Abstract
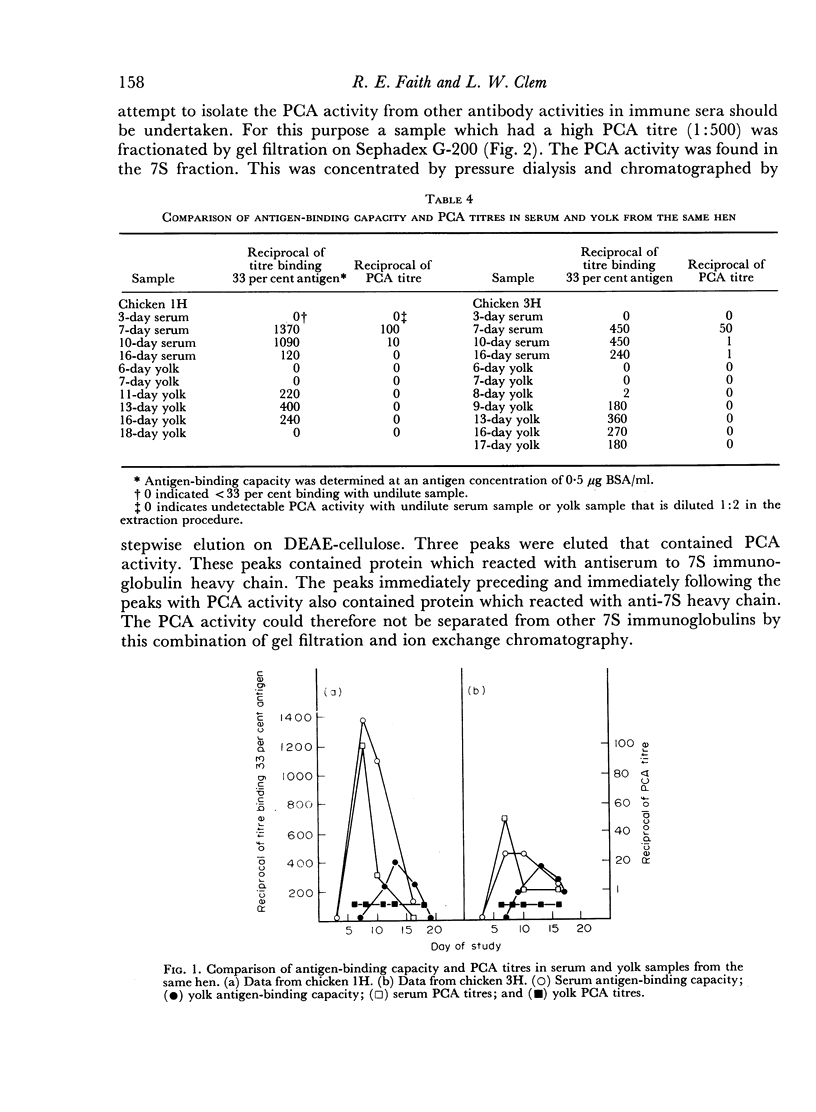
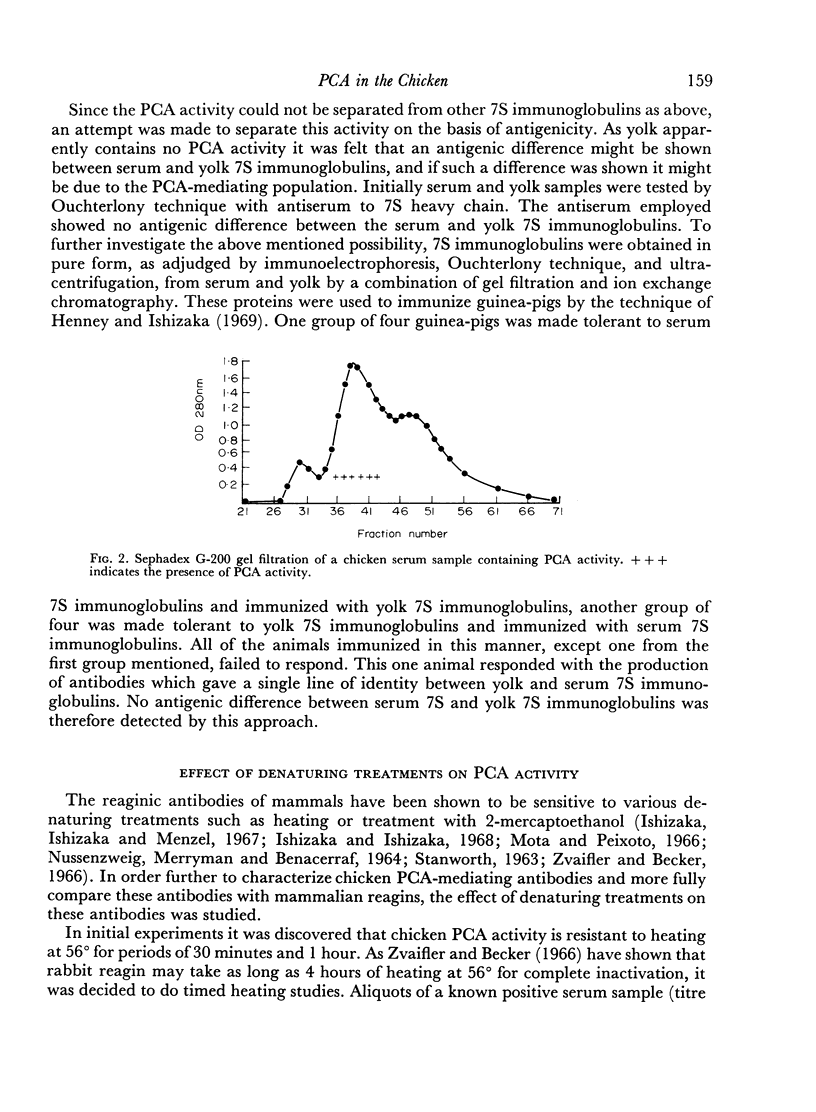
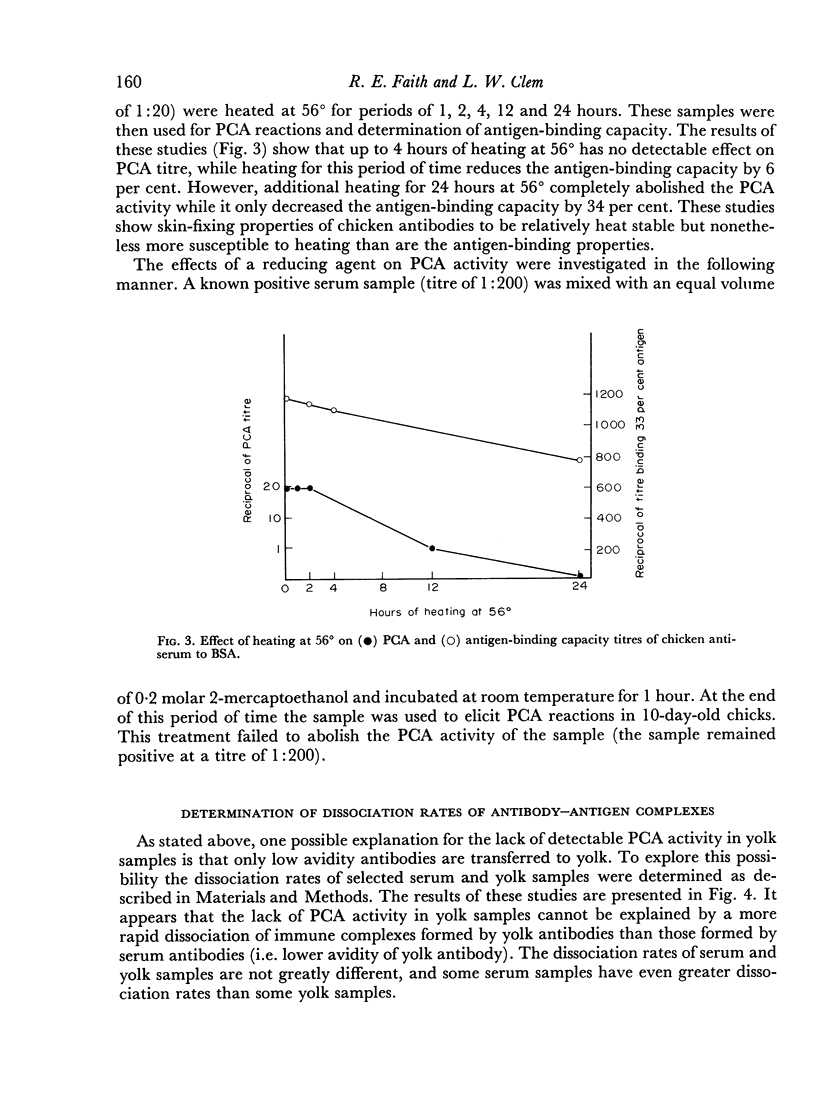
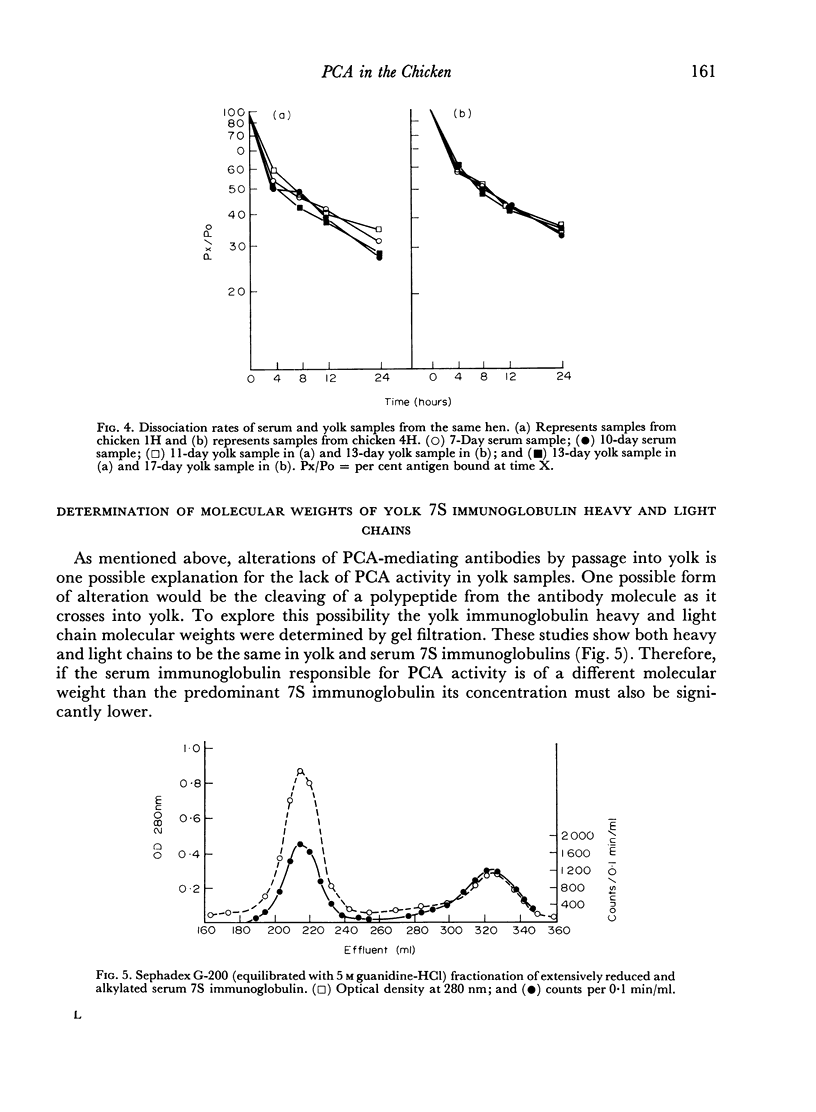
The studies reported here demonstrated that adult chickens, when immunized with bovine serum albumin, respond with the production of serum antibodies which will mediate passive cutaneous anaphylactic (PCA) reactions in 10-day-old chicks but not in adults. This difference is at least in part due to differences in histamine sensitivity between chicks and adults. The molecule responsible for this PCA activity was indistinguishable from the predominant 7S chicken immunoglobulin antigenically and by a combination of gel filtration on Sephadex G-200 and ion exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose. However, the PCA activity is apparently biologically separable from portions of the 7S serum immunoglobulin population since this activity has never been elicited by immunoglobulins derived from yolk. On the basis of stability to denaturing treatments and short tissue fixation time periods, the chicken PCA-mediating antibodies appear to resemble the γG1 homocytotrophic antibodies of mice and guinea-pigs instead of the IgE-type reagins found in some mammals. Therefore, PCA-mediating antibodies appear to be a subpopulation of the chicken 7S immunoglobulins, distinguishable by its inability to pass into the egg yolk but indistinguishable by standard chemical and immunochemical criteria.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aulisio C. G., Shelokov A. Detection of microbial antibodies in chickens: immunofluorescence studies with serum and egg yolk. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1150–1153. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabas A. Z., Barabas H. Preparation of specific anti-chicken immunoglobulin sera. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 May;4(5):603–606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CELADA F., RAMOS A. Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mice and chickens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Oct;108:129–133. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-26869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C. R., Munoz J., Bergman R. K. Reaginic-type of antibody in mice stimulated by extracts of Bordetella pertussis. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):768–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway A. M., Van Alten P. J., Hirata A. A. Passive cutaneous anaphylactic-like reactions in young chicks. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):694–696. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettinger A. C., Hirata A. A., Van Alten P. J. Differential susceptibilities of young and adult chickens to passive cutaneous anaphylactic reaction. Immunology. 1970 Aug;19(2):257–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M. The quality of antibody produced by transferred cells. Immunology. 1962 Sep;5:603–609. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D. Current aspects of the structure, function, and genetics of the immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Med. 1966;17:1–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.17.020166.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Ishizaka K. A simplified procedure for the preparation of immunoglobulin-class-specific antisera. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Human reaginic antibodies and immunoglobulin E. J Allergy. 1968 Dec;42(6):330–363. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(68)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Menzel A. E. Physicochemical properties of reaginic antibody. VI. Effect of heat on gamma-E-, gamma-G- and gamma-A-antibodies in the sera of ragweed sensitive patients. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):610–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer T. T., Cho H. C. Transfer of immunoglobulins and antibodies in the hen's egg. Immunology. 1970 Jul;19(1):157–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo R. T., Benedict A. A. Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in chickens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):256–260. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebacq-Verheyden A. M., Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. A possible homologue of mammalian IgA in chicken serum and secretions. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):165–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. A., Clem L. W. Phylogen of immunoglobulin structure and function. 3. Immunoglobulins of the chicken. J Exp Med. 1969 Dec 1;130(6):1337–1352. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.6.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. A., Wilson H. R., Clem L. W. Studies on the secretory immunologic system of fowl. I. Presence of immunoglobulins in chicken secretions. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1441–1446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTA I. THE MECHANISM OF ANAPHYLAXIS. I. PRODUCTION AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF 'MAST CELL SENSITIZING' ANTIBODY. Immunology. 1964 Nov;7:681–699. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkinson M. The transmission of passive immunity to Escherichia coli from mother to young in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Immunology. 1965 Oct;9(4):311–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVeigh T. A., Jr, Voss E. W., Jr Properties of purified mouse homocytotropic antibody. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1349–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Austen K. F., Bloch K. J. Biologic properties of rat antibodies. 3. Histamine release mediated by two classes of antibodies. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):327–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota I., Peixoto J. M. A skin-sensitizing and thermolabile antibody in the mouse. Life Sci. 1966 Sep;5(18):1723–1728. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90108-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSENZWEIG R. S., MERRYMAN C., BENACERRAF B. ELECTROPHORETIC SEPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF MOUSE ANTIHAPTEN ANTIBODIES INVOLVED IN PASSIVE CUTANEOUS ANAPHYLAXIS AND PASSIVE HEMOLYSIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:315–328. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., BARTH W. F., FAHEY J. L. THE IMMUNOGLOBULINS OF MICE. 3. SKIN SENSITIZING ACTIVITY OF MOUSE IMMUNOGLOBULINS. J Immunol. 1965 Mar;94:410–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., BENACERRAF B., BLOCH K. J. Properties of guinea pig 7S antibodies. II. Identification of antibodies involved in passive cutaneous and systemic anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:951–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlans E. Fowl antibody. 8. A comparison of natural, primary and secondary antibodies to erythrocytes in hen sera; their transmission to yolk and chick. Immunology. 1967 Jan;12(1):27–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlans E. Fowl antibody. X. The purification and properties of an antibody to the 2,4-dinitrophenyl group. Immunology. 1968 Jan;14(1):61–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlans E., Rose M. E. An IgA-like immunoglobulin in the fowl. Immunochemistry. 1972 Aug;9(8):833–838. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON R., YOUNGNER J. S., WEIGLE W. O., DIXON F. J. Antibody production and transfer to egg yolk in chickens. J Immunol. 1962 Aug;89:272–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluk P. H., Clem L. W. The unique molecular weight of the heavy chain from human IgG3. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):298–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. T. Human immunoglobulins--a guide to nomenclature and clinical application. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALMAGE D. W. The kinetics of the reaction between antibody and bovine serum albumin using the Farr method. J Infect Dis. 1960 Jul-Aug;107:115–132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/107.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORBECKE G. J., BENACERRAF B., OVARY Z. ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TWO TYPES OF 7 S GUINEA PIG GAMMA-GLOBULINS. J Immunol. 1963 Nov;91:670–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., French V. I. Antigenic heterogeneity of chicken 7S immunoglobulin. Immunochemistry. 1969 May;6(3):498–501. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J., Becker E. L. Rabbit anaphylactic antibody. J Exp Med. 1966 May 1;123(5):935–950. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


