Abstract
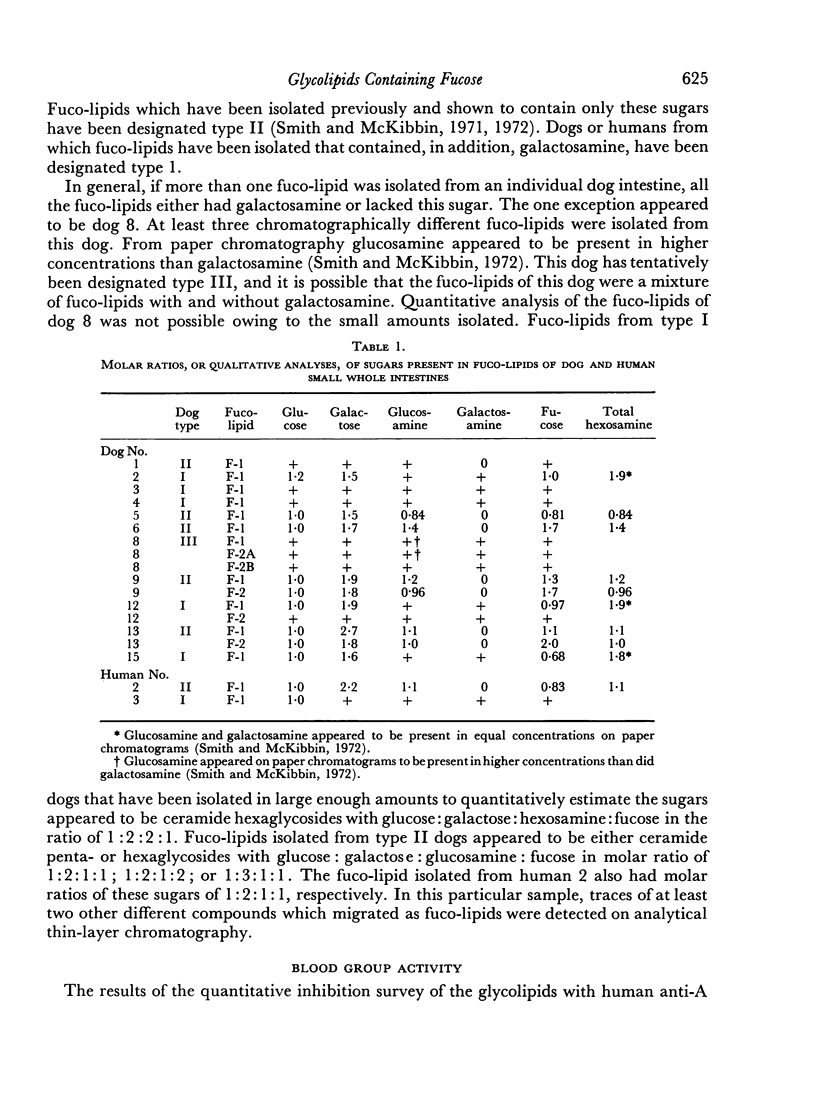
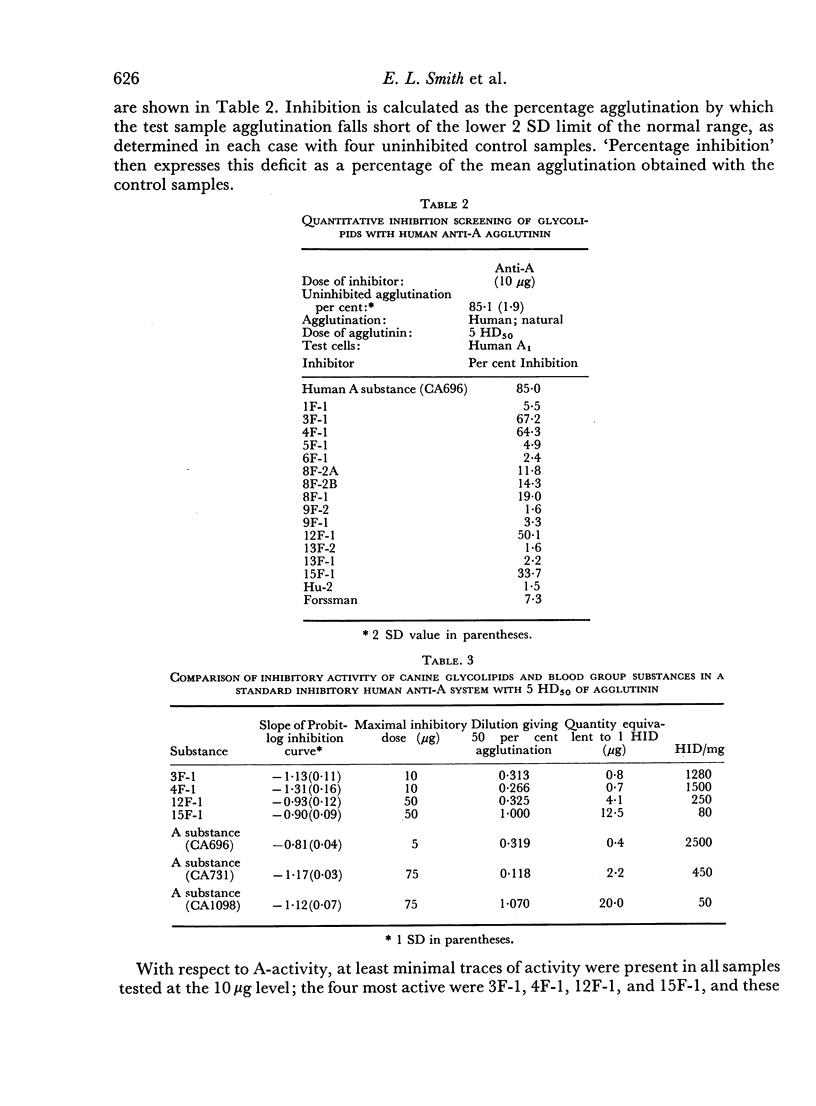
A number of fucose-containing glycolipids (fuco-lipids), which are similar in composition to those of human normal and malignant gastrointestinal tissue, have been isolated from whole small intestines of individual dogs. Dogs from which these fuco-lipids were isolated fell into two types according to the qualitative sugar composition of their fuco-lipids. Glycolipids from type I dogs contained glucose, galactose, glucosamine, galactosamine and fucose, while those from type II dogs contained the same sugars but lacked galactosamine. Fucolipids isolated from type I and II dogs were tested for both canine blood group and human A, B, H and Lea and Leb blood group activity. At the concentrations tested, only human blood group A activity was found in significant amounts, and only in those fuco-lipids which contained galactosamine (type I dogs). Of the fuco-lipids with human blood group A activity, some had activity comparable to that of glycoprotein blood group substances, while others had lower, but significant, activity. These latter fuco-lipids also had marked chromatographic differences, indicating that they are of several different structural types, a finding similar to the A active glycolipids of human red cell stroma. None of the isolated intestinal fuco-lipids had canine blood group activity. A fuco-lipid with Lea activity was also isolated in relatively large amounts from a normal human whole small intestine.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOWDLER A. J., SWISHER S. N. ELECTRONIC PARTICLE COUNTING APPLIED TO THE QUANTITATIVE STUDY OF RED CELL AGGLUTINATION. Transfusion. 1964 May-Jun;4:153–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1964.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWDLER A. J., SWISHER S. N. QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF RED CELL AGGLUTINATION: THE ANALYSIS OF A PATTERN OF AGGLUTINATION PRODUCED BY HUMAN GROUP B CELLS AND ANTI-B SERUM. Transfusion. 1964 Nov-Dec;4:419–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1964.tb02901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. M. Structures and immunochemical properties of oligosaccharides isolated from pig submaxillary mucins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):616–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. New color reactions for determination of sugars in polysaccharides. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:313–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS M. B., COLLINS W. S., AKEROYD J. H. Quantitative hemagglutination inhibition studies of blood group substances. I. Assay of the blood group A activity of substances. J Immunol. 1961 Oct;87:396–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. I., JEANLOZ R. W. Isolation and characterization of glycolipids from erythrocytes of human blood A (plus) and B (plus). J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2827–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. Chemistry and biology of lipids. XVIII. On group lipoid from human liver. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1954 Oct 25;60(3-4):331–345. doi: 10.1620/tjem.60.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANDA S. BLOOD GROUP ACTIVE GLYCOLIPID FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. Jpn J Exp Med. 1963 Dec;33:347–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. I., Koscielak J., Bloch K. J., Jeanloz R. W. Immunologic relationship between blood group substances and a fucose-containing glycolipid of human adenocarcinoma. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S., Andrews H. D. Sphingoglycolipids with Leb activity, and the co-presence of Lea-, Leb-glycolipids in human tumor tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 10;202(1):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S., Strycharz G. D. Investigations on cellular blood-group substances. I. Isolation and chemical composition of blood-group ABH and Le-b isoantigens of sphingoglycolipid nature. Biochemistry. 1968 Apr;7(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1021/bi00844a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSCIELAK J. BLOOD GROUP A SPECIFIC GLYCOLIPIDS FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 29;78:313–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91642-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSCIELAK J. Reversible inactivation of blood-group A and B substances from red cells. Nature. 1962 May 26;194:751–752. doi: 10.1038/194751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O., Kabat E. A., Layug E. J., Gruezo F. Immunochemical studies on blood groups. XXXIV. Structures of some oligosaccharides produced by alkaline degradation of blood group A, B, and H substances. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1489–1501. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKibbin J. M. The composition of the glycolipids in dog intestine. Biochemistry. 1969 Feb;8(2):679–685. doi: 10.1021/bi00830a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADIN N. S. Glycolipide chromatography. Fed Proc. 1957 Sep;16(3):825–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWISHER S. N., YOUNG L. E. The blood grouping systems of dogs. Physiol Rev. 1961 Jul;41:495–520. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1961.41.3.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui B., Hakomori S. A revised structure for the Forssman glycolipid hapten. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5766–5769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. L., McKibbin J. M. Separation of dog intestine glycolipids into classes according to sugar content by thin-layer chromatography: evidence for individual dog intestine specific glycolipids. Anal Biochem. 1972 Feb;45(2):608–616. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki C., Makita A., Yosizawa Z. Glycolipids isolated from porcine intestine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):140–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance W. R., Shook C. P., 3rd, McKibbin J. M. The glycolipids of dog intestine. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):435–445. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAKAWA T., IIDA T. Immunochemical study on the red blood cells. I. Globoside, as the agglutinogen of the ABO system on erythrocytes. Jpn J Exp Med. 1953 Aug;23(4):327–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAKAWA T., OHTA R., ICHIKAWA Y., OZAKI J. Purification du facteur déterminant le groupe sanguin du type ABO. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1958;152(8-9):1288–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakawa T., Nishimura S., Kamimura M. The chemistry of the lipids of posthemolytic residue or stroma of erythrocytes. 8. Further studies on human red cell glycolipids. Jpn J Exp Med. 1965 Jun;35(3):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. J., Hakomori S. I. A sphingolipid having a novel type of ceramide and lacto-N-fucopentaose 3. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1192–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweibaum A., Oudea P., Halpern B., Veyre C. Presence in colic glandular cells of various mammalian species of an antigen cross-reacting with human blood group A substance. Nature. 1966 Jan 8;209(5019):159–161. doi: 10.1038/209159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweibaum A., Steudler V. Présence chez le chien d'un système d'iso-anticorps naturels spécifiques d'antigènes de groupe des sécrétions digestives. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Dec;117(6):839–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


