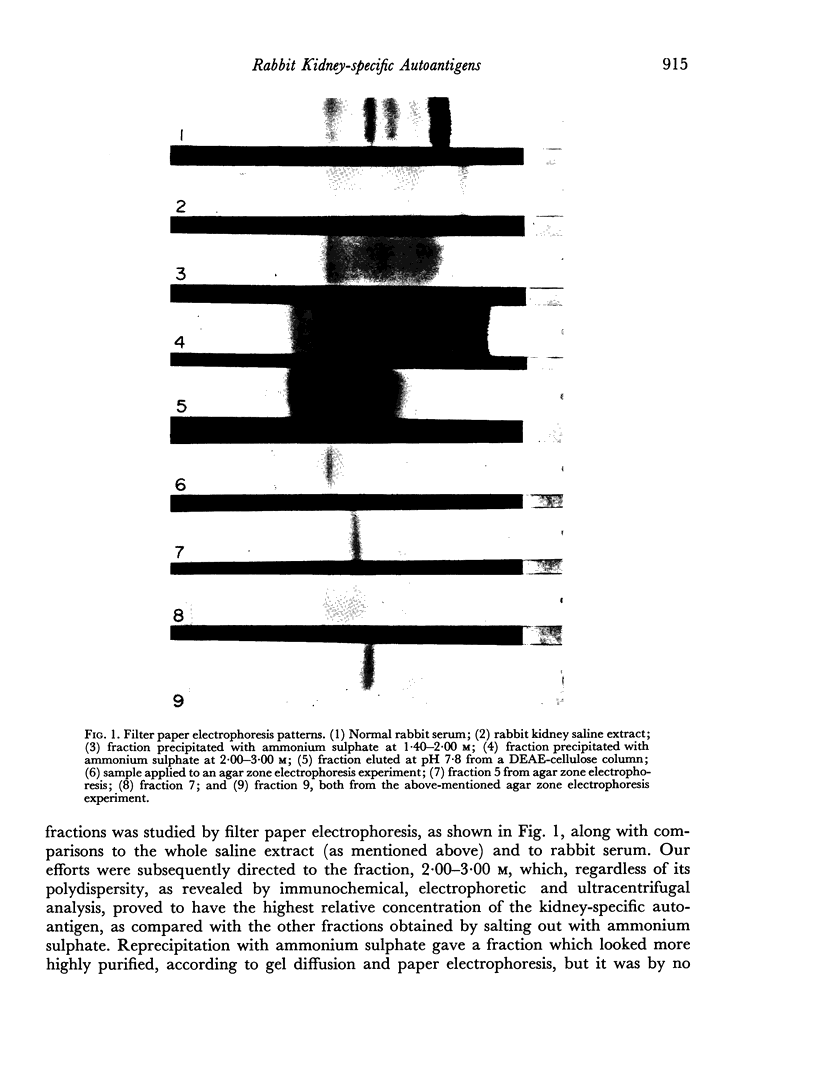
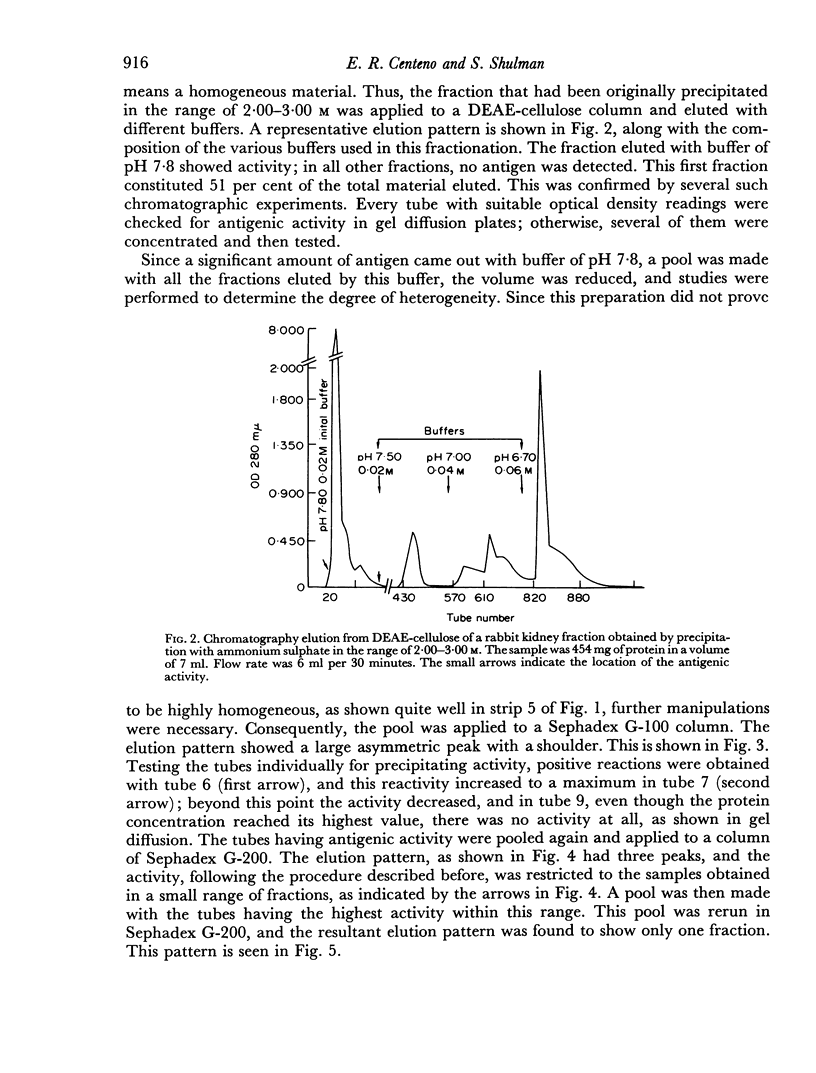
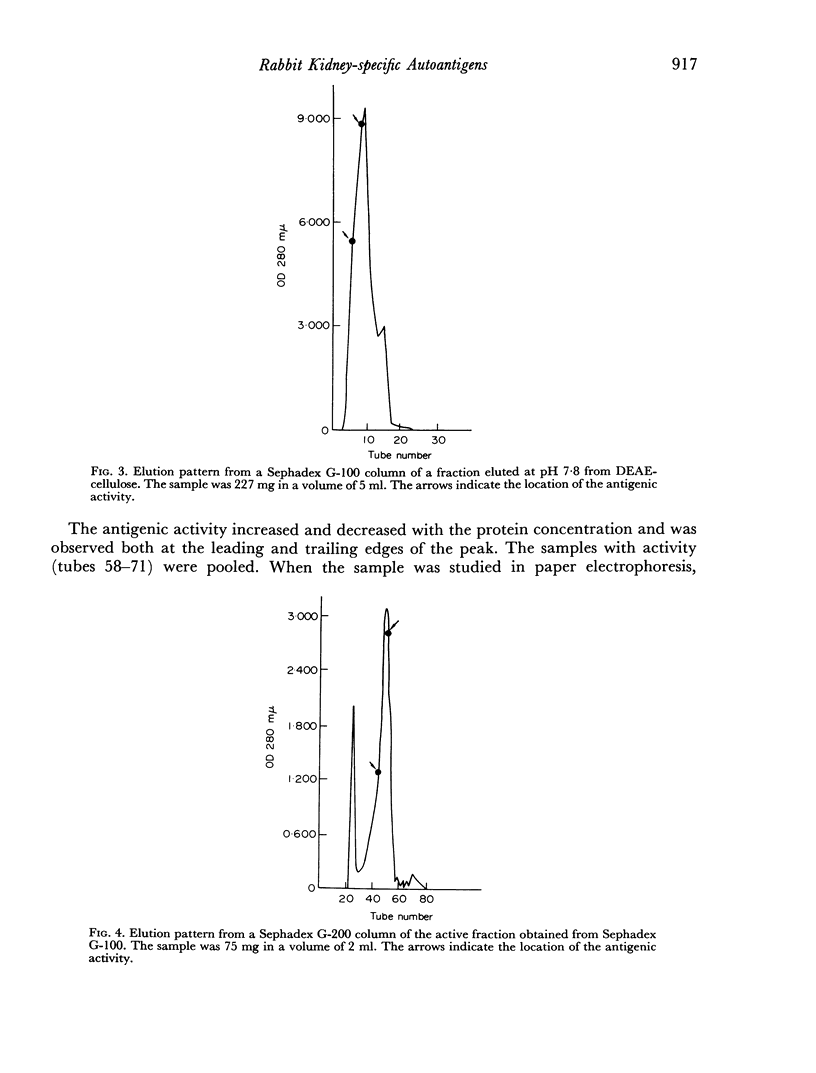
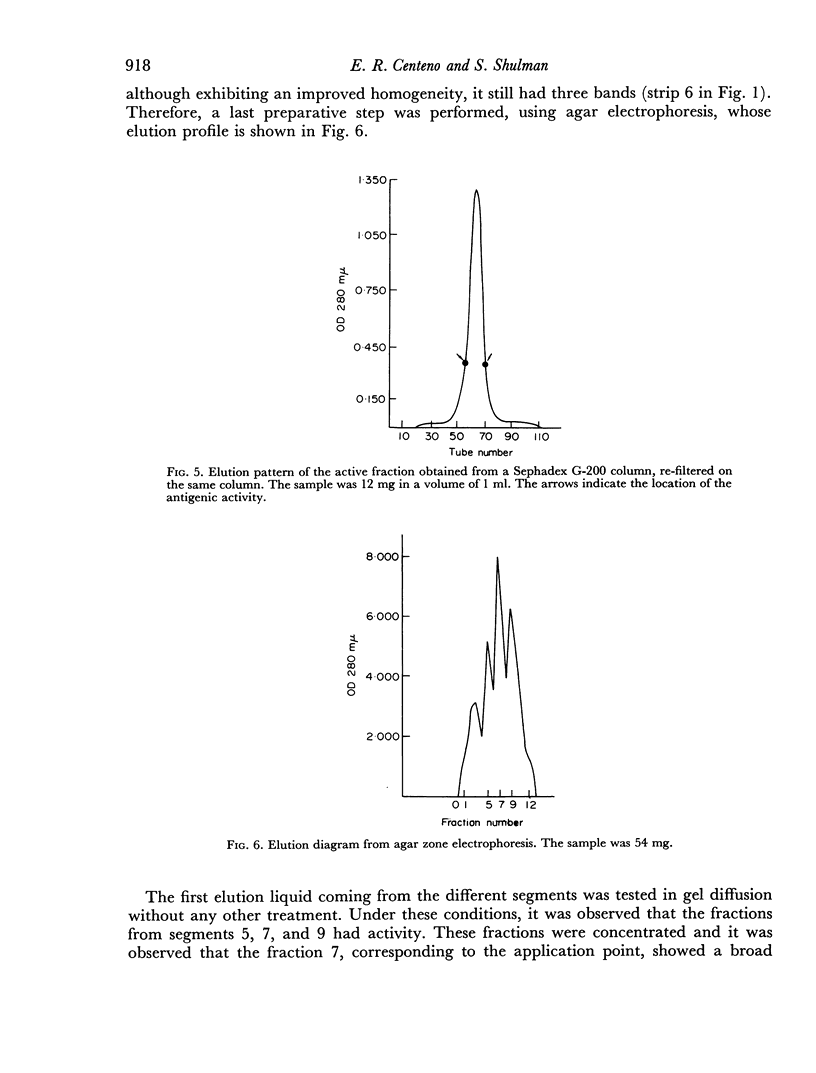
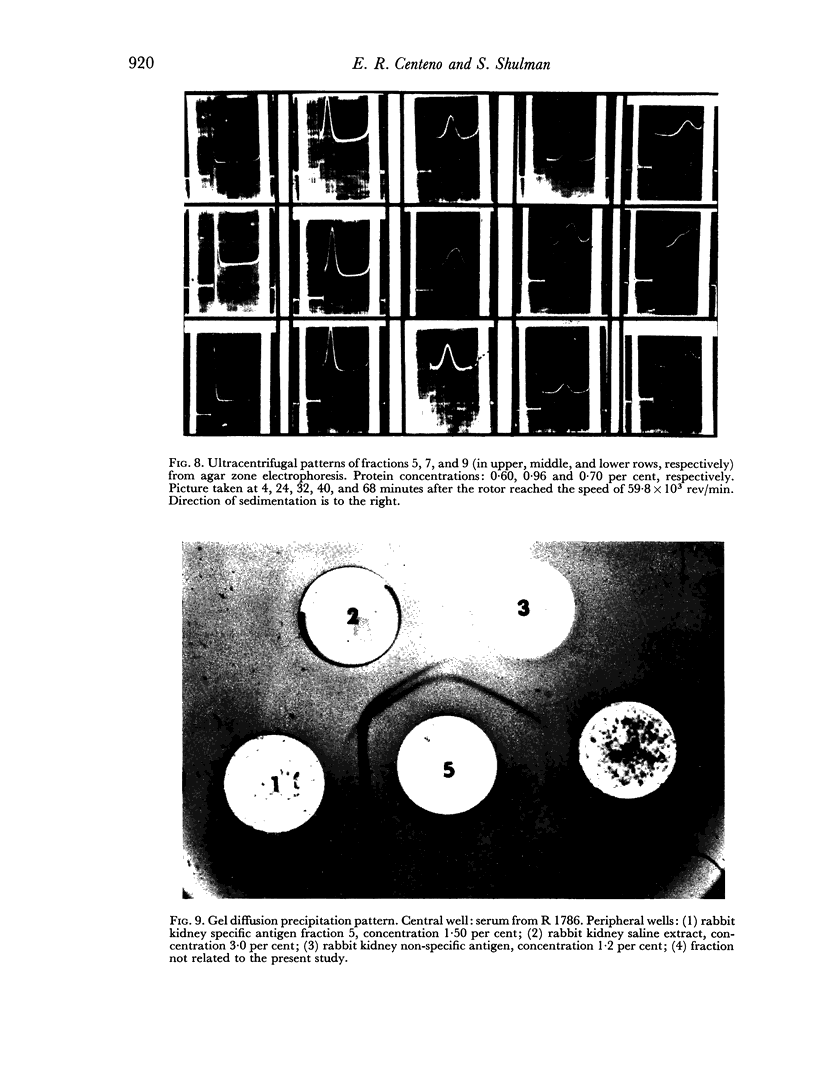
The rabbit kidney-specific autoantigens were fractionated by a first step of salting out with ammonium sulphate at 4°. The fraction that precipitated in the range from 2.00 to 3.00 M retained most of the antigenic activity. As this fraction was quite impure, it was chromatographed through DEAE-cellulose, then processed through gel filtration columns, using Sephadex G-100 and G-200, and finally purified in agar zone electrophoresis. Two antigens were isolated and both shared similar antigenic characteristics. However, they had slight differences regarding their physico-chemical properties. Sedimentation coefficients of 4.6S and 4.8S were obtained for them. Both antigens possessed a slow electrophoretic mobility, similar to that of the β-globulins. The antigen with higher sedimentation value was slightly faster electrophoretically than the other.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CENTENO E., SHULMAN S., MILGROM F., WITEBSKY E. IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES ON ADRENAL GLANDS. VI. THE MULTIPLE NATURE OF THE RABBIT ADRENAL AUTOANTIGENS. Immunology. 1965 Feb;8:160–169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centeno E. R., Shulman S. Isolation and characterization of a rabbit adrenal autoantigen. Immunology. 1973 May;24(5):901–910. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centeno E., Shullman S., Milgrom F., Witebsky E., Skelton F. Studies on organ specificity. XVII. Autoantigens of rabbit kidney. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):530–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Dixon F. J. The induction of acute glomerulonephritis in rabbits with soluble antigens isolated from normal homologous and autologous urine. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1277–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILGROM F., CENTENO E., SHULMAN S., WITEBSKY E. AUTOANTIBODIES RESULTING FROM IMMUNIZATION WITH KIDNEY. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:1009–1013. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman S., Wypych J. Kidney antigens active in isoimmunization. I. The antigenic diversity. Immunology. 1969 Nov;17(5):641–652. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J., Feldman J. D. Experimental allergic glomerulonephritis induced in the rabbit with homologous renal antigens. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):163–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]