Abstract
A comparative study of cells synthesizing immunoglobulins IgA and IgM in intestinal mucosa and various lymphoid tissues of unweaned piglets has been made by immunofluorescence.
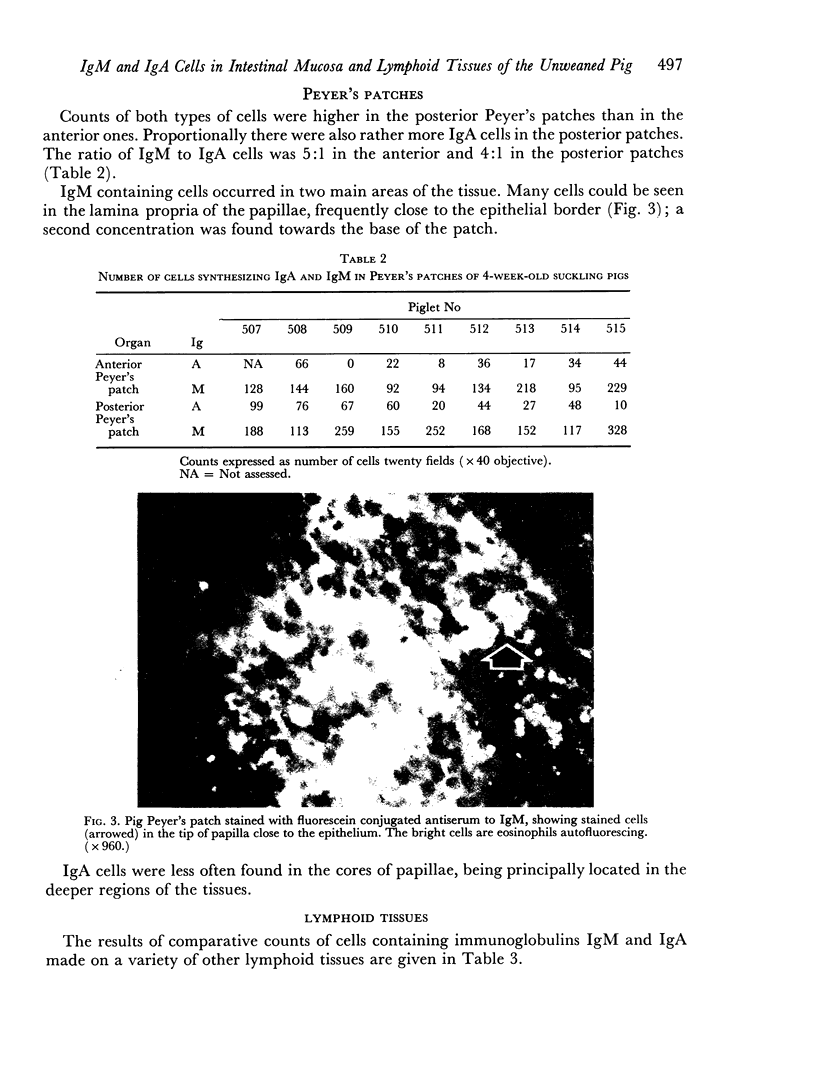
The lamina propria of the small intestine contained as many cells synthesizing IgM as those producing IgA. In all other lymphoid organs examined, including Peyer's patches, the number of IgM cells was significantly higher.
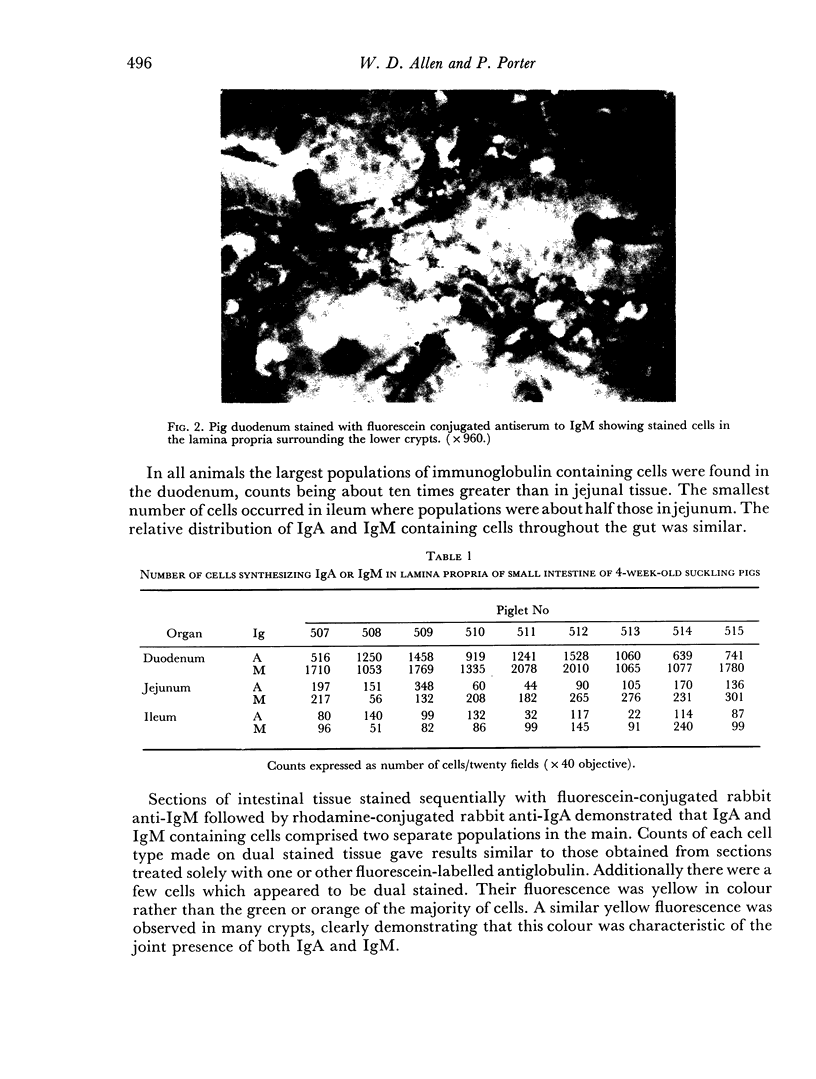
The largest population of intestinal immunocytes occurred in the lamina propria of the duodenum where the counts were ten times greater than in the jejunum or ileum.
The relevance of these findings to the earliest stages of development of secretory immunity in the young pig are considered.
Full text
PDF


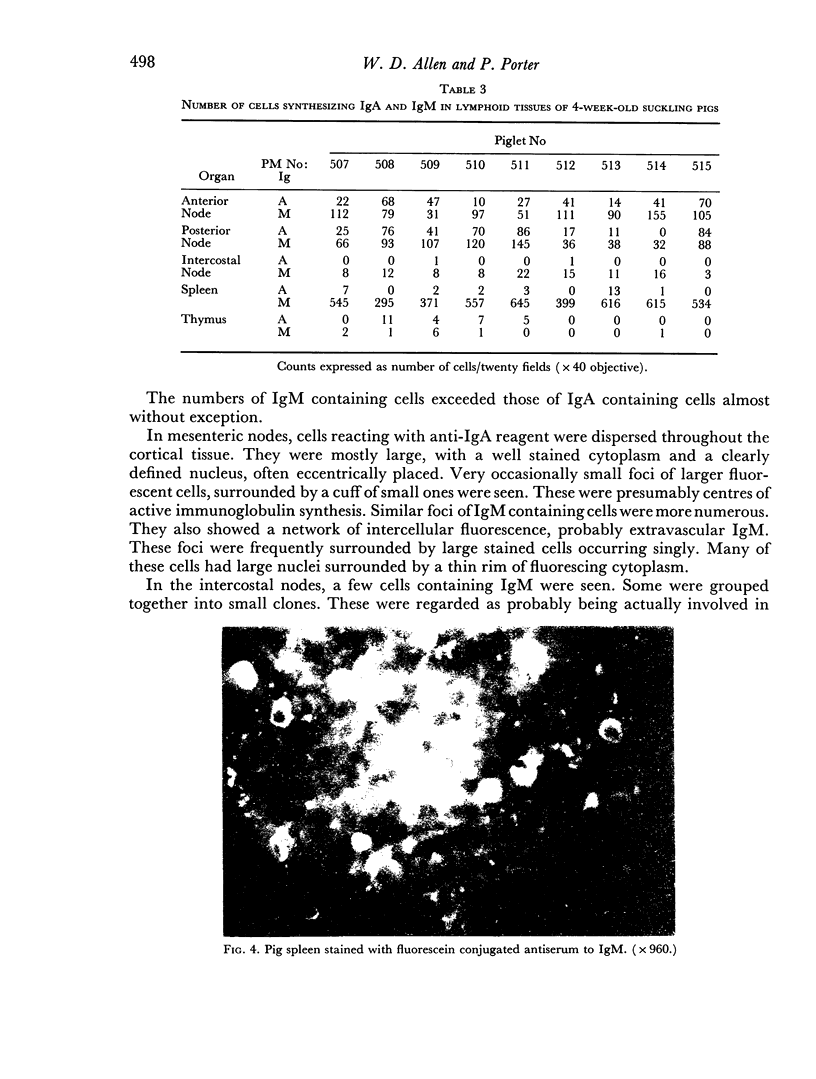



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen W. D., Porter P. The demonstration of immunoglobulins in porcine intestinal tissue by immunofluorescence with observations on the effect of fixation. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):799–806. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Dolezel J. Peyer's patches: lack of specific antibody-containing cells after oral and parenteral immunization. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):938–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne F. J., Pickup J., Honour J. W. Intestinal immunoglobulins in the pig. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):18–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRABBE P. A., CARBONARA A. O., HEREMANS J. F. THE NORMAL HUMAN INTESTINAL MUCOSA AS A MAJOR SOURCE OF PLASMA CELLS CONTAINING GAMMA-A-IMMUNOGLOBULIN. Lab Invest. 1965 Mar;14:235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. N., Turner K. Immunological responses in rats following antigenic stimulation of Peyer's patches. 3. Local and general sequelae. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Aug;46(4):415–424. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Bazin H., Eyssen H., Heremans J. F. The normal microbial flora as a major stimulus for proliferation of plasma cells synthesizing IgA in the gut. The germ-free intestinal tract. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(4):362–375. doi: 10.1159/000230130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidelman S., Davis S. D. Immunoglobulin content of intestinal mucosal plasma-cells in ataxia telangiectasia. Lancet. 1968 Apr 27;1(7548):884–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heremans J. F., Crabbé P. A., Masson P. L. Biological significance of exocrine gamma-A-immunoglobulin. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966;445:84–88. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb02343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENWORTHY R., CRABB W. E. THE INTESTINAL FLORA OF YOUNG PIGS, WITH REFERENCE TO EARLY WEANING, ESCHERICHIA COLI AND SCOURS. J Comp Pathol. 1963 Jul;73:215–228. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(63)80025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIM Y. B., WATSON D. W. MODIFICATION OF HOST RESPONSES TO BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS. II. PASSIVE TRANSFER OF IMMUNIY TO BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN WITH FRACTIONS CONTAINING 19S ANTIBODIES. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:751–759. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenworthy R. Effect of Escherichia coli on germ-free and gnotobiotic pigs. I. Light and electron microscopy of the small intestine. J Comp Pathol. 1970 Jan;80(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(70)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., ROSEN F. S. ASSOCIATION OF "NATURAL" ANTIBODIES TO GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA WITH THE GAMMA-1-MACROGLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:619–626. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Allen W. D. Intestinal IgA in the pig. Experientia. 1970 Jan 15;26(1):90–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01900412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Hill I. R. Serological changes in immunoglobulins IgG, IgA and IgM and Escherichia coli antibodies in the young pig. Immunology. 1970 Apr;18(4):565–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Noakes D. E., Allen W. D. Intestinal secretion of immunoglobulins and antibodies to Escherichia coli in the pig. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):909–920. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Tomasi T. B. A Low Molecular Weight Immunoglobulin Antigenically Related to 19 S IgM. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1329–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI105625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W. J., 3rd, Douglas H., Braude A. I., Wells W. W. Protection against lethality of E. coli endotoxin with "O" antiserum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):746–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. Distribution of various immunoglobulin containing cells in canine lymphoid tissue. Immunology. 1969 Oct;17(4):627–633. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]